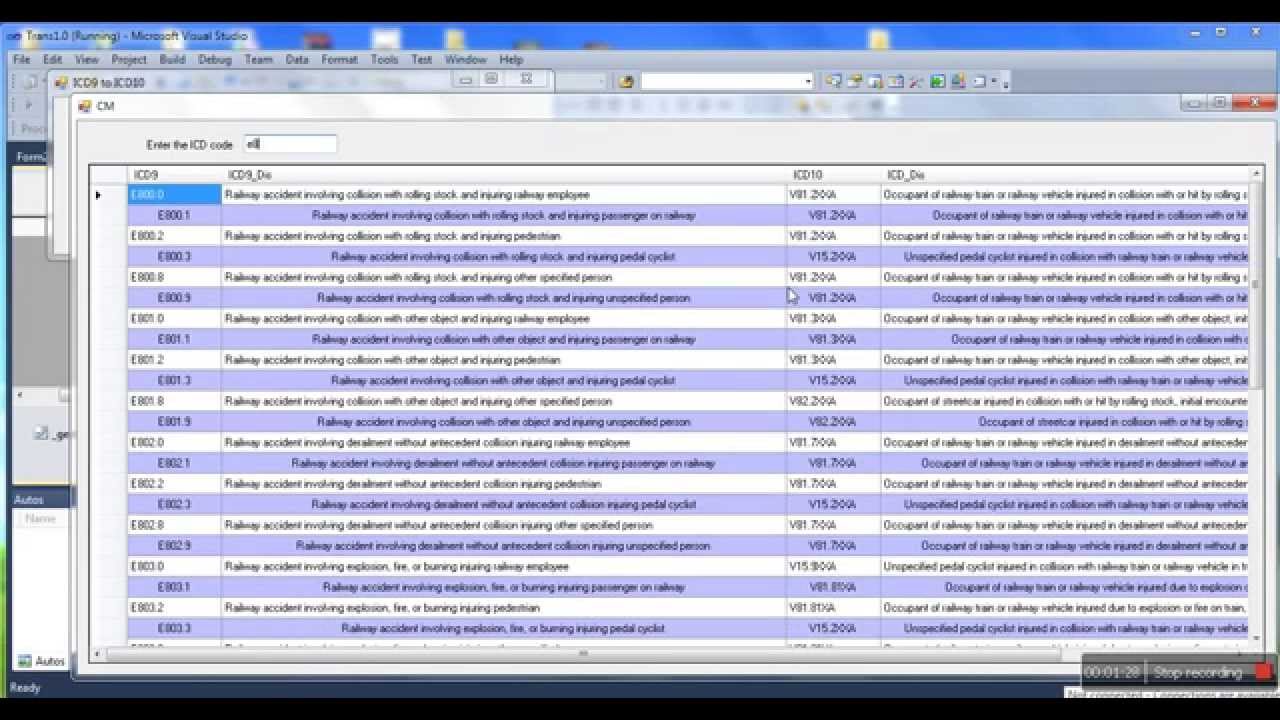
Impaired fasting glucose Billable Code. R73.01 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Impaired fasting glucose . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
How many codes in ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · Impaired fasting glucose. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. R73.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The ICD code R730 is used to code Impaired fasting glucose Impaired fasting glucose (IFG), more commonly known as pre-diabetes refers to a condition in which the fasting blood glucose level is consistently elevated above what is considered normal levels; however, it is not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes mellitus.
What does ICD - 10 stand for?
ICD-10 code R73.01 for Impaired fasting glucose is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now Official Long Descriptor Impaired fasting glucose
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Impaired fasting glucose Billable Code. R73.01 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Impaired fasting glucose . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . ↓ See below for any exclusions, inclusions or special notations.
What is IFG?
A warning of developing Type 2 Diabetes Impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG) is sometimes called pre-diabetes. This is when blood glucose levels in the body are raised, but are not high enough to mean that the person has diabetes.
What is IFG and IGT in diabetes?
Patients with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or impaired fasting glucose (IFG) are at significant risk for diabetes.Apr 15, 2004
What is the ICD-10 code for pre-diabetes?
The ICD-10 code for prediabetes is R73. 09.
What is the ICD-10 code for metabolic syndrome?
ICD-10 | Metabolic syndrome (E88. 81)
What is the difference between IGT and IFG?
IFG is defined as fasting plasma glucose 6.1 to 6.9 mmol/l. IGT is defined as a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) less than 7 mmol/l and 2-hour venous plasma glucose (after ingestion of 75 g oral glucose load) of 7.8 mmol/l or greater and less than 11.1 mmol/l.Jul 12, 2012
What are the criteria for the diagnosis of IFG or IGT?
