What is the ICD 10 code for scabies?
Scabies. B86 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM B86 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B86 - other international versions of ICD-10 B86 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia 2017 - New Code 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code M62.84 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM M62.84 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for Stung by an insect?
W57.XXXA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Bit/stung by nonvenom insect & oth nonvenom arthropods, init The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM W57.XXXA became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is Sarcoptes scabiei infection?
A contagious cutaneous inflammation caused by the bite of the mite sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by pruritic papular eruptions and burrows and affects primarily the axillae, elbows, wrists, and genitalia, although it can spread to cover the entire body.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for scabies?
ICD-10-CM Code for Scabies B86.
What is diagnosis code L98 9?
ICD-10 code: L98. 9 Disorder of skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified.
What does diagnosis R53 83 mean?
Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is the ICD-10 code for Norwegian itch?
ICD-10-CM has a wealth of options for coding itchy conditions, including but not limited to the following: Norwegian itch (ICD-10-CM code B86) is also known as Boeck scabies, crusted scabies or sarcopic itch (caused by sarcoptes scabiei).
What is the ICD-10 code for skin breakdown?
Non-pressure chronic ulcer of skin of other sites limited to breakdown of skin. L98. 491 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L98.
What is the ICD-10 code for moisture associated skin damage?
IRRITANT CONTACT DERMATITIS DUE TO EXPOSURE TO UNSPECIFIED MOISTURE SOURCE (ICD-10-CM CODE L24. A0)
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is R53 81?
R53. 81: “R” codes are the family of codes related to "Symptoms, signs and other abnormal findings" - a bit of a catch-all category for "conditions not otherwise specified". R53. 81 is defined as chronic debility not specific to another diagnosis.
Is R53 83 a billable code?
R53. 83 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you describe scabies rash?
Rash: Many people get the scabies rash. This rash causes little bumps that often form a line. The bumps can look like hives, tiny bites, knots under the skin, or pimples. Some people develop scaly patches that look like eczema.
What is treatment of scabies?
Treating scabies The 2 most widely used treatments for scabies are permethrin cream and malathion lotion (brand name Derbac M). Both medications contain insecticides that kill the scabies mite. Permethrin 5% cream is usually recommended as the first treatment. Malathion 0.5% lotion is used if permethrin is ineffective.
What is the symptoms of scabies?
The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies. Scabies is found worldwide and affects people of all races and social classes.
What is skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders?
Panniculitis. Panniculitis is a group of conditions that causes inflammation of your subcutaneous fat. Panniculitis causes painful bumps of varying sizes under your skin. There are numerous potential causes including infections, inflammatory diseases, and some types of connective tissue disorders like lupus.
What does a lesion look like?
Skin lesions are areas of skin that look different from the surrounding area. They are often bumps or patches, and many issues can cause them. The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery describe a skin lesion as an abnormal lump, bump, ulcer, sore, or colored area of the skin.
What is subcutaneous fascia?
Subcutaneous fascia is an elastic layer of connective tissue, formed by loosely packed interwoven collagen fibers mixed with abundant elastic fibers [6,8], making it a unique fibroelastic layer that is easily stretched in various directions and then returned to its initial state.
What is the ICD-10 code for right knee pain?
M25. 561 Pain in right knee - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is the code for scabies?
The infected person's clothes, bedding and towels should be washed in hot water and dried in a hot dryer. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Codes. B86 Scabies.
What is scabies B86?
Scabies B86-. A contagious cutaneous inflammation caused by the bite of the mite sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by pruritic papular eruptions and burrows and affects primarily the axillae, elbows, wrists, and genitalia, although it can spread to cover the entire body. A contagious skin inflammation caused by the bite of the mite.
Where does scabies spread?
Scabies spreads quickly in crowded conditions where there is frequent skin-to-skin contact between people. Hospitals, child-care centers and nursing homes are examples.
When will the ICd 10-CM M62.84 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M62.84 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is the ICd 10 code for a stung animal?
Bitten or stung by nonvenomous insect and other nonvenomous arthropods, initial encounter 1 V00-Y99#N#2021 ICD-10-CM Range V00-Y99#N#External causes of morbidity#N#Note#N#This chapter permits the classification of environmental events and circumstances as the cause of injury, and other adverse effects. Where a code from this section is applicable, it is intended that it shall be used secondary to a code from another chapter of the Classification indicating the nature of the condition. Most often, the condition will be classifiable to Chapter 19, Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes ( S00-T88 ). Other conditions that may be stated to be due to external causes are classified in Chapters I to XVIII. For these conditions, codes from Chapter 20 should be used to provide additional information as to the cause of the condition.#N#External causes of morbidity 2 W50-W64#N#2021 ICD-10-CM Range W50-W64#N#Exposure to animate mechanical forces#N#Type 1 Excludes#N#Toxic effect of contact with venomous animals and plants ( T63.-)#N#Exposure to animate mechanical forces 3 W57#N#ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code W57#N#Bitten or stung by nonvenomous insect and other nonvenomous arthropods#N#2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code#N#Type 1 Excludes#N#contact with venomous insects and arthropods ( T63.2-, T63.3-, T63.4-)#N#Bitten or stung by nonvenomous insect and other nonvenomous arthropods
What is W57.XXXA?
