Which ICD 10 code should not be used for reimbursement purposes?
H34.819 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H34.819 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for unspecified corneal edema?
Unspecified corneal edema 1 H18.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM H18.20 became effective on October 1, 2019. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H18.20 - other international versions of ICD-10 H18.20 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for trauma to the eye?
H18.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18.20 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H18.20 - other international versions of ICD-10 H18.20 may differ. injury (trauma) of eye and orbit ( S05.-)
What is the ICD 10 code for retinal detachment of epithelium?
Serous detachment of retinal pigment epithelium, unspecified eye. H35.729 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H35.729 became effective on October 1, 2018.
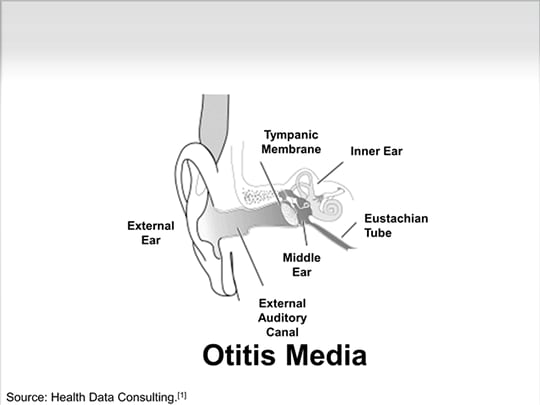
What is HZO in ophthalmology?
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO), commonly known as shingles, is a viral disease characterized by a unilateral painful skin rash in one or more dermatome distributions of the fifth cranial nerve (trigeminal nerve), shared by the eye and ocular adnexa.
What is the ICD 10 code for epithelial defect?
Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18. 52 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does zoster without complications mean?
A common dermal and neurologic disorder caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus that has remained dormant within dorsal root ganglia, often for decades, after the patient's initial exposure to the virus in the form of varicella (chickenpox).
What is the ICD 10 code for zoster Ophthalmicus?
B02. 39 - Other herpes zoster eye disease | ICD-10-CM.
What is an epithelial defect?
Corneal epithelial defects are focal areas of epithelial (outermost corneal layer) loss; they can be due to mechanical trauma, corneal dryness, neurotrophic disease, post surgical changes, infection, or any other of a variety of etiologies.
What is persistent epithelial defects?
Persistent corneal epithelial defects (PEDs or PCEDs) result from the failure of rapid re-epithelialization and closure within 10-14 days after a corneal injury, even with standard supportive treatment [4, 5]. If left untreated, PEDs can result in significant complications, including infection and vision loss.
What is the difference between localized and disseminated shingles?
With localized herpes zoster, the rash usually appears as a wide strip on one side of the body. With disseminated (more widespread) herpes zoster, the rash covers a wider area of the body.
What are the three stages of shingles?
Shingles' clinical manifestations are divided into 3 distinct phases: preeruptive, acute eruptive, and chronic. The preeruptive phase (or preherpetic neuralgia stage) usually lasts about 48 hours but can stretch to 10 days in some cases.
Can you get shingles if you had the vaccine?
Can you get shingles after you've been vaccinated? While the shingles vaccine is highly effective, some people can still get shingles. However, people who do get shingles after getting the shingles vaccine usually have milder symptoms and a shorter illness.
What is the ICD 9 code for shingles?
053.9ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 053.9 : Herpes zoster without mention of complication.
What disseminated shingles?
Disseminated shingles is a widespread form of shingles that covers more areas of the body. Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a skin rash that causes blisters across one side of the body. The same virus that causes chickenpox, the varicella-zoster virus, causes shingles.
What causes shingles in the eye?
Shingles of the eye is a painful viral infection on the eye. It can also cause swelling of the eyelid. Most people have a rash and blisters on the forehead, nose, and upper eyelid. It's caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox.
What is J34 89?
ICD-10 code J34. 89 for Other specified disorders of nose and nasal sinuses is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What are punctate epithelial erosions?
Punctate epithelial erosions (PEE) are evidence of ocular surface dryness. They represent areas of epithelial cell loss and therefore stain positively with fluorescein. The distribution of the PEE can provide information regarding the underlying etiology.
What is epithelial ingrowth?
Epithelial ingrowth is the presence of corneal epithelium in an area where it does not belong. After LASIK, epithelial ingrowth can occur in the interface between the flap and the stromal bed of the patient's cornea.
What can cause corneal abrasion?
Your cornea can be scratched by contact with dust, dirt, sand, wood shavings, metal particles, contact lenses or even the edge of a piece of paper. Corneal abrasions caused by plant matter (such as a pine needle) usually require special attention as they can cause a delayed inflammation inside the eye (iritis).
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2019 icd 10 code for tear of the long biceps tendon
- 2. icd 10 code for chronic feet issue
- 3. icd 10 code for attention to colostomy
- 4. icd 10 code for nonunion of the scaphoid bone
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for aki
- 6. icd 10 code for severe acute pancreatitis
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for ankle stiffness
- 8. icd 10 code for observation after fall
- 9. icd 10 code for right bicep tendonitis
- 10. icd 10 code for pronator syndrome