In ICD-10-CM, spiglian hernias are coded to K43.6 Other and unspecified ventral hernia with obstruction, without gangrene
Gangrene
Death of body tissues due to ischemia.
What is the ICD 10 code for Spigelian hernia?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K43.9 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Ventral hernia without obstruction or gangrene. Epigastric hernia; Hernia of anterior abdominal wall; Hypogastric hernia; Midline abdominal hernia; Midline hernia; Spigelian hernia; Ventral hernia; Epigastric hernia; Ventral hernia NOS. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K43.9.
What is the ICD 10 code for inguinal hernia incarcerated?
· 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. K43.6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Other and unsp ventral hernia with obstruction, w/o gangrene; The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K43.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 for hernia without gangrene?
· 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K43.0 Incisional hernia with obstruction, without gangrene 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code K43.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K43.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for abdominal hernia?
· A hernia caused by weakness of the anterior abdominal wall due to midline defects, previous incisions, or increased intra-abdominal pressure. Ventral hernias include umbilical hernia, incisional, epigastric, and spigelian hernias. ICD-10-CM K43.9 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 39.0): 393 Other digestive system diagnoses with mcc

What is the ICD-10 code for incarcerated hernia?
Incisional hernia with obstruction, without gangrene K43. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is a spigelian hernia the same as a ventral hernia?
What is a spigelian hernia? A spigelian hernia is a hernia through the spigelian fascia or layer of tissue that separates two groups of abdominal muscles. The muscles are called the rectus muscles and the lateral obliques. This type of hernia is also sometimes called a lateral ventral hernia.
Is an incarcerated hernia is the same as an irreducible hernia?
An irreducible hernia - also known as an incarcerated hernia - is a hernia that cannot be pushed back, manually, through the opening in the abdomen. An irreducible hernia is trapped outside the abdomen muscle wall. Although some irreducible hernias are not painful the bulge under the skin can grow hard.
What does incarcerated hernia mean?
If you aren't able to push the hernia in, the contents of the hernia may be trapped (incarcerated) in the abdominal wall. An incarcerated hernia can become strangulated, which cuts off the blood flow to the tissue that's trapped. A strangulated hernia can be life-threatening if it isn't treated.
What is an incarcerated spigelian hernia?
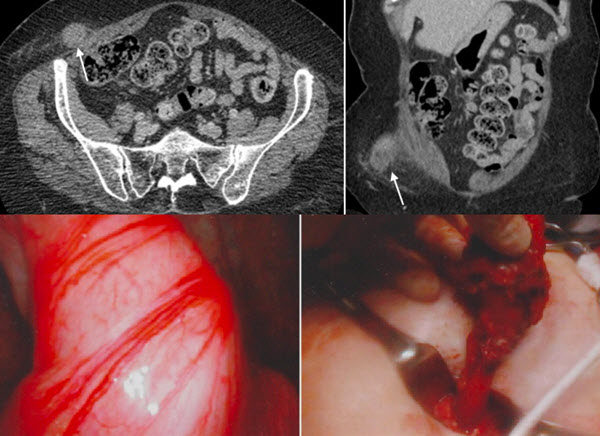
Abstract. Spigelian hernias are rare abdominal wall defects that occur at the semilunar line lateral to the rectus abdominis muscle. The majority of patients present with symptomatic incarceration of preperitoneal fat or intra-abdominal viscera. Radiographic studies are beneficial in confirming the diagnosis.
Where is a spigelian hernia?
Spigelian hernia occurs through slit like defect in the anterior abdominal wall adjacent to the semilunar line. Most of spigelian hernias occur in the lower abdomen where the posterior sheath is deficient. The hernia ring is a well-defined defect in the transverses aponeurosis.
What is a spigelian hernia and what causes it?
The spigelian fascia is a layer of tissue that separates the two muscle groups at the front of your abdomen. When a slit-like opening occurs in this fascia, it's called a spigelian hernia. This condition usually affects the intestines and omentum, a layer of tissue that lies over the abdominal organs.
Is incarcerated hernia an obstruction?
Hernias. Incarcerated hernias account for 10 to 20% of cases of small bowel obstruction. These patients usually require urgent operation as they are at significant risk for strangulation and are not likely to resolve their obstruction spontaneously.
How do you tell if a hernia is incarcerated?
What are the symptoms of an incarcerated abdominal hernia?Painful enlargement of a previous hernia or defect.Inability to manipulate the hernia (either spontaneously or manually) through the fascial defect.Nausea, vomiting, and symptoms of bowel obstruction (possible)
What does incarcerated mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of incarceration 1 : a confining or state of being confined. 2 : abnormal retention or confinement of a body part specifically : a constriction of the neck of a hernial sac so that the hernial contents become irreducible.
What it means to be incarcerated?
Definition of incarcerated 1 : confined in a jail or prison Michigan law allows convicted felons to vote and run for office unless they are currently incarcerated, or if their offenses are fraud-related or constitute a breach of public trust.
