How do you code severe sepsis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G97.2 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Intracranial hypotension following ventricular shunting. any associated diagnoses or complications. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G97.2. Intracranial hypotension following ventricular shunting. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Code Also.
How to code severe sepsis?
Apr 11, 2022 · Sepsis with Hypotension - AHA Coding Clinic® for ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS (ICD-9) $197 Certifications. ×. Certification from QPro.com. Enhance your career, show your qualifications. Prove your worth, get promoted, increase income. Comprehensive 100 question tests. Safe, friendly, online certification. learn more.
Why are lactic acid levels elevated in sepsis patients?
Oct 01, 2021 · Severe sepsis with septic shock. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. R65.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R65.21 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Nanda nursing diagnosis of hypotension?
ICD-10-CM Description A41.9 Sepsis, unspecified organism; Septicemia NOS Created July 2021 Admitted for sepsis and a localized infection (pneumonia). Sepsis due to localized infection Assign sepsis first: A41.9 Assign localized infection (pneumonia) second: J18.9 Admitted for a localized infection (pneumonia) but sepsis develops after admission.
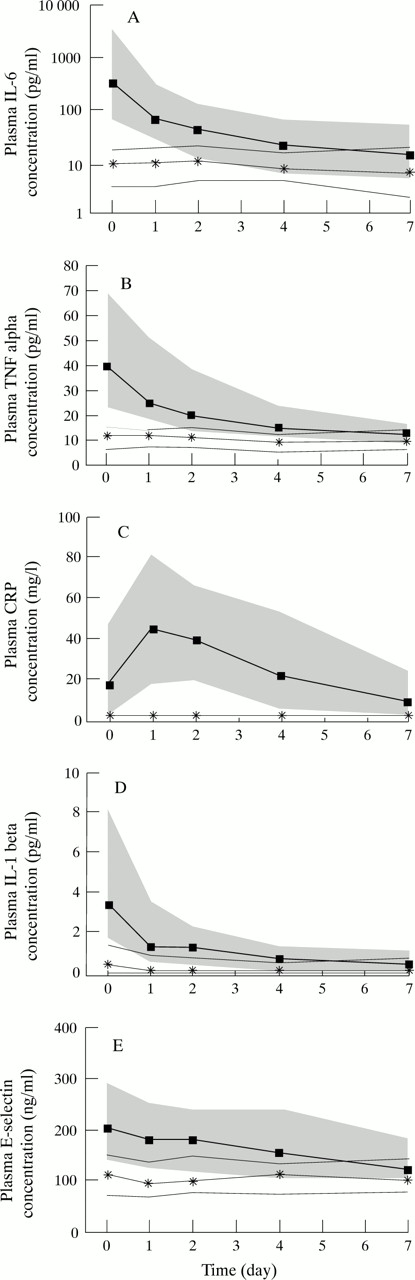
Do you code Hypotension with sepsis?
Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2003, pages 79-81, stated, "Septic shock is sepsis with hypotension, a failure of the cardiovascular system." Our coders have interpreted this literally, meaning anytime sepsis with hypotension is documented that septic shock should be coded.
What is the ICD-10 code for septic?
A41.9ICD-10-CM Code for Sepsis, unspecified organism A41. 9.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute Hypotension?
I95ICD-10 code I95 for Hypotension is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is severe sepsis ICD-10?
ICD-10 code R65. 21 for Severe sepsis with septic shock is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Can sepsis be coded as primary diagnosis?
According to the guidelines above, sepsis would be the appropriate principal diagnosis if it is the reason the patient is admitted, and meets the definition of principal diagnosis.Dec 5, 2016
What is the correct ICD 10 code for thrombocytopenia?
ICD-10 | Thrombocytopenia, unspecified (D69. 6)
What is the medical code for hypotension?
I95.9ICD-10 code I95. 9 for Hypotension, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is transient hypotension?
Conclusions: Transient hypotension is common in the ICU and is associated with increased acute mortality and decreased functional status in patients with head injury. The impact of this secondary insult is greatest in patients with less severe primary injury.
What is iatrogenic hypotension?
Drug-induced hypotension in old age may lead to severe emergency situations. In view of the great number of drugs with desired lowering of blood pressure or hypotensive side effects used for therapy of old patients an accurate indication is imperative.
What is diagnosis code R65 2?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R65. 2: Severe sepsis.
How do you code severe sepsis with septic shock?
For cases of septic shock, a minimum of two codes is needed to report severe sepsis with septic shock. Chapter-specific guidelines state, “First code for the underlying systemic infection, followed by R65. 21, septic shock. If the causal organism is not documented, assign code A41.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R50 9?
