What is the ICD 10 Index for parkinsonism (idiopathic)?
References in the ICD-10-CM Index to Diseases and Injuries applicable to the clinical term "parkinsonism (idiopathic) (primary)" Parkinsonism (idiopathic) (primary) - G20 Parkinson's disease arteriosclerotic - G21.4 Vascular parkinsonism dementia - G31.83 Dementia with Lewy bodies
What is the ICD 10 code for autonomic neuropathy?
2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G90.0: Idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy. ICD-10-CM Codes. ›. G00-G99 Diseases of the nervous system. ›. G89-G99 Other disorders of the nervous system. ›.
What is the a'billable'code for parkinsonism?
A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability.
What is the ICD 10 code for progressive progressive degeneration?
Progressive, degenerative disorder of the nervous system characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, and gait abnormalities; caused by a loss of neurons and a decrease of dopamine in the basal ganglia. ICD-10-CM G20 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0):

What is the ICD-10 code for idiopathic Parkinson's disease?
ICD-10 code G20 for Parkinson's disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
Is idiopathic Parkinson's disease the same as Parkinson's disease?
Most people with parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinson's disease, also known as Parkinson's. Idiopathic means the cause is unknown. The most common symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson's are tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Parkinson's disease with dementia?
Disease, Parkinson: You will see Parkinsonism dementia listed with the codes G31. 83 and F02. 80.
What is the diagnosis code for Parkinson's disease?
Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology.
How is idiopathic Parkinson's disease diagnosed?
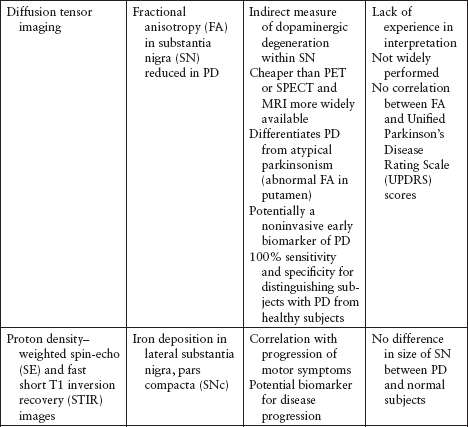
Imaging studies to evaluate Parkinson's disease and Parkinsonian syndromes include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which examines the structure of the brain, and DaTscan, an imaging test approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to detect the dopamine function in the brain.
What are the 2 types of Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease that affects dopamine-producing nerve cells in the brain. There are three main types of PD—idiopathic, early-onset, and familial.
What is the correct code and sequencing for dementia and Parkinson's disease?
In the tabular code G20 represents PD, and it would be sequenced first, followed by the manifestation(s). Code F02. 80 and F02. 81 represent the manifestation of dementia in diseases classified elsewhere, with or without behavioral disturbance.
What is the ICD 10 code for unspecified neurocognitive disorder?
ICD-10-CM Code for Unspecified symptoms and signs involving cognitive functions and awareness R41. 9.
What is secondary Parkinson's disease?
Definition. Secondary parkinsonism is when symptoms similar to Parkinson disease are caused by certain medicines, a different nervous system disorder, or another illness. Parkinsonism refers to any condition that involves the types of movement problems seen in Parkinson disease.
What is I10 diagnosis?
ICD-Code I10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Essential (Primary) Hypertension.
What is the ICD-10 code for tremors?
ICD-10 code R25. 1 for Tremor, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for bradykinesia?
8X5, and consistent nonfluctuating bradykinesia could be coded with T42. 8X6. There is currently an ICD-10-CM code for dystonia (G24) and subcodes for different types of dystonia (G24. 0–G24.
What is Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease is a disorder that affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. In parkinson's, neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements.
How old do you have to be to get Parkinson's?
They may also have problems such as depression, sleep problems or trouble chewing, swallowing or speaking. Parkinson's usually begins around age 60, but it can start earlier.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is neurocognitive disorder?
Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior.
What are the symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
The early stages of PD include the following signs and symptoms: Slight shaking of a finger, hand, leg, chin, or lip. Stiffness or difficulty walking. Difficulty getting out of a chair.
How many people are affected by Parkinson's disease?
As a neurodegenerative disease of the brain, which impacts an individual’s motor function, Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the most common neurological disorder, affecting approximately one million people in the United Status. It is estimated that approximately 60,000 Americans are diagnosed with PD each year, and this number does not reflect ...
What is the PD G20 code?
With PD G20 code, you will be coding associated signs and symptoms or those complications not necessarily inherent to the disease. Most of these complications will be found in Chapter 18, as signs and/or symptoms.
What is the third category of medication for PD?
The third category of drugs prescribed for PD includes medications that help control the non-motor symptoms of the disease ; that is, the symptoms that don't affect movement. For example, people with PD-related depression may be prescribed antidepressants.
What is the second category of PD drugs?
The second category of PD drugs affects other neurotransmitters in the body in order to ease some of the symptoms of the disease. For example, anticholinergic drugs interfere with production or uptake of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. These can be effective in reducing tremors.