What is the ICd 10 code for an inguinal hernia?
Unilateral inguinal hernia, with obstruction, without gangrene 1 K00-K95#N#2021 ICD-10-CM Range K00-K95#N#Diseases of the digestive system#N#Type 2 Excludes#N#certain conditions originating in the perinatal period ( P04 - P96)#N#certain infectious and parasitic diseases ( A00-B99)#N#complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O00-O9A)#N#congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities ( Q00-Q99)#N#endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases ( E00 - E88)#N#injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes ( S00-T88)#N#neoplasms ( C00-D49)#N#symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified ( R00 - R94)#N#Diseases of the digestive system 2 K40-K46#N#2021 ICD-10-CM Range K40-K46#N#Hernia#N#Includes#N#acquired hernia#N#congenital [except diaphragmatic or hiatus] hernia#N#recurrent hernia#N#Note#N#Hernia with both gangrene and obstruction is classified to hernia with gangrene.#N#Hernia 3 K40#N#ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K40#N#Inguinal hernia#N#2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code#N#Includes#N#bubonocele#N#direct inguinal hernia#N#double inguinal hernia#N#indirect inguinal hernia#N#inguinal hernia NOS#N#oblique inguinal hernia#N#scrotal hernia#N#Inguinal hernia
When will the ICD-10-CM K40.3 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K40.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a K40.3?
Unilateral inguinal hernia, with obstruction, without gangrene. K40.3 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. Short description: Unilateral inguinal hernia, with obstruction, w/o gangrene.
What is a hernia in the abdominal wall?
By Rhonda Buckholtz#N#Hernias occur when the contents of a body cavity bulge out of the area where they are normally contained. These contents, usually portions of intestine or abdominal fatty tissue, are enclosed in the thin membrane that naturally lines the inside of the cavity. Hernias may not produce symptoms, or they may cause slight to severe pain. Nearly all have the potential of becoming strangulated.#N#Strangulation occurs when the contents of the hernia bulge out and apply enough pressure that blood vessels in the hernia are constricted, cutting off blood supply. If the blood supply is cut off at the hernia opening in the abdominal wall, it becomes a medical and surgical emergency.#N#Identify Hernia Type#N#There are several different types of hernias. The ability to identify the various types of hernias is critical to appropriate diagnosis coding in ICD-10-CM.#N#Inguinal#N#Inguinal (groin) hernias make up approximately 75 percent of all abdominal wall hernias, and occur up to 25 times more often in men than in women. There are two different types of inguinal hernias: direct and indirect.#N#Both types occur in the groin area where the skin of the thigh joins the torso (the inguinal crease), but they have slightly different origins.
What is a hernia in the womb?
A diaphragmatic hernia is a rare birth defect in which there is an abnormal opening in the diaphragm. This type of hernia occurs while the baby is developing in the womb, and prevents the lungs from growing normally. ICD-10-CM coding example: A 17-year-old female presents with congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
How is a femoral hernia repaired?
The femoral hernia was repaired by suturing the iliopubic tract to Cooper’s ligament. K41.90 Unilateral femoral hernia, without obstruction or gangrene, not specified as recurrent. Umbilical. Umbilical hernias are common and make up approximately 10 to 30 percent of hernia cases.
What is a femoral hernia?
Femoral hernias are normally confined to a tight space, and sometimes they become large enough to allow abdominal contents (usually intestine) to protrude into the canal. They cause a bulge just below the inguinal crease in roughly the mid-thigh area, and usually occur in women. ICD-10-CM coding example:
Where do inguinal hernias occur?
There are two different types of inguinal hernias: direct and indirect. Both types occur in the groin area where the skin of the thigh joins the torso (the inguinal crease), but they have slightly different origins. Indirect inguinal hernia (indirect hernia):
Where does hernia protrude from?
This type of hernia protrudes from the pelvic cavity through an opening in the pelvic bone. Due to the lack of visible bulging, this hernia is very difficult to diagnose. Epigastric. Epigastric hernia occurs between the navel and the lower part of the rib cage in the midline of the abdomen.
Can a hernia cause pain?
Hernias may not produce symptoms, or they may cause slight to severe pain. Nearly all have the potential of becoming strangulated. Strangulation occurs when the contents of the hernia bulge out and apply enough pressure that blood vessels in the hernia are constricted, cutting off blood supply.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for scapholunate ligament tear
- 2. icd 10 code for military sexual trauma
- 3. what is billable icd 10 code for degenerative joint disease
- 4. icd 9 code for hammer toes bilat
- 5. icd 10 code for chronic left hip osteomyelitis
- 6. icd 10 code for 2 cm lung mass
- 7. icd 10 code for bmi of 38.5
- 8. icd 10 code for surgical wound abdomen
- 9. icd 10 code for acute upper respiratory infection
- 10. icd 10 code for dating and viability ultrasound