What is the ICD 10 code for lymphocytosis?
Lymphocytosis (symptomatic) 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. D72.820 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM D72.820 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the CPT code for intraepithelial lymphocytosis?
If you read the path carefully it states intraepithelial lymphocytosis which is not the same as the D72 code because this was not a study of the blood sample it was a tissue sample so you would use the K31.89 for this one. You must log in or register to reply here.
What is the ICD 10 code for noninfective colitis?
Other specified noninfective gastroenteritis and colitis 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code K52.89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM K52.89 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the new ICD 10 for leukocytosis?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM D72.829 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D72.829 - other international versions of ICD-10 D72.829 may differ. A transient increase in the number of leukocytes in a body fluid. Transient increase in the number of leukocytes in a body fluid.
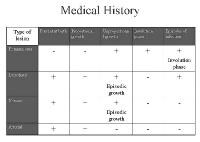
What is the ICD-10 code for colonic mucosa?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K63. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K63.
What is the ICD-10 code for intraepithelial lymphocytosis?
ICD-10 code D72. 820 for Lymphocytosis (symptomatic) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism .
What is the ICD-10-CM code for lymphopenia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Lymphocytopenia D72. 810.
What does lymphocytosis mean?
Lymphocytosis (lim-foe-sie-TOE-sis), or a high lymphocyte count, is an increase in white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes help fight off diseases, so it's normal to see a temporary increase after an infection.
What are intraepithelial lymphocytes?
Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) that reside within the epithelium of the intestine form one of the main branches of the immune system. IELs are almost exclusively antigen-experienced T cells that are heterogeneous in phenotype, ontogeny, antigen specificity and function.
What is focal intraepithelial lymphocytes?
Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) represent an abundant and heterogeneous population of antigen-experienced T cells that reside in the intestinal epithelium. They are composed of T cells bearing the αβ (αβ IELs >90 %) or the γδ T cell receptor (γδ IELs <10 %).
What is the difference between leukopenia and lymphopenia?
In fact, some people use the terms “leukopenia” and “neutropenia” interchangeably. Another common type of leukopenia is lymphocytopenia, which is when you have too few lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are the WBCs that protect you from a variety of infections and also from cancerous cells.
What is lymphocytes in hematology?
(LIM-foh-site) A type of immune cell that is made in the bone marrow and is found in the blood and in lymph tissue. The two main types of lymphocytes are B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. B lymphocytes make antibodies, and T lymphocytes help kill tumor cells and help control immune responses.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What are the 2 main types of lymphocytes?
These antigen-presenting cells subsequently migrate into lymphoid tissue. There are two major types of lymphocyte: B lymphocytes, which mature in the bone marrow; and T lymphocytes, which mature in the thymus.
What cells are classed as lymphocytes?
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell that is part of the immune system. There are two main types of lymphocytes: B cells and T cells. The B cells produce antibodies that are used to attack invading bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
What is the most common cause of lymphocytosis?
Reactive lymphocytosis is most commonly related to viral infections, particularly infectious mononucleosis and viral hepatitis, and it may also be seen with bacterial infections. The reactive cells are usually CD8+ T cells and are large with abundant cytoplasm.
The ICD code D728 is used to code Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is white blood cells (the leukocyte count) above the normal range in the blood. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response, most commonly the result of infection, but may also occur following certain parasitic infections or bone tumors.
Coding Notes for D72.820 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #814-816 - Reticuloendothelial and immunity disorders with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'D72.820 - Lymphocytosis (symptomatic)'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code D72.820. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 288.61 was previously used, D72.820 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
Where is T cell lymphoma most often found?
Clinical Information. A primary peripheral t-cell lymphoma in the gastrointestinal tract, most often in the jejunum, associated with a history of celiac disease or other gastrointestinal diseases. An uncommon mature t-cell lymphoma of intraepithelial lymphocytes.
Gastritis
Cite this page: Morrow M Lymphocytic gastritis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stomachlymphocyticgastritis.html. Accessed February 21st, 2022.
Lymphocytic gastritis
Cite this page: Morrow M Lymphocytic gastritis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stomachlymphocyticgastritis.html. Accessed February 21st, 2022.
Noninfectious colitis
Cite this page: Yearsley MM. Lymphocytic colitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colonlymphocytic.html. Accessed February 12th, 2022.
Lymphocytic colitis
Cite this page: Yearsley MM. Lymphocytic colitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colonlymphocytic.html. Accessed February 12th, 2022.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right upper lobe squamous cell cancer
- 2. icd 10 code for ebstein's anomaly
- 3. icd 10 cm code for mdd recurrent moderate
- 4. 2015 icd 10 code for sprain popliteaous tendon
- 5. icd 9 code for ulcer of esophagus
- 6. icd 10 code for iron and tibc
- 7. icd 10 code for angioectasia
- 8. icd 10 code for normal non-enhanced head
- 9. icd 9 code for panic disorder
- 10. icd code for telehealth