What causes a Bartholin cyst?
Some symptoms of an infected Bartholin’s include:
- Pain and discomfort in the vulva and vaginal areas, especially when walking or running, having sexual intercourse, or even while putting in or taking out a tampon. ...
- Swelling or large lumps in the area inside the vulva. ...
- Tenderness and pain to the touch
- Redness around the area
- Unusual discharge, which is typically the cyst draining
How do I know if a Bartholin cyst is infected?
Part 2 Part 2 of 3: Trying Medical Treatments
- Opt for surgical drainage. [7] ... ...
- Take antibiotics. [8] ... ...
- Ask your doctor about "marsupialization." If your Bartholin cyst recurs, you can speak to your physician about a procedure called marsupialization.
What antibiotic is used for Bartholin cyst?
If a patient has a Bartholin gland cyst that ruptures spontaneously, all she may need is hot sitz baths. Occasionally, use of broad-spectrum antibiotics is indicated if secondary infection develops. Simple lancing and drainage of the Bartholin gland cyst is mentioned here only to discourage its routine use.
Does anyone know what a Bartholin cyst is?
A Bartholin cyst is a lump near the opening to your vagina. You may have pain in this area when you walk or have sex. A Bartholin cyst is caused by blockage of your Bartholin gland. You have a Bartholin gland on each side of your vagina. The glands produce fluid to moisten your vagina. Over time the fluid can build up in the gland and form a cyst.
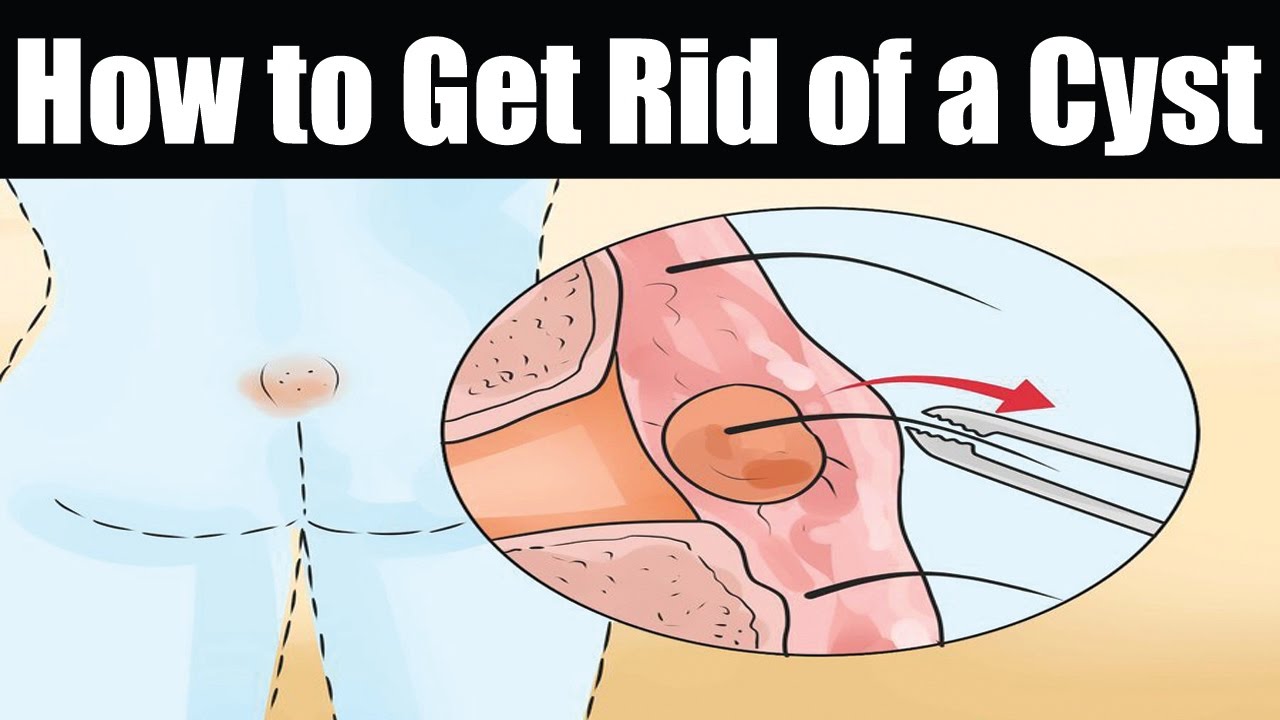
What is an infected Bartholin cyst?
