How many codes in ICD 10?
Jun 19, 2020 · Click to see full answer. Hereof, what is the ICD 10 code for traumatic intraparenchymal hemorrhage? S06. 369A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM S06. 369A became effective on October 1, 2019.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Nov 11, 2020 · S06. 369A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. What is Intraparenchymal hemorrhage? A parenchymal hemorrhage, or an intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH), is a bleed that occurs within the brain parenchyma, the functional tissue in the brain consisting of neurons and glial cells.
What is the ICD 10 code for benign essential hypertension?
Oct 01, 2021 · Other nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. I61.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I61.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is ICD 10 used for?
The ICD code I616 is used to code Intraparenchymal hemorrhage Intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH) is one extension of intracerebral hemorrhage (the other is intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)) with bleeding within brain parenchyma. Multiple intraparenchymal hemorrhage Source: Wikipedia MS-DRG Mapping
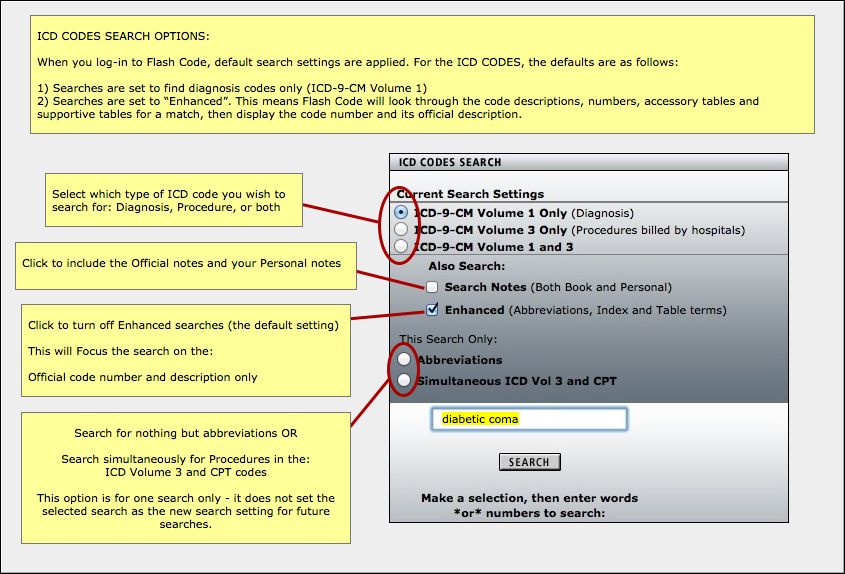
What is Intraparenchymal hemorrhage?
A parenchymal hemorrhage, or an intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH), is a bleed that occurs within the brain parenchyma, the functional tissue in the brain consisting of neurons and glial cells.
What is Intraparenchymal hematoma of brain?
This type of hematoma, also known as intraparenchymal hematoma, occurs when blood pools in the tissues of the brain. There are many causes, including trauma, rupture of a bulging blood vessel (aneurysm), poorly connected arteries and veins from birth, high blood pressure, and tumors.Jun 13, 2020
Where is an intraparenchymal hemorrhage located?
An intraparenchymal hemorrhage occurs within the brain tissue itself and is usually the result of high blood pressure (hypertension), a tumor, a cavernous malformation, or an arteriovenous malformation (AVM).
How do you code hemorrhagic conversion?
What are the correct code assignments for spontaneous hemorrhagic conversion of a cerebral infarction? Answer: Assign both code 434.91, Cerebral artery occlusion, unspecified, with cerebral infarction and code 431, Intracerebral hemorrhage. Hemorrhage can spontaneously occur after the original infarct.Mar 14, 2018
Is an IPH a stroke?
There are two types of hemorrhagic stroke. Intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH) is characterized by bleeding within the brain itself, whereas subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is characterized by vessel rupture in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)–filled subarachnoid space surrounding the brain.
What is the difference between ICH and SAH?
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH; Figure 1) refers to nontraumatic bleeding into the brain parenchyma. (Intracerebral hemorrhage, often abbreviated ICH, is used more often in the clinical literature.) Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) refers to bleeding into the space between the pia and the arachnoid membranes.
What is a IPH?
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis (IPH) is a rare and life threatening condition, found primarily in children, that causes recurrent episodes of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage.Apr 4, 2014
What is the ICD 10 code for intraparenchymal hemorrhage?
I61.8Other nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage I61. 8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I61. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is intraparenchymal the same as intracerebral?
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH) is one form of intracerebral bleeding in which there is bleeding within brain parenchyma. The other form is intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH). Intraparenchymal hemorrhage accounts for approximately 8-13% of all strokes and results from a wide spectrum of disorders.
What is ICD-10 for CVA?
I63.99.
What is the ICD-10 code for hemorrhagic shock?
1.
What is the ICD-10 code for hemorrhagic stroke?
