What is the ICD 10 code for food impaction?
Sep 28, 2017 · 0. Sep 28, 2017. #1. We are receiving denials from insurance companies when we bill for EGD's with diagnosis code T18.120A (food bolus in esophagus). They are asking for external cause for this. We have been unable to find one that would fit with "patient taking too large of a bite of food."
Is there a diagnosis code for food bolus in esophagus?
Jun 09, 2020 · Food impaction may also happen if you do not have teeth or do not chew your food completely. What is the ICD 10 code for leukocytosis? 829 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of elevated white blood cell count, unspecified. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the ICD 10 code for intestinal impaction?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K01.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Impacted teeth. Failure of tooth eruption associated with tooth impaction; Failure of tooth eruption with tooth impaction; Impacted teeth with abnormal position; Impacted tooth, malposition; Impacted tooth, non-supranumerary; Nonsupranumerary impacted tooth. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K01.1.
What is the NCCI code for bolus push into the stomach?
Jun 12, 2020 · Furthermore, what is a food bolus? GG Food bolus impactions are acute events that, for the most part, are immediately recognized by the patient. Most food bolus impactions resolve without intervention, either by moving forward to the stomach or by the patient regurgitating the ingested contents. Considering this, what is the ICD 10 code for foreign body …
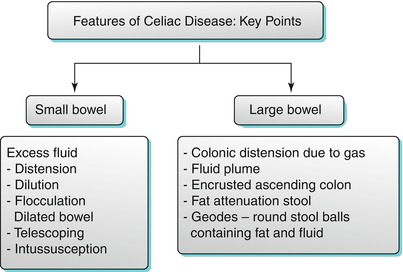
What is food bolus impaction?
What is the ICD-10 code for impaction?
What is the ICD-10 code for painful swallowing?
What is the ICD-10 code for difficulty swallowing?
What is the ICD-10 code for fecal retention?
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic constipation?
What can pharyngitis lead to?
What is painful swallowing called?
What is the difference between dysphagia and odynophagia?
What is oral dysphagia?
What is esophageal dysphagia?
What is the ICD-10 code for sore throat?
How do you get food unstuck from your esophagus?
Ways to remove food stuck in throat The 'Coca-Cola' trick. Research suggests that drinking a can of Coke, or another carbonated beverage, can help dislodge food stuck in the esophagus. Simethicone. Water. A moist piece of food. Alka-Seltzer or baking soda. Butter. Wait it out.
When I eat sometimes food gets stuck?
Esophageal dysphagia refers to the sensation of food sticking or getting hung up in the base of your throat or in your chest after you've started to swallow. Some of the causes of esophageal dysphagia include: Achalasia.
How does glucagon help with food impaction?
Glucagon is the mainstay pharmacological treatment. It is an endogenous polypeptide secreted from alpha cells in the islets of Langerhans. At pharmacological doses, it relaxes the esophageal smooth muscle and the lower esophageal sphincter, promoting the spontaneous passage of an impacted food bolus (30).
What is a food bolus impaction?
Emergency medicine, general surgery, gastroenterology. An esophageal food bolus obstruction is a medical emergency caused by the obstruction of the esophagus by an ingested foreign body.
What is steakhouse syndrome?
Steakhouse syndrome is when a mass of food becomes stuck on the way to the stomach. It gets stuck in the tube that connects the mouth and stomach. The Esophagus.
How do you remove impaction from food?
Acceptable methods for the management of esophageal food impactions include en bloc removal, piecemeal removal, and gentle push technique. Endoscopic removal of all objects larger than 2.5 cm from the stomach. Endoscopic removal of sharp-pointed objects or objects larger than 6 cm in the proximal duodenum.
When I swallow it feels like something is stuck in my chest?
The most common symptom of esophageal cancer is a problem swallowing, with a feeling like the food is stuck in the throat or chest, or even choking on food. The medical term for trouble swallowing is dysphagia. They might avoid bread and meat, since these foods typically get stuck.
What is Egj outflow obstruction?
Esophagogastric junction (EGJ) outflow obstruction is characterized by elevated relaxation pressure in combination with intact or weak peristalsis and can be diagnosed using high-resolution manometry (HRM) (1,2). Patients without mechanical obstruction are considered to have primary EGJ outflow obstruction.
What is Bartlett's esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is more common in people who have had GERD for a long period of time or who developed it at a young age.
What is esophageal dysmotility?
Esophageal motility refers to contractions occurring in the esophagus, which propel the food bolus forward toward the stomach. When contractions in the esophagus become irregular, unsynchronized or absent, the patient is said to have esophageal dysmotility.
What is reflux esophagitis?
Reflux esophagitis is an esophageal mucosal injury that occurs secondary to retrograde flux of gastric contents into the esophagus. Clinically, this is referred to as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Typically, the reflux disease involves the distal 8-10 cm of the esophagus and the gastroesophageal junction.
What is dyskinesia of esophagus?
Diffuse spasms of the body of the esophagus cause non-peritalsis and food gets stuck in the mid-esophagus, causing dysphagia. Esophageal dyskinesia is considered a common cause for unexplained chest pain. Patients develop chest pain due to spasmodic contractions of the esophagus as well as due to esophageal distension.
What is a irregular Z line?
Background: Subtle irregularity and short tongues of columnar appearing mucosa (CAM) at the Z-line are frequently observed during EGD. An irregular Z-line was defined as any discrete tongue or exaggerated waviness of the Z-line which extended proximally less than 1 cm.
What is a schatzki ring?
A Schatzki ring is a circular band of mucosal tissue that can form at the end of the food pipe closest to the stomach. The ring of tissue causes the food pipe, or esophagus, to narrow. When a ring forms, a person may have no symptoms. Or, they may have difficulty swallowing, which the medical community calls dysphagia.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for urachal remnant
- 2. icd 10 code for malignant brain tumor
- 3. icd 10 code for pulmonary mucomyositis
- 4. icd 10 code for vitamin b complex deficiency
- 5. icd 9 code for immunization
- 6. icd 9 code for generalized muscle weakness
- 7. icd 10 code for bilateral shoulder degenerative osteoarthritis
- 8. icd 10 code for infiltrates
- 9. icd code for this 72 year old male amitted with dementia with lewey bodies
- 10. icd 10 code for right anterior process of the calcaneus symptomatic nonunion