What is the ICD 10 code for hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code E87.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.5 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What happens if potassium levels are high in hyperkalemia?
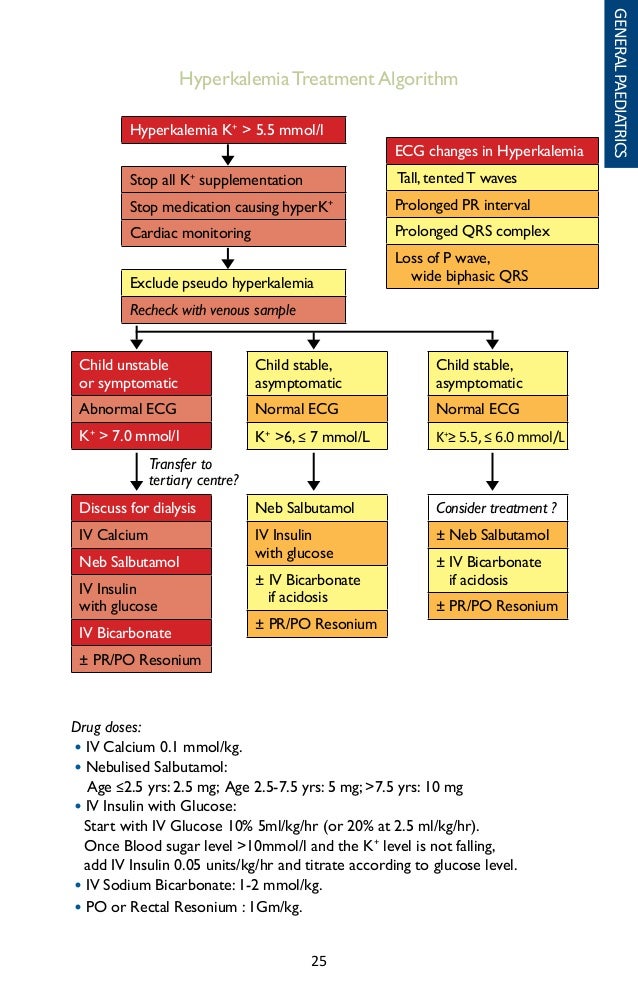
As potassium levels continue to rise, there may be flattened p-waves, a prolonged PR-interval, and other anomalies. If hyperkalemia is left untreated idioventricular rhythms may occur and a sine-wave pattern. Severe hyperkalemia can lead to asystolic cardiac arrest.
How is the diagnosis of hyperkalemia made?
Copyright© 2013 The Permanente Journal Diagnosis of hyperkalemia is usually based on laboratory studies, although the electrocardiogram (ECG) may contain changes suggestive of hyperkalemia.
What is hyperkalemia Mayo Clinic?
By Mayo Clinic Staff Hyperkalemia is the medical term that describes a potassium level in your blood that's higher than normal. Potassium is a chemical that is critical to the function of nerve and muscle cells, including those in your heart. Your blood potassium level is normally 3.6 to 5.2 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).

What is the ICD-10 code for high potassium?
ICD-10 code E87. 5 for Hyperkalemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for E87 5?
E87. 5 Hyperkalemia - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is the 2021 ICD-10 code for hypokalemia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Hypokalemia E87. 6.
Can Z76 89 be used as a primary diagnosis?
The patient's primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient's primary diagnostic code is Z76. 89, look in the list below to see which MDC's "Assignment of Diagnosis Codes" is first.
What is the medical code for potassium?
001180: Potassium | Labcorp.
What is I10 diagnosis?
ICD-Code I10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Essential (Primary) Hypertension.
Where can I find a list of ICD-10 codes?
ICD-10 CM Guidelines, may be found at the following website: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/icd/Comprehensive-Listing-of-ICD-10-CM-Files.htm.
What are some common ICD-10 codes?