What are the most common drugs for PD?
The first category includes drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain. The most common drugs for PD are dopamine pre cursors—substances such as levodopa that cross the blood-brain barrier and are then changed into dopamine.
PD Progression & Motor Complications
PD is a chronic, progressive disorder affecting approximately 1 million people in the US. 3-5 Disease progression causes greater morbidities and disabilities because of advancing fluctuations in motor and nonmotor symptoms.
Limitations of Current ICD-10-CM Coding for PD
Unlike other neurologic disorders (eg, migraine and epilepsy), there is only a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, namely G20. 22 The single, nonspecific code for PD cannot accurately capture motor fluctuations and dyskinesia that emerge with PD progression.
Recommendations for PD ICD-10-CM Coding
Based on this review, the panel recommends the ICD-10-CM coding structure for PD be expanded to provide specificity to distinguish motor complications of dyskinesia and/or “OFF” episodes (Table 2; Figure 1).
Revising PD ICD-10-CM Coding May Improve Care
The current, single, nonspecific ICD-10-CM code for PD does not accurately specify patients with motor complications, including “OFF” episodes and dyskinesia.
Support for Revision of ICD-10-CM Codes for PD
The American Academy of Neurology supports the need to update the ICD-10-CM coding to better reflect the progression of PD. Patient advocacy groups also support this need, including the Michael J.
Summary
Revision of the ICD-10-CM coding structure for PD is a major unmet need for a population that is expected to continue to increase over the next decade. The treatment paradigm for PD continues to evolve with specific medications now available for PD dyskinesia and for the on-demand management of “OFF” episodes in PD.
What is the ICD code for secondary parkinsonism?
G21.9 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of secondary parkinsonism, unspecified. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code G21.9 and a single ICD9 code, 332.1 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the most common cause of parkinsonism?
The neurodegenerative condition Parkinson's disease (PD) is the most common cause of parkinsonism. However, a wide range of other etiologies may lead to a similar set of symptoms, including some toxins, a few metabolic diseases, and a handful of neurological conditions other than Parkinson's. Specialty:
Is Parkinson's disease a neurodegenerative disease?
Parkinsonism shares symptoms found in Parkinson's disease, from which it is named; but parkin sonism is a symptom complex, and differs from Parkinson disease which is a progressive neurodegenerative illness. The underlying causes of parkinsonism are numerous, and diagnosis can be complex. The neurodegenerative condition Parkinson's disease (PD) is the most common cause of parkinsonism. However, a wide range of other etiologies may lead to a similar set of symptoms, including some toxins, a few metabolic diseases, and a handful of neurological conditions other than Parkinson's.
PD Progression & Motor Complications
Limitations of Current ICD-10-CM Coding For PD
- Unlike other neurologic disorders (eg, migraine and epilepsy), there is only a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, namely G20.22 The single, nonspecific code for PD cannot accurately capture motor fluctuations and dyskinesia that emerge with PD progression. Based on the limitations of a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, a 7-member panel (6 movement disorder ...
Recommendations For PD ICD-10-CM Coding
- Based on this review, the panel recommends the ICD-10-CMcoding structure for PD be expanded to provide specificity to distinguish motor complications of dyskinesia and/or “OFF” episodes (Table 2; Figure 1). The proposed changes include delineating between individuals without dyskinesia or fluctuations (G20.01), without dyskinesia but with fluctuations (G20.02), with dyski…
Revising PD ICD-10-CM Coding May Improve Care
- The current, single, nonspecific ICD-10-CM code for PD does not accurately specify patients with motor complications, including “OFF” episodes and dyskinesia. Consequently, the prevalence of these symptoms and their effect on patients, caregivers, and the overall health care system is extremely difficult to screen, document, and track in a systematic fashion. There is a pressing n…
Support For Revision of ICD-10-CM Codes For PD
- The American Academy of Neurology supports the need to update the ICD-10-CMcoding to better reflect the progression of PD. Patient advocacy groups also support this need, including the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research (MJFF) and the Unified Parkinson’s Advocacy Council (UPAC), which is a group of national, regional, and state organizations including the Par…
Summary
- Revision of the ICD-10-CM coding structure for PD is a major unmet need for a population that is expected to continue to increase over the next decade. The treatment paradigm for PD continues to evolve with specific medications now available for PD dyskinesia and for the on-demand management of “OFF” episodes in PD. The recommended changes to the ICD-10-CMcoding stru…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 for career vocational code
- 2. icd 10 code for malignant hyperthermia
- 3. icd-10 code for hepatitis b panel
- 4. icd 9 code for trilineage hematopoiesis
- 5. icd 9 code for bilateral knee anterior cruciate ligament
- 6. icd 10 cm code for underweight
- 7. icd 10 code for unimmunized status
- 8. icd 10 code for unspecified foreign body left index finger
- 9. icd 10 code for inquinal hernia
- 10. icd 9 code for retroperitoneal mass