What is the ICD 10 for GERD?
ICD-10-CM Code. K21.9. K21.9 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . The use of ICD-10 code K21.9 can also apply to:
What is diagnosis code k08.122 in ICD-10?
The ICD-10-CM code K08.122 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like complete edentulism class ii, complete edentulism class ii due to periodontal disease or complete edentulism due to periodontal disease. Other disorders of teeth and supporting structures ( K08)
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is diagnosis code 10?
What is an ICD-10 diagnosis code? The ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) is a system used by physicians and other healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
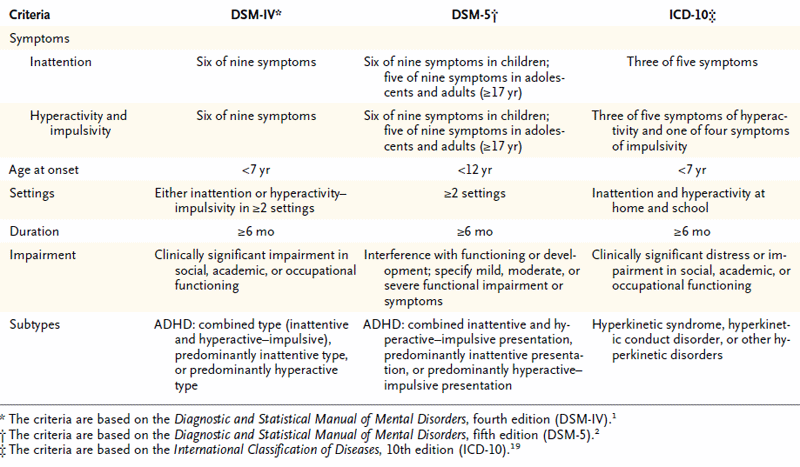
What is the difference between hyperkinetic disorder and ADHD?
In the current edition of ICD-10 (WHO, 1993), ADHD is called “Hyperkinetic Disorder” (HKD). DSM-IV and ICD- 10 have the same 18 symptoms for diagnosis, with only slight differences in the way the symptoms are worded. Both have the same 9 IA symptoms for the diagnosis of ADHD/HKD.
What is ICD-10 code F90?
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorders.
What is the F code for ADD?
Code F90. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Unspecified Type. It is A behavior disorder originating in childhood in which the essential features are signs of developmentally inappropriate inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
Is F90 9 a billable code?
F90. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What does diagnosis Z79 899 mean?
ICD-10 Code for Other long term (current) drug therapy- Z79. 899- Codify by AAPC. Factors influencing health status and contact with health services. Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status.
What does F41 1 mean?
ICD-10 Code F41.1. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is part of a cluster of diagnoses called the anxiety disorders. Anxiety disorders are a group of psychiatric conditions that include: Generalized anxiety disorder.
What does F43 23 mean?
ICD-Code F43. 23 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Adjustment Disorder with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood.
What is the ICD-10 code for ADHD ADD without hyperactivity?
ICD-10 code: F98. 80 Attention deficit disorder without hyperactivity with onset usually occurring in childhood and adolescence.
What is the ICD-10 code for ADHD inattentive type?
ICD-10 Code for Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, predominantly inattentive type- F90. 0- Codify by AAPC.
What is F43 22 code?
ICD-10 code F43. 22 for Adjustment disorder with anxiety is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
What does F90 0 mean on a prescription?
ICD-10 code: F90.0. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurobehavioral disorder that usually first becomes apparent in childhood.
What is R46 89?
R46. 89 - Other symptoms and signs involving appearance and behavior | ICD-10-CM.
What is the code for hyperkinetic disorder?
Accordingly, the main subdivision is made according to the presence or absence of these associated features. The code used should be F90.0 when the overall criteria for hyperkinetic disorder (F90.-) are met but those for F91.- (conduct disorders) are not.
Why are hyperkinetic children prone to accidents?
Hyperkinetic children are often reckless and impulsive, prone to accidents, and find themselves in disciplinary trouble because of unthinking (rather than deliberately defiant) breaches of rules.
When hyperkinesis was present in childhood, but has disappeared and been succeeded by another condition, such as answer?
When hyperkinesis was present in childhood, but has disappeared and been succeeded by another condition, such as dissocial personality disorder or substance abuse, the current condition rather than the earlier one is coded.
Which disorder takes precedence over a pervasive developmental disorder?
Mixed disorders are common, and pervasive developmental disorders take precedence when they are present. The major problems in diagnosis lie in differentiation from conduct disorder: when its criteria are met, hyperkinetic disorder is diagnosed with priority over conduct disorder.
Is learning disorder a part of hyperkinetic disorder?