Top 10 Outpatient Diagnoses at Hospitals by Volume, 2018RankICD-10 CodeNumber of Diagnoses1.Z12317,875,1192.I105,405,7273.Z233,219,5864.Z00003,132,4636 more rows
What ICD-10 code covers routine labs?
From ICD-10: For encounters for routine laboratory/radiology testing in the absence of any signs, symptoms, or associated diagnosis, assign Z01. 89, Encounter for other specified special examinations.
When do you use Z76 89?
ICD-10 code Z76. 89 for Persons encountering health services in other specified circumstances is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is a diagnostic code Z76 9?
ICD-10 code: Z76. 9 Person encountering health services in unspecified circumstances.
Can Z51 11 be a primary diagnosis?
11 or Z51. 12 is the only diagnosis on the line, then the procedure or service will be denied because this diagnosis should be assigned as a secondary diagnosis. When the Primary, First-Listed, Principal or Only diagnosis code is a Sequela diagnosis code, then the claim line will be denied.
What is low potassium?
Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of potassium in the blood. Abnormally low potassium concentration in the blood. It may result from potassium loss by renal secretion or by the gastrointestinal route, as by vomiting or diarrhea.
What is the term for a lower than normal level of potassium in the blood?
Hypokalemia ; lower than normal levels of potassium in the circulating blood.
What causes low potassium levels in the body?
Abnormally low potassium concentration in the blood; may result from excessive potassium loss by the renal or gastrointestinal route, from decreased intake, or from transcellular shifts; manifested clinically by neuromuscular disorders ranging from weakness to paralysis, by electrocardiographic abnormalities, and by renal and gastrointestinal disorders.
When will the ICd 10 E87.6 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Why is potassium so high?
Causes. Having high levels of potassium ('hyperkalemia'), can often be worse than having a deficiency. Dehydration, kidney failure, diabetes, and internal bleeding can all lead to high potassium levels.
Why is potassium important for the body?
Potassium is crucial for heart function , smooth muscle contraction, and digestion. Additionally, it acts as an electrolyte, conducting electricity in the body. When potassium levels stray too far from the norm, a variety of adverse consequences can occur in the body.
Is 6.2 mEq/L too much potassium?
Your Potassium value of 6.2 mEq/L is too high. A good Potassium is usually between 3.6 and 5 mEq/L.
What causes hyperkalemia in the kidneys?
Another condition that is a common cause of hyperkalemia is end-stage renal disease. When the kidneys fail, excess potassium cannot be removed, and it accumulates in the blood.
What is the effect of high potassium levels on the body?
The amount of potassium (K+) in the blood determines the excitability of nerve and muscle cells, including the heart muscle or myocardium.
What is the best way to remove potassium from the body?
One example of a diuretic which does not spare potassium is furosemide. Resins like Kayexalate can also be used to remove potassium from the body.
How long does it take for potassium to be shifted to intracellular space?
The onset of effect will take 15-30 min.
What does potassium do to the heart?
The amount of potassium (K+) in the blood determines the excitability of nerve and muscle cells, including the heart muscle or myocardium. When potassium levels in the blood rise, this reduces the electrical potential and can lead to potentially fatal abnormal heart rhythms.
Can hyperkalemia cause a T wave?
Mild hyperkalemia can cause peaked T waves. As potassium levels continue to rise, there may be flattened p-waves, a prolonged PR-interval, and other anomalies. If hyperkalemia is left untreated idioventricular rhythms may occur and a sine-wave pattern. Severe hyperkalemia can lead to asystolic cardiac arrest.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for ashton adams
- 2. icd 10 code for pressure ulcer of sacral region stage 2
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for nonsustained vt
- 4. icd 10 code for skin cancer screening preventive
- 5. icd 10 code for polycystic ovarian disease
- 6. icd 10 code for other cholelithiasis without obstruction
- 7. icd-10 code for retention of urine
- 8. icd-10 code for thoracic kyphosis
- 9. icd 9 code for hypoxic encephalopathy
- 10. icd 10 code for mental status no change