W57.XXXA describes the circumstance causing an injury, not the nature of the injury. This chapter permits the classification of environmental events and circumstances as the cause of injury, and other adverse effects. Where a code from this section is applicable, it is intended that it shall be used secondary to a code from another chapter ...
When will the 2022 ICd-10-CM W57.XXXA be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM W57.XXXA became effective on October 1, 2021.
When will the ICd 10 D86.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D86.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can sarcoidosis affect any organ?
Sarcoidosis can affect any organ in your body. No one is sure what causes sarcoidosis. It affects men and women of all ages and races. It occurs mostly in people ages 20 to 50, african americans, especially women, and people of northern european origin.
Does sarcoidosis need treatment?
Not everyone who has the disease needs treatment. If you do, prednisone, a type of steroid, is the main treatment. What: sarcoidosis: sarcoidosis: a disorder of unknown etiology that affects many organ systems with noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas. It has a special predilection for the lung and lymph tissues.
Does sarcoidosis affect the ankles?
It has a special predilection for the lung and lymph tissues. Why: sarcoidosis can result in an a cute arthritis commonly affecting the ankles and knees and less commonly the proximal interphalangeal joints, wrists, and elbows. The acute arthritis is symmetric and lasts for a few weeks.
What is the parasitic infestation of scabies?
Human scabies is a parasitic infestation caused by Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. Scabies occurs worldwide but is most common in hot, tropical countries and in areas of high population density. Human scabies is a parasitic infestation caused by Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. The microscopic mite burrows into the skin and lays eggs, ...
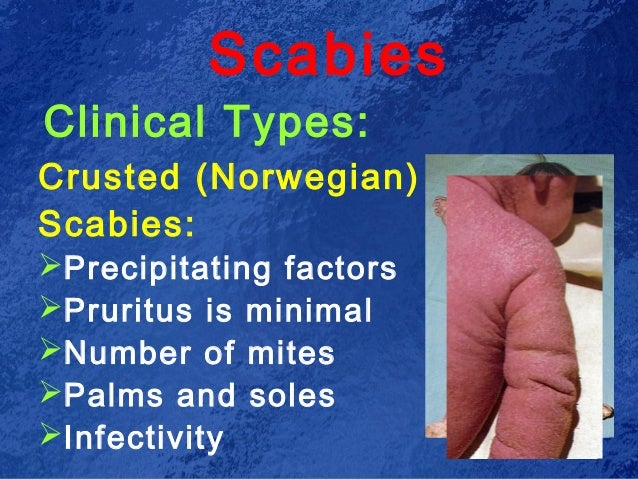
What is the name of the disease that causes a person to have a crusty scaby?
Immunosuppressed individuals, including people living with HIV/AIDS, may develop an uncommon manifestation called crusted (Norwegian) scabies. Crusted scabi es is a hyper-infestation with thousands to millions of mites, producing widespread scale and crust, often without significant itching.
How long does it take for scabies to develop?
Scabies mites burrow into the top layer of the epidermis where the adult female lays eggs. The eggs hatch in 3-4 days and develop into adult mites in 1–2 weeks. After 4–6 weeks the patient develops an allergic reaction to the presence of mite proteins and faeces in the scabies burrow, causing intense itch and rash.
How is scabies transmitted?
Scabies is usually transmitted person-to-person through close skin contact (e.g. living in the same residence) with an infested individual. The risk of transmission increases with the level of infestations, with highest risk due to contact with individuals with crusted scabies.
What are the consequences of scabies?
Scabies infestation may be complicated by bacterial infection, leading to the development of skin sores that, in turn, may lead to the development of more serious consequences such as septicaemia, heart disease and chronic kidney disease.
Can mites cause skin sores?
This condition has a high mortality if untreated due to secondary sepsis. Mite effects on immunity, as well as the direct effects of scratching, can lead to inoculation of the skin with bacteria, leading to the development of impetigo (skin sores), especially in the tropics.
Do scabies kill eggs?
Because people in the early stage of new infestation may be asymptomatic and because the treatments for scabies do not kill the parasite’s eggs, best results are obtained by treating the whole household at the same time and repeating treatment in the time frame appropriate for the chosen medication.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of urinary retention
- 2. icd 10 code for incomplete miscarriage
- 3. icd 10 code for periodic limb movement disorder
- 4. icd 10 diagnosis code for ra
- 5. icd 10 code for keratit scar right upper lid
- 6. icd 9 code for foot contusion
- 7. icd 10 code for lavator muscle tendernes
- 8. icd 10 code for dvt left lower leg
- 9. icd 10 code for high grade sbo
- 10. icd 10 code for receeding gums