Learning disorders and motor clumsiness occur with undue frequency, and should be noted separately when present; they should not, however, be part of the actual diagnosis of hyperkinetic disorder.
Is hyperkinesis a secondary problem?
Secondary complications include dissocial behaviour and low self-esteem. There is accordingly considerable overlap between hyperkinesis and other patterns of disruptive behaviour such as “unsocialized conduct disorder”. Nevertheless, current evidence favours the separation of a group in which hyperkinesis is the main problem.
Is hyperkinesis an ICD?
A diagnosis of hyperkinesis, the ICD equivalent of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, depends on this set of symptoms, which can be evaluated by psychiatrists and other mental health professionals . Also see the separate page on the DSM approach to ADHD (“ ADD and ADHD: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms ”).
Your attentiveness, your urge to move about, and your behavior towards other people are impaired as part of a disorder
You probably find it hard to concentrate on something for a long time. You are probably easily distracted and do many different things quickly, one after the other. With this type of disorder, the person often finds it difficult to wait. They often act spontaneously and without thinking.
Information
This information is not intended for self-diagnosis and does not replace professional medical advice from a doctor.
Source
Provided by the non-profit organization “Was hab’ ich?” gemeinnützige GmbH on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG).
Information
In outpatient care, the ICD code on medical documents is always appended with a diagnostic confidence indicator (A, G, V or Z): A (excluded diagnosis), G (confirmed diagnosis), V (tentative diagnosis) and Z (condition after a confirmed diagnosis).
Source
Provided by the non-profit organization “Was hab’ ich?” gemeinnützige GmbH on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG).
Further articles
Children with ADHD are particularly inattentive, impulsive, and active. The symptoms markedly improve in adulthood or may even disappear.
What is hyperkinetic disorder?
Hyperkinetic disorder is a psychiatric syndrome emerging in early childhood that features an enduring pattern of severe, developmentally inappropriate inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity across different settings ( e.g., home and school) that significantly impair academic, social and work performance. Specialty:
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code F90.9 and a single ICD9 code, 314.9 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICd code for attention deficit disorder?
F90.9 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, unspecified type. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the ICd code for hyperkinetic disorder?
The ICD code F90 is used to code Hyperkinetic disorder. Hyperkinetic disorder is a psychiatric syndrome emerging in early childhood that features an enduring pattern of severe, developmentally inappropriate inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity across different settings (e.g., home and school) that significantly impair academic, ...
What is the ICD code for acute care?
F90. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code F90 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the five child codes of F90 that describes the diagnosis 'attention-deficit ...
What is hyperkinetic conduct disorder?
Hyperkinetic conduct disorder. Long term current use of medication for add and or adhd. Long term current use of medication for attention deficit disorder (add) or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd) Clinical Information.
When will the ICD-10-CM F90.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F90.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.

Diagnosis
Symptoms
- This group of disorders is characterized by: early onset; a combination of overactive, poorly modulated behaviour with marked inattention and lack of persistent task involvement; and pervasiveness over situations and persistence over time of these behavioural characteristics. Hyperkinetic disorders always arise early in development (usually in the first 5 years of life). Thei…
Clinical significance
- It is widely thought that constitutional abnormalities play a crucial role in the genesis of these disorders, but knowledge on specific etiology is lacking at present. In recent years the use of the diagnostic term attention deficit disorder for these syndromes has been promoted. It has not been used here because it implies a knowledge of psychological processes that is not yet availa…
Prognosis
- Secondary complications include dissocial behaviour and low self-esteem. There is accordingly considerable overlap between hyperkinesis and other patterns of disruptive behaviour such as unsocialized conduct disorder. Nevertheless, current evidence favours the separation of a group in which hyperkinesis is the main problem.
Epidemiology
- Hyperkinetic disorders are several times more frequent in boys than in girls. Associated reading difficulties (and/or other scholastic problems) are common.
Causes
- Acute onset of hyperactive behaviour in a child of school age is more probably due to some type of reactive disorder (psychogenic or organic), manic state, schizophrenia, or neurological disease (e.g. rheumatic fever).
Usage
- This coding should be used when both the overall criteria for hyperkinetic disorders (F90.-) and the overall criteria for conduct disorders (F91.-) are met.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for foreign body cornea in left eye
- 2. icd-9 code for gastritis
- 3. icd 10 code for 32723
- 4. icd 9 code for bronchospastic lung disease
- 5. icd 10 code for vocal cord polyp
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for pleuritic chest pain
- 7. ghi insurance icd-9 code for annual gynecological exam
- 8. icd 10 code for dvt left common femoral vein
- 9. icd 10 code for renal absces
- 10. icd 10 cm 2020 code guidelines for general medicine