Abscess - Bartholin; Infected Bartholin gland. Bartholin abscess is the buildup of pus that forms a lump (swelling) in one of the Bartholin glands. These glands are found on each side of the vaginal opening.
What is the difference between a Bartholin cyst and abscess?
Often, a Bartholin's cyst is small and shows no symptoms. It can grow large and cause discomfort when walking, sitting, or having sexual intercourse. Bartholin's gland abscess is an infection of the gland or duct leading from it. The abscess can form without a cyst having been present.
Is Bartholin cyst a viral infection?
A Bartholin's abscess typically occurs when bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter a cyst in one of the glands. Rarely, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, are responsible.
How do you describe a Bartholin cyst on a physical?
The following physical examination findings are seen in Bartholin cysts: Patients may have a painless, unilateral labial mass without signs of surrounding cellulitis. If large, the cyst may be tender. Discharge from ruptured cyst should be nonpurulent.
How is an infected Bartholin cyst treated?
TreatmentSitz baths. Soaking in a tub filled with a few inches of warm water (sitz bath) several times a day for three or four days may help a small, infected cyst to rupture and drain on its own.Surgical drainage. You may need surgery to drain a cyst that's infected or very large. ... Antibiotics. ... Marsupialization.
How does a Bartholin cyst get infected?
A Bartholin's cyst can become infected, forming an abscess. A number of bacteria may cause the infection, including Escherichia coli (E. coli) and bacteria that cause sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia.
What is the best antibiotic for Bartholin cyst?
Medication and antibiotics are used to treat Bartholin's abscesses as the infection is mostly caused by pathogens. Antibiotic therapy may not be necessary for healthy women with uncomplicated abscesses. Antibiotic therapies include Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline and Azithromycin.
What's the difference between a boil and a cyst?
Boils and cysts can both look like bumps on your skin. The main difference between a cyst and a boil is that a boil is a bacterial or fungal infection. Most cysts are slow-growing and benign (noncancerous), and they aren't contagious. Boils, on the other hand, can spread bacteria or fungi on contact.
What happens when you pop a Bartholin cyst?
If a Bartholin abscess bursts, it may resolve on its own in a few days without treatment. However, it is advisable to visit the doctor to avoid the spread of the infection. Your doctor will usually advise you to soak the labia in warm water (sitz bath) and prescribe you antibiotics and pain medications.
What does it mean when you have a bump inside your vag?
You may see or feel sores, bumps, or spots in or around the vaginal area. These may be painful or you may not feel them at all. Sores and lumps may be symptoms of an STD. Causes of lumps, growths, or swelling could be due to a number of reasons, including skin tags, human papillomavirus (HPV), or a cyst.
Can you get cysts on your vag lips?
The cyst can sometimes affect the outer pair of lips surrounding the vagina (labia majora). One side may look swollen or bigger than usual. If the cyst becomes infected, it can cause a painful collection of pus (abscess) to develop in one of the Bartholin's glands.
Is a Bartholin abscess an emergency?
Many women with a Bartholin gland abscess seek out emergency care, but this infection also appears to be a common complaint in the general practitioner's office, and it presents pathology that is quite applicable to outpatient therapy.
The ICD code N750 is used to code Bartholin's cyst
A Bartholin's cyst, also known as Bartholinitis occurs when a Bartholin's gland is blocked and the gland becomes inflamed. Sizes range from that of a pea to that of an egg and form just within each side of the lower part of the opening of the vagina. An abscess may form if the cyst becomes infected.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #742-743 - Uterine and adnexa procedure for non-malignancy with CC or MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'N75.0 - Cyst of Bartholin's gland'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code N75.0. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code N75.0 and a single ICD9 code, 616.2 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
A fluid-filled sac (cyst) has formed in a gland near the entrance to your vagina
The vagina is tube-shaped and leads from the outside of the body to the uterus. There are two glands at the entrance to the vagina. Each gland is roughly the size of a pea. The glands produce a fluid when you are sexually aroused.
Information
This information is not intended for self-diagnosis and does not replace professional medical advice from a doctor.
Source
Provided by the non-profit organization “Was hab’ ich?” gemeinnützige GmbH on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG).

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for urinery frequency/ hesistancey
- 2. icd 10 code for infection left leg
- 3. icd 10 pcs code for anterior and posterior nasal packing
- 4. icd 10 code for percc rash
- 5. icd 10 code for left wrist de quervain's tenosynovitis
- 6. icd 9 code for pessary maintenance
- 7. icd 10 code for otomycosis, right ear
- 8. icd 10 code for hostory of uti
- 9. icd 10 code for splinter in foot
- 10. icd 10 code for bereavement disorder