The case definition of using the ICD-10-CM code of I60 or I61 as the primary diagnosis to identify acute hemorrhagic stroke yielded a PPV and sensitivity of 98.2% and 93.1%, respectively.Jan 14, 2021
The ICD code I616 is used to code Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH) is one extension of intracerebral hemorrhage (the other is intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)) with bleeding within brain parenchyma.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #020-022 - Intracranial vascular procedures with pdx hemorrhage with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'I61.6 - Nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage, multiple localized'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code I61.6. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code I61.6 and a single ICD9 code, 431 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is a coded reaction to a medication?
Coughing up blood. Heavy periods. Remember for coding, if the patient is taking their medication as prescribed and develops an adverse reaction, such as bleeding, this is coded as an adverse reaction to the prescribed medication and not a poisoning.
How do platelets respond to a hemorrhage?
When the body is bleeding a signal is sent and the platelets respond by traveling to the area of the bleeding. Once they have arrived at the site of the hemorrhage, they grow long tentacles and resemble spiders or an octopus when viewed under a microscope. Before they are signaled for clotting, they are plate shaped.
What is the purpose of anticoagulant therapy?
Anticoagulation and Antiplatelet Therapy. Anticoagulants and antiplatelets are used for the prevention and treatment of blood clots that occur in blood vessels. Oftentimes, anticoagulants and antiplatelets are referred to as “blood thinners,” but they don’t actually thin the blood at all. These drugs slow down the body’s process of making clots.
What prevents platelets from sticking together?
Antiplatelets prevent platelets from sticking together. Fun Fact! Clots that are formed in the vein are mostly made of fibrin. This includes the diagnoses that we see of deep-vein-thrombosis (DVT). However, clots in the arteries typically are formed with mostly platelets.
How do clot drugs work?
These drugs slow down the body’s process of making clots. Their main function is to keep the patient’s blood from clotting or turning into solid clumps of cells. These drugs do this by interfering with either fibrin or platelets in the blood.
How long can you take blood clot medication?
The length for taking these medications depends on the reason for needing to start them in the first place. They can prescribed for a few weeks or for the rest of your life. The site of the blood clot (if that is why they are prescribed) also helps to determine the length the medication will be needed.
Do anticoagulants dissolve blood clots?
Anticoagulants do NOT dissolve blood clots. They only help prevent new clots from occurring, or existing clots from enlarging, but they do not aid in dissolving the old clot. The body will dissolve the clot naturally if it can be dissolved.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
S06.36. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code S06.36 is a non-billable code.
What is the ICd code for cerebral contusion?
The ICD code S063 is used to code Cerebral contusion. Cerebral contusion, Latin contusio cerebri, a form of traumatic brain injury, is a bruise of the brain tissue. Like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple microhemorrhages, small blood vessel leaks into brain tissue. Contusion occurs in 20–30% of severe head ...
What is the ICD code for traumatic hemorrhage of cerebrum?
ICD Code S06.36 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the ten child codes of S06.36 that describes the diagnosis 'traumatic hemorrhage of cerebrum, unspecified' in more detail.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
Is cerebral laceration a contusion injury?
A cerebral laceration is a similar injury except that, according to their respective definitions, the pia-arachnoid membranes are torn over the site of injury in laceration and are not torn in contusion.
What is the ICD-10 code for cerebral hemorrhage?
I61.9 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage, unspecified. The code I61.9 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code I61.9 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like cerebral hemorrhage, hemorrhagic cerebral infarction, nontraumatic intraparenchymal cerebral hemorrhage, silent micro-hemorrhage of brain, spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage , spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage with compression of brain, etc.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like I61.9 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
When to use I61.9?
Unspecified diagnosis codes like I61.9 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition.
What are the different types of hemorrhage?
The following clinical terms are approximate synonyms or lay terms that might be used to identify the correct diagnosis code: 1 Cerebral hemorrhage 2 Hemorrhagic cerebral infarction 3 Nontraumatic intraparenchymal cerebral hemorrhage 4 Silent micro-hemorrhage of brain 5 Spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage 6 Spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage with compression of brain
What is a stroke called?
Also called: Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. A stroke is a medical emergency. There are two types - ischemic and hemorrhagic. Hemorrhagic stroke is the less common type. It happens when a blood vessel breaks and bleeds into the brain. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die.
What causes a numbness in the arm and leg?
Causes include a bleeding aneurysm, an arteriovenous malformation (AVM), or an artery wall that breaks open. Symptoms of stroke are. Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg (especially on one side of the body) Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination. Sudden severe headache with no known cause. It is important to treat strokes as quickly as possible. With a hemorrhagic stroke, the first steps are to find the cause of bleeding in the brain and then control it.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code I61.9 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for colitis
- 2. icd 10 code for unsure lmp date
- 3. icd 10 code for systolic and diastolic chf
- 4. icd 10 code for angina and cad
- 5. icd-10 diagnosis code for fever of 103 in a 4 year old
- 6. icd 10 code for victim of bullying
- 7. icd 10 code for knot of neck
- 8. icd 10 code for left sciatica radiculopathy
- 9. icd 10 code for mpn
- 10. icd 10 code for e11.59