Bladder disorder, unspecified. N32.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM N32.9 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for bladder disease?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to N32.9: Disease, diseased - see also Syndrome bladder N32.9. urinary (tract) N39.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N39.9 Disorder (of) - see also Disease bladder N32.9 Lesion(s) (nontraumatic) bladder N32.9
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary tract infection?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N32.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 N32.9 may differ. A non-neoplastic or neoplastic disorder affecting the urinary bladder. A representative example of non-neoplastic bladder disorder is bacterial bladder infection.
What is the ICD 10 code for atrophic bladder cancer?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to N32.89: Adhesions, adhesive (postinfective) K66.0 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K66.0 Atrophy, atrophic (of) bladder N32.89 Calcification bladder N32.89 Cicatrix (adherent) (contracted) (painful) (vicious) L90.5 - see also Scar ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code L90.5
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary incontinence?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N32.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 N32.9 may differ. A non-neoplastic or neoplastic disorder affecting the urinary bladder.
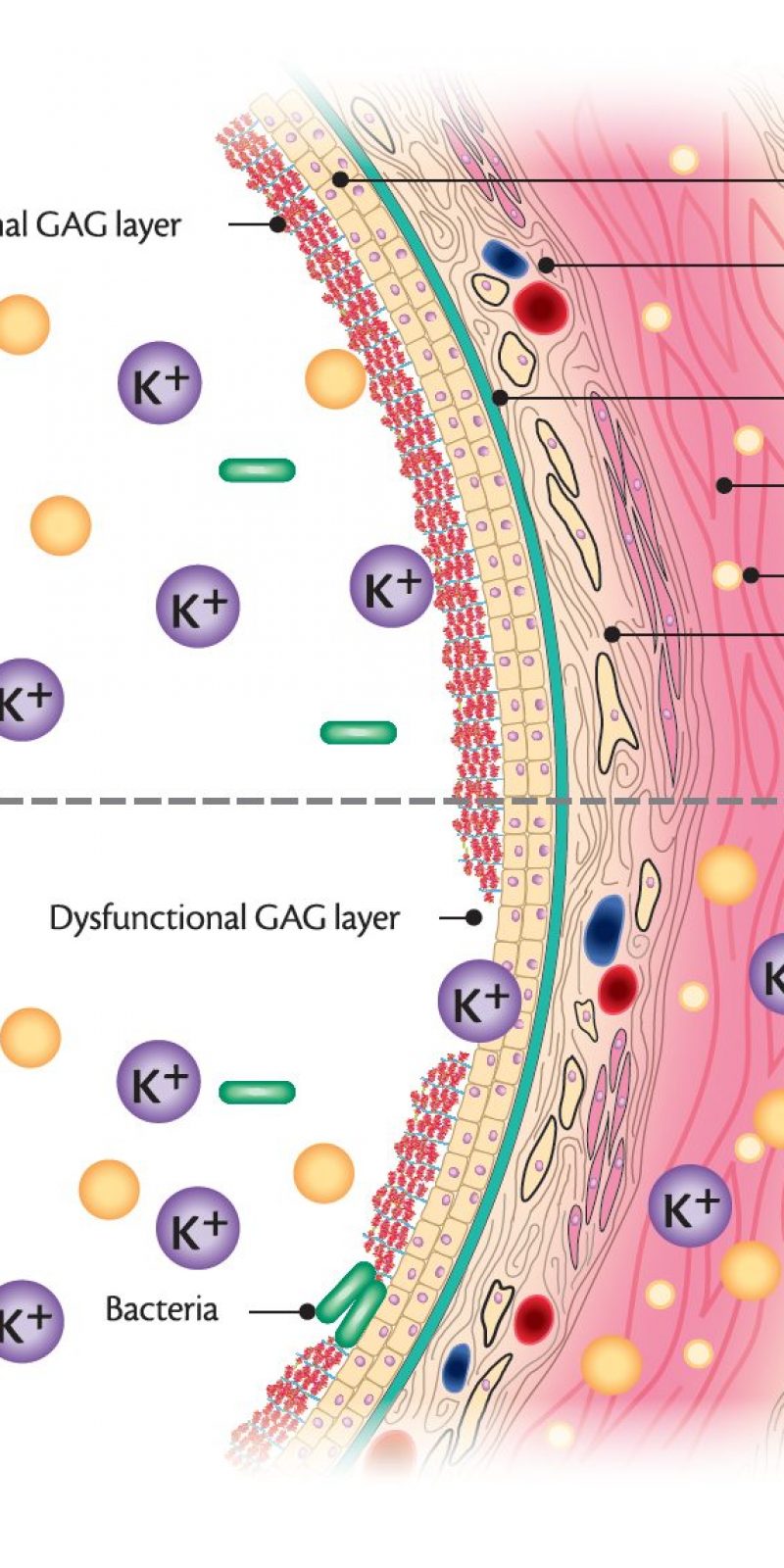
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic cystitis?
