How do I get rid of a bed bug infestation?
Search Page 1/1: bedbug infestation. 19 result found: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B88.9 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Infestation, unspecified. Infestation of skin; Skin infestation; Infestation (skin) NOS; Infestation by mites NOS; Skin parasites NOS. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B88.9.
How to prevent and control a bed bug infestation?
Oct 01, 2021 · Infestation, unspecified. B88.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B88.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B88.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 B88.9 may differ.
How to identify and stop bed bug bites?
Oct 01, 2021 · B88.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B88.0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B88.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 B88.0 may differ. A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here".
Why are bed bug infestations so easily spread?
Oct 01, 2021 · Z20.7 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Cntct w & expsr to pediculosis, acariasis & oth infestations. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z20.7 became effective on October 1, …
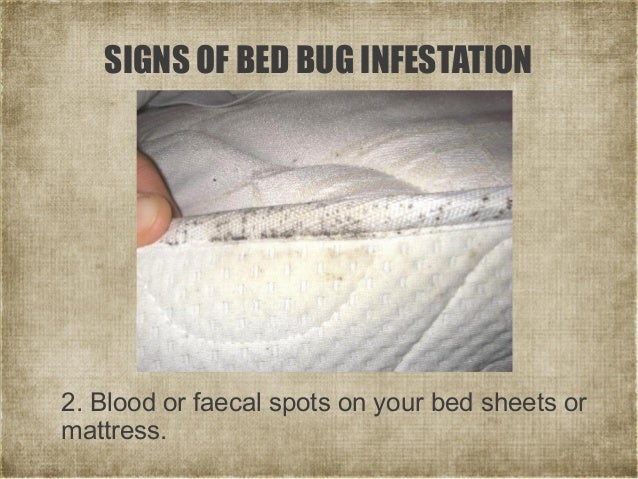
What is the ICD-10 code for exposure to scabies?
Valid for SubmissionICD-10:Z20.7Short Description:Cntct w & expsr to pediculosis, acariasis & oth infestationsLong Description:Contact with and (suspected) exposure to pediculosis, acariasis and other infestations
What is the ICD-10 code for Acariasis infestation?
B88.0B88. 0 - Other acariasis | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for multiple insect bites?
919.4 - Insect bite, nonvenomous, of other, multiple, and unspecified sites, without mention of infection | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for skin infection?
ICD-10 code: L08. 9 Local infection of skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
What is the ICD-10 code for folliculitis?
The ICD-10-CM code L73. 9 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like acute folliculitis, agminate folliculitis, bacterial folliculitis, chronic folliculitis, disorder of sebaceous gland , folliculitis, etc.
What is the ICD-10 code for blepharitis?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H01. 0: Blepharitis.
How do you code bed bug bites?
Because the patient presented with bites on hands, arms, legs, and face, code choices would be:910.4 Superficial injury of face, neck, and scalp except eye; Insect bite, nonvenomous, ... 913.4 Superficial injury of elbow, forearm, and wrist; Insect bite, nonvenomous, without mention of infection.More items...•Mar 1, 2011
How do you code insect bites?
2 – T63. 4. You can also report an external cause code to indicate bug bites (e.g., W57. XXXA, “ Bitten or stung by nonvenomous insect and other nonvenomous arthro- pods, initial encounter”).
What is the ICD-10 code for multiple trauma?
T07ICD-10 code T07 for Unspecified multiple injuries is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is the ICD-10 code for skin and soft tissue infection?
9 for Local infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 code for skin lesion?
ICD-10-CM Code for Disorder of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified L98. 9.
What is the ICD-10 code for wound culture?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R89. 5: Abnormal microbiological findings in specimens from other organs, systems and tissues.
What is the B88.8 code?
B88.8 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other specified infestations. The code B88.8 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code B88.8 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
How do parasites get into your body?
You can get them from contaminated food or water, a bug bite, or sexual contact. Some parasitic diseases are easily treated and some are not.
Can cats transmit toxoplasmosis?
Some parasitic diseases occur in the United States. Contaminated water supplies can lead to Giardia infections. Cats can transmit toxoplasmosis, which is dangerous for pregnant women. Others, like malaria, are common in other parts of the world. If you are traveling, it's important to drink only water you know is safe.
What is the B88.2 code?
B88.2 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other arthropod infestations. The code B88.2 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code B88.2 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
How do parasites get into your body?
You can get them from contaminated food or water, a bug bite, or sexual contact. Some parasitic diseases are easily treated and some are not.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code B88.2:
Can cats carry giardia?
Contaminated water supplies can lead to Giardia infections. Cats can transmit toxoplasmosis, which is dangerous for pregnant women. Others, like malaria, are common in other parts of the world. If you are traveling, it's important to drink only water you know is safe. Prevention is especially important.
What do bed bugs bite?
They usually bite extremities and areas of the body that aren’t covered with clothing. Bedbug bites can be confused easily with mosquito or flea bites, so don’t jump to conclusions—if you suspect bedbugs, investigate further: Search the area where you just slept.
What is the ICD-10 code for bedbug bites?
In coding for bedbug bites, it will still direct you to insect bite, (nonvenomous) of location, but your location must#N#be documented. For example:#N#S60.460x Insect bite (nonvenomous) of right index finger#N#S60.461x Insect bite (nonvenomous) of left index finger
What to do for a bite that takes longer to heal?
Stronger antibiotics, anti-itch creams, and antihistamines may be used for bites that take longer to heal. Oral antibiotics might be necessary if infection starts to spread. Presenting Patient. An 18-year-old male presented with a three-week history of pruritic skin lesions on his hands, arms, feet, legs, and face.
What is the diagnosis code for a bite?
Choose diagnosis codes by site and reaction. Because the patient presented with bites on hands, arms, legs, and face, code choices would be:#N#910.4 Superficial injury of face, neck, and scalp except eye; Insect bite, nonvenomous,#N#without mention of infection#N#913.4 Superficial injury of elbow, forearm, and wrist; Insect bite, nonvenomous, without mention of infection#N#914.4 Superficial injury of hand (s) except finger (s) alone; Insect bite, nonvenomous, without mention of infection#N#916.4 Superficial injury of hip, leg, and ankle; Insect bite, nonvenomous, without mention of infection#N#917.4 Superficial injury of foot and toe (s); Insect bite, nonvenomous, without mention of infection#N#If the sites had been infected, you’d use the fourth-digit subdivision of “5” (Insect bite, nonvenomous, infected), rather than “4,” for categories 910-919.
What to do if you find an insect?
If you find an insect, put it in a plastic bag and compare it with a good reference image, or take it to an entomologist (a bug expert). Make sure you have a positive identification before you hire an exterminator. Exterminators can cost hundreds of dollars or more.
Can a bed bug bite cause a second time?
Bedbug bite symptoms may get progressively worse each time a person is bitten. Even if there are no symptoms for the first bite, the second time could result in marks.
Can you throw out a bedbug?
Vacuuming, washing linens, and thoroughly cleaning won’t eliminate bedbugs, and neither will throwing out a mattress.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for carotid stenosis
- 2. icd 10 code for clc
- 3. icd 10 pcs code for evacuation of a large thigh soft tissue hematoma
- 4. icd 10 code for 27801
- 5. icd 10 code for human papillomavirus positive
- 6. icd-9-cm code for old cva
- 7. icd 10 code exam for crohn's disease
- 8. icd 10 code for adrenal hemorrhage
- 9. icd 10 code for perinephric fluid collection
- 10. icd 9 code for portacath placement