What is the ICD 10 code for Impacted cerumen in ear?
Oct 01, 2021 · Impacted cerumen, unspecified ear 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Questionable As Admission Dx H61.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H61.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for bilateral impingement cerumen?
Oct 01, 2021 · Impacted cerumen, bilateral. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Questionable As Admission Dx. H61.23 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H61.23 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the CPT code for cerumen removal?
Impacted cerumen, unspecified ear BILLABLE | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 H61.20 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of impacted cerumen, unspecified ear. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. MS-DRG Mapping DRG Group #154-156 - Other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with MCC.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for ear wax?
H61.20 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of impacted cerumen, unspecified ear. The code H61.20 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code H61.20 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like excessive cerumen in ear …
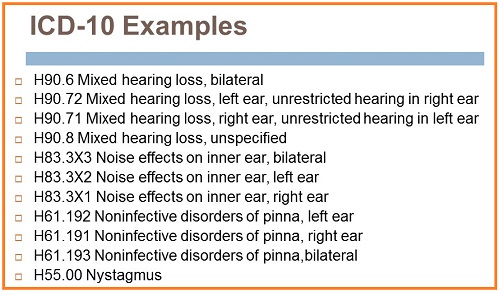
What is diagnosis code H61 23?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H61. 23: Impacted cerumen, bilateral.
What is impacted cerumen?
Cerumen impaction is defined as an accumulation of cerumen that causes symptoms or prevents assessment of the ear canal, tympanic membrane, or audiovestibular system; complete obstruction is not required.3 Cerumen impaction is a common reason for consultation with primary care physicians and is present in about 10% of ...Oct 15, 2018
Is cerumen impaction a diagnosis?
Cerumen typically is asymptomatic and does not impair physical examination. Physicians should diagnose impaction only when an accumulation of cerumen is associated with symptoms (e.g., otalgia, tinnitus, vertigo) or prevents necessary assessment of the ear. Total occlusion is not necessary for diagnosis.Nov 1, 2009
What is ICD 9 code impacted cerumen?
380.4 Impacted cerumen - ICD-9-CM Vol.
What causes impacted cerumen?
The most common cause of impactions is the use of cotton swabs (and other objects such as bobby pins and rolled napkin corners), which can remove superficial wax but also pushes the rest of the wax deeper into the ear canal. Hearing aid and earplug users are also more prone to earwax blockage.Jul 15, 2020
What can be done for cerumen impaction?
Lifestyle and home remediesSoften the wax. Use an eyedropper to apply a few drops of baby oil, mineral oil, glycerin or diluted hydrogen peroxide in your ear canal. ... Use warm water. ... Dry your ear canal.Feb 5, 2021
Who is at risk for cerumen impaction?
The prevalence of cerumen impaction varies greatly,[16] approximately 10% of the children, 5% of normal healthy adults, up to 57% of older patients in nursing homes, and 36% of patients with mental retardation. [17] It is the most common ear disorder among school children.
What is removal impacted cerumen?
Impacted cerumen removal is the extraction of hardened or accumulated cerumen (ear wax) from the external auditory canal by mechanical means, such as irrigation or debridement.
What is the ICD-10 code for constipation unspecified?
K59.00ICD-10 | Constipation, unspecified (K59. 00)
What is bilateral impacted cerumen?
Impacted cerumen (se-ROO-men) is when earwax (cerumen) builds up in the ear and blocks the ear canal; it can cause temporary hearing loss and ear pain.
What are the symptoms of impacted cerumen?
These are the most common symptoms of impacted earwax:Hearing loss.Earache.Sense of ear fullness.Itching in the ear.Dizziness.Ringing in the ears.Cough.
What is the ICd 10 code for impacted cerumen?
H61.20 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of impacted cerumen, unspecified ear. The code H61.20 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code H61.20 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like c/o - wax in ear, ear symptom, excessive cerumen in ear canal, impacted cerumen, o/e - wax in auditory canal , wax in ear canal, etc.#N#The code H61.20 is not usually sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used as a principal diagnosis.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like H61.20 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code H61.20 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What causes a person to lose balance?
A variety of conditions may affect your hearing or balance: 1 Ear infections are the most common illness in infants and young children. 2 Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud noises, medicines or a variety of other causes. 3 Meniere's disease may be the result of fluid problems in your inner ear; its symptoms include tinnitus and dizziness. 4 Ear barotrauma is an injury to your ear because of changes in barometric (air) or water pressure.
Why do my ears roar?
Ear infections are the most common illness in infants and young children. Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud noises, medicines or a variety of other causes. Meniere's disease may be the result of fluid problems in your inner ear; its symptoms include tinnitus and dizziness.
Where do vibrations travel?
The vibrations travel to your inner ear, a snail-shaped organ. The inner ear makes the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain. Your brain recognizes them as sounds. The inner ear also controls balance.
How do sound waves travel?
You use all of them in hearing. Sound waves come in through your outer ear. They reach your middle ear, where they make your eardrum vibrate. The vibrations are transmitted through three tiny bones, called ossicles, in your middle ear. The vibrations travel to your inner ear, a snail-shaped organ.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for postoperative infection
- 2. icd 10 code for pancreatic cystic lesion
- 3. icd 10 code for chronic hepatitis b
- 4. icd-10 code for malignant pleural effusion
- 5. icd 10 code for cad with cabg
- 6. icd 10 code for graves orbitopathy
- 7. icd-10-cm code for m70606
- 8. icd 10 code for complication of jackson pratt drain
- 9. icd 10 code for right distal foot ulcer
- 10. icd 10 code for homocystinuria