Full Answer
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
How many codes in ICD 10?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...
What is ICD 10 code for mediastinal mass?
What is the diagnosis code for mediastinal mass? Malignant neoplasm of mediastinum, part unspecified C38. 3 is a billable/specific ICD -10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
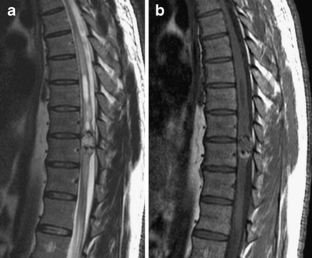
What is this G95 9?
ICD-10 code: G95. 9 Disease of spinal cord, unspecified.
What is an intradural mass?
A spinal cord tumor, also called an intradural tumor, is a spinal tumor that that begins within the spinal cord or the covering of the spinal cord (dura). A tumor that affects the bones of the spine (vertebrae) is called a vertebral tumor.
What is a D49 2 skin neoplasm?
D49. 2 Neoplasm of unsp behavior of bone, soft tissue, and skin - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is the ICD-10 code for spinal mass?
Malignant neoplasm of spinal cord C72. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C72. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a intradural extramedullary mass?
Intradural extramedullary (IDEM) tumors are generally benign neoplasms arising in the spinal canal, accounting for about two-thirds of primary spinal tumors and 15% of tumors affecting the Central Nervous System (1–3).
Where is intradural extramedullary?
Intradural extramedullary tumors are located inside the dura, but outside of the spinal cord. They might develop from nerve roots or from the inside surface of the dura mater. Meningiomas and nerve sheath tumors make up the majority of intradural extramedullary tumors. Both kinds of tumors are usually benign.
What is a ICD code D48 5?
5: Neoplasm of uncertain or unknown behaviour: Skin.
When do you use D48 5?
Use the “uncertain” behavior diagnosis code when histologic confirmation whether the neoplasm is malignant or benign cannot be made by the pathologist. Look up the path report diagnosis in the ICD-10-CM Index to if you have a path report. Use D48. 5 is for uncertain behavior of the skin.
What is the difference between neoplasm of uncertain and unspecified?
Consequently, an “unspecified” condition is reported while awaiting additional information. “Neoplasm of uncertain behavior” is frequently documented to describe a mass that is awaiting confirmatory biopsy results.
What is G95 89?
89 - Other specified diseases of spinal cord.
What is an epidural mass?
Metastatic epidural spinal cord compression is defined as the presence of tumor in the spinal canal causing compression of the spinal cord.
What are spinal tumors?
A spinal tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue within or surrounding the spinal cord and/or spinal column. These cells grow and multiply uncontrollably, seemingly unchecked by the mechanisms that control normal cells. Spinal tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
What Are Intradural Extramedullary Tumors?
Intradural extramedullary tumors are just one of several types of spinal cord tumors. Spinal cord tumors can be either extradural or intradural; extradural tumors exist outside of the dura mater, the thin membrane that protects the brain and spinal cord, while intradural tumors exist inside of it.
Discovering Intradural Extramedullary Tumors
If an intradural extramedullary tumor can be discovered in the early stages, there is a much greater chance of treating it and alleviating any of the symptoms you may already be experiencing. Typically, you will feel back or neck pain first.
Treatment Options
Depending upon when the intradural extramedullary tumor is discovered, there are several treatment options that may be possible. The treatment option recommended by your physician depends on whether or not the tumor is cancerous or noncancerous. Even if noncancerous, the tumor is still dangerous because it can affect you neurologically.
Factors that Affect Treatment Options
Once you have researched the different treatment options available for intradural extramedullary tumors and have spoke with a doctor, the time will come to make a decision. Surgery is usually the preferred treatment option, but it can depend on several factors.
Final Thoughts
Intradural extramedullary tumors are complex conditions that arise from a complex part of the anatomy. There can be a lot of research involved in navigating your treatment process, which can be overwhelming.
What is the most common intradural neoplasm?
In children, the most common intradural extramedullary neoplasms are drop metastases from primary brain tumors (most commonly medulloblastoma ). In adults, the most common drop metastases are from glioblastoma.
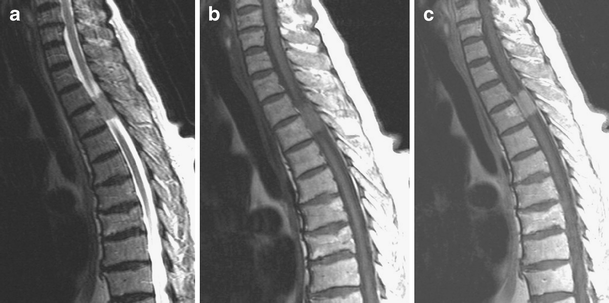
Where is a mass lesion found?
In general, a mass lesion is demonstrated within the spinal canal, sometimes with extension into the neural foramina and extradural paraspinal region (which is more suggestive of a nerve sheath tumor).
What is contrast enhanced MRI?
MRI. Contrast-enhanced MRI is the modality of choice to fully characterize these masses. The key benefits of MRI are greater sensitivity of detection and the ability to narrow the diagnostic differential by defining signal characteristics and the relationship of the mass to the cord, dura, and nerve roots.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for bowel obstruction
- 2. icd 10 code for status post acute bronchitis
- 3. icd 10 code for delayed primary closure
- 4. icd-10 code for congestive heart failure due to hypertension
- 5. icd 10 code for carpal tunnel
- 6. icd 10 code for acute seizure
- 7. icd 10 code for avascular necrosis of right femoral head
- 8. icd 10 pcs code for insertion of hemodialysis catheter
- 9. icd 10 code for scoliosis lumbosacral
- 10. icd 10 code for non functioning left kidney