ICD-10 code: R50. 9 Fever, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
What is septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to?
Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to group a streptococcus. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to group b streptococcus. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to meningococcal septicemia.
What is septic shock?
Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to anaerobic septicemia. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to chromobacterium. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to coagulate-negative staphylococcu.
What is transient hypotension?
Transient hypotension. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by a blood pressure that is below the normal expected for an individual in a given environment. Abnormally low blood pressure that can result in inadequate blood flow to the brain and other vital organs.
Why does blood pressure drop?
In other people, blood pressure drops below normal because of some event or medical condition. Some people may experience symptoms of low pressure when standing up too quickly. Low blood pressure is a problem only if it causes dizziness, fainting or in extreme cases, shock.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if severe sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
What is post-procedural sepsis?
Post-procedural Sepsis and Sepsis Due to a Device, Implant, or Graft. A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to wound infection, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.
When to query a physician for sepsis?
You must query the physician when the term “sepsis syndrome” is documented as a final diagnosis. Know when to Query. Sepsis is a complicated condition to code, and it is often necessary to query the physician to code the case correctly.
Can you code for sepsis?
Documentation issues: You can code for sepsis when the physician documents the term “sepsis.”. Documentation should be consistent throughout the chart. Occasionally, during an extended length of stay, sepsis may resolve quickly and the discharging doctor may not include the diagnosis of sepsis on the discharge summary.
Is sepsis a systemic infection?
term “sepsis” must also be documented to code a systemic infection. This is a major change from ICD-9-CM. If the term “sepsis” is not documented with “SIRS” when it’s due to a localized infection, you must ask for clarification from the physician.
Is septic shock documented without sepsis?
Documentation issues: The term “septic shock” is occasionally documented without the term “sepsis.”. According to the guidelines, for all cases of septic shock the code for the underlying systemic infection is sequenced first, followed by R65.21 Severe sepsis with septic shock or T81.12- Postprocedural septic shock.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
How to improve sepsis documentation?
To improve sepsis documentation, coding staff needs to work closely with clinical documentation improvement specialists (CDIs), and everyone must be clear on what documentation is needed to correctly code sepsis. A physician champion can be helpful to establish guidelines for the physicians and standard terminology to use when documenting sepsis. A coding tip sheet that includes various scenarios is a helpful tool for the coding department to standardize definitions and the interpretation of the coding guidelines. A regular audit of sepsis DRGs or sepsis as a secondary code can help to identify documentation issues and coders who need more education. Sepsis is never going to be easy to code, but with continuous education and teamwork across departments, the sepsis beast can be conquered.
How does sepsis affect the body?
Sepsis is an extreme response to infection that develops when the chemicals the immune system releases into the bloodstream to fight infection cause widespread inflammation. This inflammation can lead to blood clots and leaky blood vessels, and without timely treatment, may result in organ dysfunction and then death. Severe cases of sepsis often result from a body-wide infection that spreads through the bloodstream, but sepsis can also be triggered by an infection in the lungs, stomach, kidneys, or bladder. Thus, it is not necessary for blood cultures to be positive to code sepsis (guideline I.C.1.d.1.a.i).
What is septic shock?
Septic shock refers to circulatory failure associated with severe sepsis. It is a life-threatening condition that happens when the exaggerated response to infection leads to dangerously low blood pressure (hypotension). Septic shock is a form of organ failure.
What is the most common type of infection that leads to sepsis?
Localized Infection. Almost any type of infection can lead to sepsis. Infections that lead to sepsis most often start in the lung, urinary tract, skin, or gastrointestinal tract. When localized infections are contained, they tend to be self-limiting and resolve with antibiotics.
When is a localized infection coded?
If the patient is admitted with a localized infection and the patient does not develop sepsis or severe sepsis until after the admission, the localized infection is coded first, followed by the appropriate codes for sepsis or severe sepsis, if applicable .
What is systemic infection?
A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to postoperative wound infections, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for degenerative spondylolisthesis
- 2. icd 10 code for stage 2 sacral decubitus ulcer
- 3. icd 10 code for sacroiliitis not elsewhere classified
- 4. icd-10 code for cellulitis bilateral hands
- 5. icd 10 code for pregnancy hypertension
- 6. icd 10 code for hematoma on her left leg just above the ankle
- 7. icd 10 code for blister right great toe
- 8. icd 10 code for spinal cord stimulator battery failure
- 9. icd 10 code for infected ruptured kidney cyst
- 10. icd 10 code for physical exam with abnormal findings