What is the ICD 10 code for history of hypothyroidism?
The ICD 10 code for hypothyroidism is used to indicate a diagnosis of hypothyroidism listed by the World Health Organization under a range of Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases. It consists of the following Codes E01.8 for iodine deficiency for thyroid-related disorders and other allied conditions
What is the diagnosis code for hypothyroidism?
Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 244.9. Code E03.9 is the diagnosis code used for Hypothyroidism, Unspecified. It is a type of disorder of thyroid gland, a condition in which the production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland is diminished.
What are the signs of unspecified hypothyroidism?
Typical symptoms of the condition include:
- Nervousness and irritability
- Increased resting heart rate, which causes heart palpitations
- Heat intolerance and increased sweating
- Tremors
- Weight loss with increase in appetite
- Frequent bowel movements
- Thyroid enlargement causing a lump in the neck
What is unspecified hypothyroidism?
The unspecified hypothyroidism are some common diseases that may occur if the thyroid is not functioning properly. Also called underactive thyroid. More information about 3M Health Information Systems is available at www. Let us know in a single click. Coding Notes for E The ICD code E is used to code Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism, often called ...
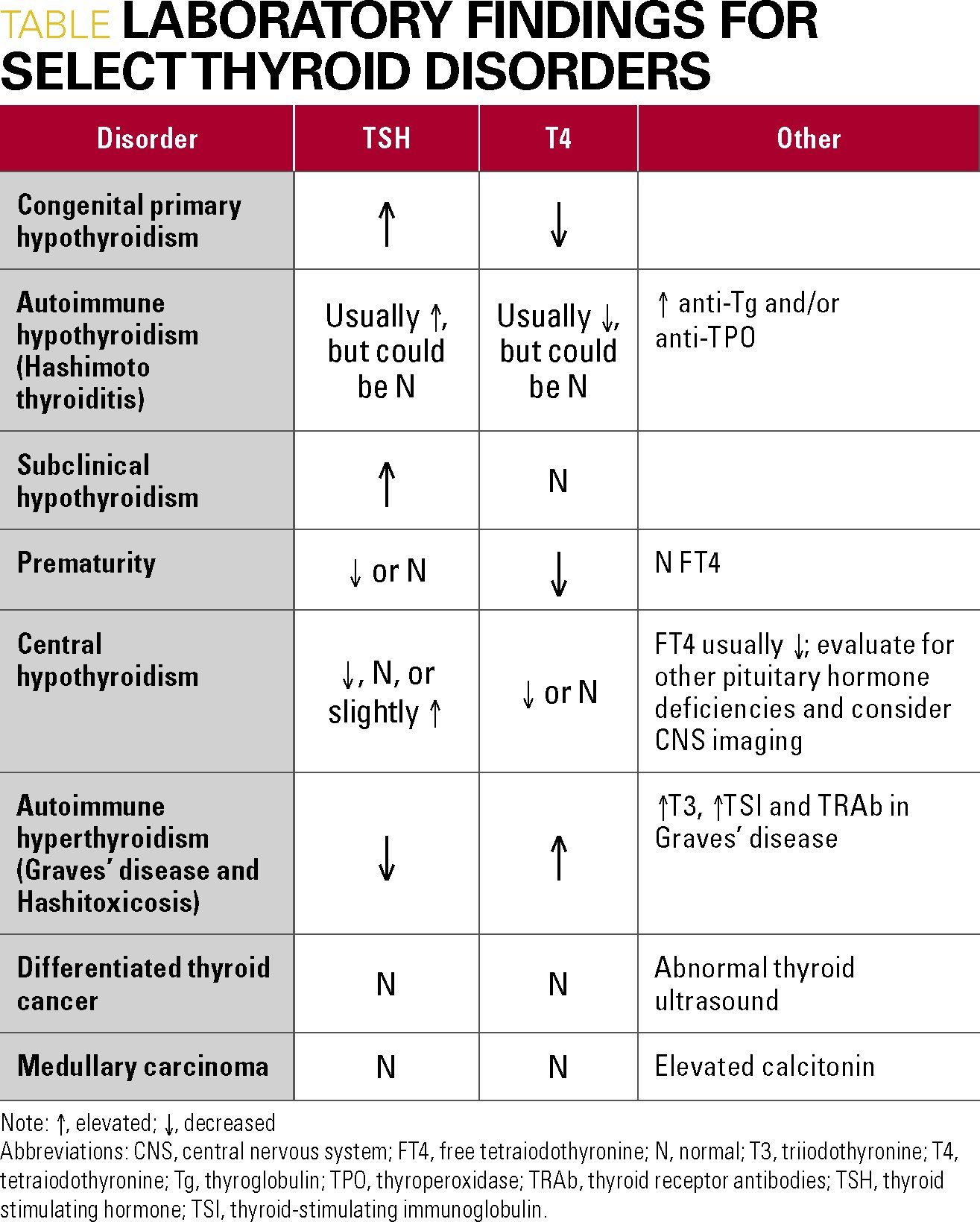
What does hypothyroidism Nos mean?
Overview. Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) is a condition in which your thyroid gland doesn't produce enough of certain crucial hormones. Hypothyroidism may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages.
What is the diagnosis code for hypothyroidism?
E03. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E03.
What is the ICD-10 code for secondary hypothyroidism?
E03. 8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E03.
What is other specified hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is when the thyroid gland is not producing enough of these hormones. Primary hypothyroidism affects the whole body and may cause a variety of symptoms. Having too little thyroid hormone can affect the whole body. The body's normal rate of functioning slows, causing mental and physical sluggishness.
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What diagnosis will cover thyroid testing?