ICD-10 code N30. 20 for Other chronic cystitis without hematuria is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the ICD-10 code for cystitis unspecified?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cystitis, unspecified without hematuria N30. 90.
What is cystitis unspecified without hematuria?
Cystitis (sis-TIE-tis) is the medical term for inflammation of the bladder. Most of the time, the inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection, and it's called a urinary tract infection (UTI).
What is ICD-10 code for urinary tract infection?
0 Urinary tract infection, site not specified.
Are cystitis and UTI the same thing?
Cystitis is a urinary tract infection (UTI) that affects the bladder. It's common, particularly in women. It often gets better by itself, but may sometimes be treated with antibiotics. Some people get cystitis frequently and may need regular or long-term treatment.
What is cystitis and hematuria?
Hemorrhagic cystitis is a bladder condition that causes pain and hematuria (blood in the urine). It can develop as a complication of cancer treatment, including chemotherapy and radiation, or it can result from bladder infections.
How can you tell the difference between UTI and interstitial cystitis?
The Difference Between a UTI and IC In women who have interstitial cystitis, urine culture results will be negative, meaning that no bacteria are found in the urine as with a urinary tract infection. With IC, women may also experience pain during sexual intercourse, another symptom not commonly associated with a UTI.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute cystitis without hematuria?
ICD-10 code N30. 00 for Acute cystitis without hematuria is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What causes cystitis in a woman?
Cystitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection, although it sometimes happens when the bladder is irritated or damaged for another reason.
What is an acute bladder infection?
Acute cystitis is a sudden inflammation of the urinary bladder. Most of the time, a bacterial infection causes it. This infection is commonly referred to as a urinary tract infection (UTI). Irritating hygiene products, a complication of certain diseases, or a reaction to certain drugs can also cause acute cystitis.
What is the ICD-9 code for bladder infection?
ICD-9 code 599.0 for Urinary tract infection site not specified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -OTHER DISEASES OF URINARY SYSTEM (590-599).
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the term for inflammation of the bladder?
cystitis - inflammation of the bladder, often from an infection. urinary incontinence - loss of bladder control. interstitial cystitis - a chronic problem that causes bladder pain and frequent, urgent urination. bladder cancer.
What is a neoplastic bladder?
A representative example of neoplastic bladder disorder is bladder carcinoma. Disease or disorder of the urinary bladder, the musculomembranous sac in the anterior of the pelvic cavity that serves as a reservoir for urine, which it receives through the ureters and discharges through the urethra.
How do doctors diagnose bladder problems?
doctors diagnose bladder diseases using different tests. These include urine tests, x-rays, and an examination of the bladder wall with a scope called a cystoscope. Treatment depends on the cause of the problem. It may include medicines and, in severe cases, surgery.
What is a UTI after a procedure?
Uti (urinary tract infection) after procedure. Clinical Information. A bacterial infectious process affecting any part of the urinary tract, most commonly the bladder and the urethra. Symptoms include urinary urgency and frequency, burning sensation during urination, lower abdominal discomfort, and cloudy urine.
How to tell if you have a UTI?
if you think you have a uti, it is important to see your doctor. Your doctor can tell if you have a uti by testing a sample of your urine. Treatment with medicines to kill the infection will make it better, often in one or two days.
What are the infections that affect the secretion and elimination of urine?
Infections affecting stuctures participating in the secretion and elimination of urine: the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. Inflammatory responses of the epithelium of the urinary tract to microbial invasions. They are often bacterial infections with associated bacteriuria and pyuria.
What is discharge of urine after completion of urinary control?
Involuntary discharge of urine after expected age of completed development of urinary control. This can happen during the daytime (diurnal enuresis) while one is awake or during sleep (nocturnal enuresis). Enuresis can be in children or in adults (as persistent primary enuresis and secondary adult-onset enuresis).
What are the different types of incontinence?
Major types of incontinence include urinary urge incontinence and urinary stress incontinence. Urinary incontinence is loss of bladder control. Symptoms can range from mild leaking to uncontrollable wetting. It can happen to anyone, but it becomes more common with age.
Is enuresis a symptom of incontinence?
Involuntary loss of urine, such as leaking of urine. It is a symptom of various underlying pathological processes. Major types of incontinence include urinary urge incontinence and urinary stress incontinence.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for painful gouty tophi with bone spur, medial hallux ipj
- 2. icd-10 code for black stool
- 3. icd 10 code for pain in thoracic spine
- 4. 2019 icd 10 code for chronic l4 compression fracture
- 5. icd 10 code for intramuscular hematoma
- 6. icd 10 code for e coli wound infection
- 7. icd-10-cm code for arterial stricture
- 8. what is the icd-10 code for subfascial mass of the abdomen
- 9. icd 10 code for gastrocnemius strain
- 10. icd-10-pcs code for ed bedside screening ultrasound