The World Health Organization (WHO) criteria for impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) are an FPG of less than 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L), if measured, and a venous plasma glucose of 140 mg/dL to just below 200 mg/dL (≥7.8 to <11.1mmol/L) 2 hours after a 75-g glucose load with one intervening plasma glucose value at or above 200 ...
What are the ICD-10 codes for diabetes?
Common Diabetes ICD-10 Diagnosis Codes.E10.22/E11.22 Diabetes, Renal Complication.PLUS.Diabetes, Circulatory/Vascular Complication.Diabetes, Neurological Complication.E10.9. Type 1 Diabetes, w/o complication. E11.9. ... Diabetes, with other Spec. Complications.Type 1 Diabetes with Hypoglycemia.More items...
What ICD-10 covers hemoglobin A1C?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R73. 09: Other abnormal glucose.
What ICD-10 code covers TSH?
Abnormal results of thyroid function studies R94. 6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R94. 6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the correct ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia?
ICD-10 | Thrombocytopenia, unspecified (D69. 6)
What is the ICD-9 code for metabolic syndrome?
This report uses ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes (277.7 and E88. 81, respectively) for the metabolic syndrome (MetS) to summarize trends in the incidence and prevalence of this condition among active component members of the U.S. Armed Forces between 2002 and 2017.
What is E88 81?
E88.81 Metabolic syndrome.
What is the code for impaired fasting glucose?
R73.01 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of impaired fasting glucose. The code R73.01 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the ICd 10 list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code R73.01:
What is it called when your blood sugar is too high?
Diabetes is a disease in which your blood sugar levels are too high. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. Even if you don't have diabetes , sometimes you may have problems with blood sugar that is too low or too high.
How to keep blood sugar levels in target range?
Keeping a regular schedule of eating, activity, and taking any medicines you need can help. If you do have diabetes, it is very important to keep your blood sugar numbers in your target range. You may need to check your blood sugar several times each day.
What is the name of the test that checks blood sugar?
Your health care provider will also do a blood test called an A1C. It checks your average blood sugar level over the past three months. If your blood sugar is too high, you may need to take medicines and/or follow a special diet. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
What is the main source of energy in the body?
Blood Sugar. Also called: Blood glucose. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main sugar found in your blood. It comes from the food you eat, and is your body's main source of energy. Your blood carries glucose to all of your body's cells to use for energy. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood sugar levels are too high.
What is the ICD code for diabetes mellitus?
The ICD code R730 is used to code Impaired fasting glucose. Impaired fasting glucose (IFG), more commonly known as pre-diabetes refers to a condition in which the fasting blood glucose level is consistently elevated above what is considered normal levels; however, it is not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes mellitus.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
Can IFG progress to type 2 diabetes?
IFG can progress to type 2 diabetes mellitus if lifestyle changes are not made. There is a 50% risk over 10 years of progressing to overt diabetes.
What is the ICD code for diabetes mellitus?
The ICD code R730 is used to code Impaired fasting glucose. Impaired fasting glucose (IFG), more commonly known as pre-diabetes refers to a condition in which the fasting blood glucose level is consistently elevated above what is considered normal levels; however, it is not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes mellitus.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
Can IFG progress to type 2 diabetes?
IFG can progress to type 2 diabetes mellitus if lifestyle changes are not made. There is a 50% risk over 10 years of progressing to overt diabetes.
What does it mean to be obese?
A person is considered obese if they have a body mass index (bmi) of 30 or more. Obesity means having too much body fat. It is different from being overweight, which means weighing too much. The weight may come from muscle, bone, fat and/or body water.
What is postpartum obesity?
Postpartum obesity. Clinical Information. A condition marked by an abnormally high, unhealthy amount of body fat. A disorder characterized by having a high amount of body fat. A status with body weight that is grossly above the acceptable or desirable weight, usually due to accumulation of excess fats in the body.
Why does obesity occur over time?
Obesity occurs over time when you eat more calories than you use. The balance between calories-in and calories-out differs for each person. Factors that might tip the balance include your genetic makeup, overeating, eating high-fat foods and not being physically active.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for high blood sugar
- 2. icd 10 code for generalized body weakness
- 3. icd-10-cm code for copd
- 4. icd 9 code for cad unspecified
- 5. icd-10 code for permeunaual perimeus
- 6. icd 10 code for sub carinal mass
- 7. icd 10 code for atherosclerotic hd of native w/o angina recpetors
- 8. icd 10 code for s/p stroke
- 9. icd code for left knee pain
- 10. icd 10 code for left pressure heel stageii