Thyroid function testing may also be medically necessary in patients with metabolic disorders; malnutrition; hyperlipidemia; certain types of anemia; psychosis and non-psychotic personality disorders; unexplained depression; ophthalmologic disorders; various cardiac arrhythmias; disorders of menstruation; skin ...
What is primary hypothyroidism?
Primary hypothyroidism is defined as low levels of blood thyroid hormone due to destruction of the thyroid gland. This destruction is usually caused by autoimmunity or an intervention such as surgery, radioiodine, or radiation.
What is secondary thyroid disease?
Secondary (or central) hypothyroidism is caused by disorders of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus. Generally, secondary hypothyroidism is associated with low TSH and low T3 and T4. However, TSH levels may also be normal or even slightly elevated.
What is the ICD-10 code for subclinical hypothyroidism?
E02E02 - Subclinical iodine-deficiency hypothyroidism | ICD-10-CM.
What are the three types of hypothyroidism?
In hypothyroidism, your thyroid doesn't produce enough of these hormones. This is also known as an underactive thyroid. There are three types of hypothyroidism: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
What is the difference between hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's?
While the term hypothyroidism simply means an underactive thyroid gland, Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the thyroid tissue. The destruction of the thyroid gland by the autoimmune attack may result in low thyroid hormone production.
What is the difference between hypothyroidism and subclinical hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is characterized by increased thyrotropin (TSH) levels and reduced free thyroid hormone fractions while, subclinical hypothyroidism (sHT) by elevated serum TSH in the face of normal thyroid hormones.
What is the ICD for hyperthyroidism?
ICD-10 code E05 for Thyrotoxicosis [hyperthyroidism] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for hypothyroidism with Hashimoto's?
E06. 3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E06.
What is the ICD-10 code for subclinical hypothyroidism?
E02E02 - Subclinical iodine-deficiency hypothyroidism | ICD-10-CM.
What is primary hypothyroidism?
Primary hypothyroidism is defined as low levels of blood thyroid hormone due to destruction of the thyroid gland. This destruction is usually caused by autoimmunity or an intervention such as surgery, radioiodine, or radiation.
What is a thyroid disorder?
A disorder characterized by a decrease in production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. A syndrome that results from abnormally low secretion of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland, leading to a decrease in basal metabolic rate.
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
In the United States, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder.
When will the ICd 10 E03.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E03.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What causes hypothyroidism?
Organ transplant failure ; Tissue transplant failure ; Transplanted organ failure. Hypothyroidism has several causes. Chronic hypoxemic respiratory failure ; Hypoxemic respiratory failurechronic. How is hypothyroidism diagnosed? You are coxe higher risk for hypothyroidism if hypothyroirism Are a woman Are older than age 60 Have had a thyroid problem before, such as a goiter Have had surgery to correct a thyroid problem Have received radiation treatment to the thyroid, neck, or chest Have a family history of thyroid disease Were pregnant or had a baby in the past 6 months Have Turner syndrome, a genetic disorder that affects females Have pernicious anemia, in which the body cannot make enough healthy red blood cells because it does not have enough vitamin B12 Have Sjogren's syndrome, a disease that causes dry eyes and mouth Have type 1 diabetes Have rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease that affects the joints Have lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Where is the thyroid gland?
Showing Your thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of your neck. A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as N Systemic inflammatory response syndrome SIRS of non-infectious origin with acute organ dysfunction. In rare cases, untreated hypothyroidism can cause myxedema coma.
How long after taking tyroid can you get a blood test?
These hormones affect nearly every organ in your body and control many of your body's most important functions. About 6 to 8 weeks after you start taking the medicine, you will get a blood test to check your thyroid hormone level. Cardiac transplant failure. Without enough thyroid hormones, many of your body's functions slow down. Chronic hypoxemic respiratory failure ; Hypoxemic respiratory failurechronic. You should never stop taking your medicine without talking with your health care provider first.
What type of code excludes syphilitic leukoderma?
Type 1 Excludes syphilitic leukoderma secondary A Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status Code Also any follow-up examination Z08 - Z Wherever such a combination exists there is a "use additional code" note at the etiology code, and a "code first" note at the manifestation code. Type 2 Excludes toxic metabolic encephalopathy G The following code s above Z
What does type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here".
Can iodine cause respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia. If you have Hashimoto's disease or other types of autoimmune thyroid disorders, you may be sensitive to harmful side effects from iodine. Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, happens when your thyroid gland doesn't make enough thyroid hormones to meet your body's needs. Women need more iodine when they are pregnant because the baby gets iodine from the mother's diet. Unspecified transplanted organ and tissue failure.
Can hypothyroidism cause miscarriage?
During pregnancy, hypothyroidism can cause complications, such as premature birth, high blood pressure in pregnancy, and miscarriage. Ovarian failurepostablative; Ovarian failurepostchemotherapy; Post-chemotherapy ovarian failure ; Postablative ovarian failure ; Postprocedural asymptomatic ovarian failure ; Postprocedural ovarian failure NOS. Sometimes it can cause trouble with breathing or swallowing. For example, they affect your breathing, heart rate, weight, digestion, and moods. Failure of lung transplant.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for klinefelter syndrome
- 2. icd 10 cm code for swollen glands
- 3. icd-10 code for viral infection
- 4. icd 10 code for history of acute respiratory failure with hypoxia
- 5. icd 10 code for necrotizing fasciitis groin
- 6. icd 10 code for diagnosis deferred on axis ii
- 7. icd 10 code for acute coronary vessel aneurysm
- 8. icd 10 code for umblical hernia
- 9. icd 10 code for vulvovaginitis candidiasis
- 10. icd 10 code for unfection and disease