What is the difference between ICD9 and ICD10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code J98.11 and a single ICD9 code, 518.0 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICD 10 equivalent of ICD 9 code 518?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code J98.11 and a single ICD9 code, 518.0 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is a type 1 exclude note in J98?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as J98. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
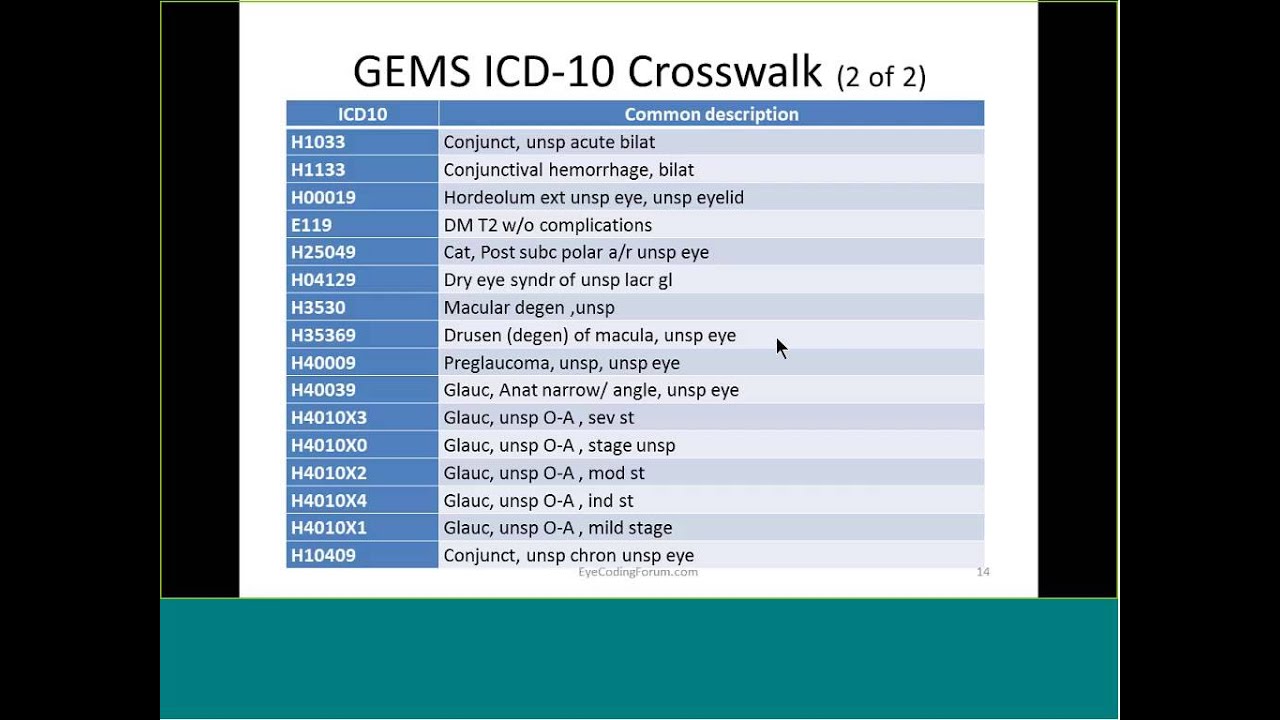
What is the ICD-10 code for left lower lobe atelectasis?
J98. 11 - Atelectasis | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated D dimer?
For elevated D-dimer, look to ICD-10-CM R79. 1 Abnormal coagulation profile.
What is Subsegmental atelectasis?
Terminology. The term subsegmental atelectasis includes any loss of lung volume so small that it does not cause indirect signs of volume loss (as might be seen with larger atelectases).
What is atelectasis?
Atelectasis, the collapse of part or all of a lung, is caused by a blockage of the air passages (bronchus or bronchioles) or by pressure on the lung. Risk factors for atelectasis include anesthesia, prolonged bed rest with few changes in position, shallow breathing and underlying lung disease.
What does it mean when your D-dimer is elevated?
Having a high D-dimer level in your blood can be a sign of a blood clotting disorder since the level of D-dimer can rise greatly when there's significant formation and breakdown of blood clots in your body.
What is positive D-dimer?
A D-dimer test is a blood test that checks for, or monitors, blood-clotting problems. A positive test means the D-dimer level in the body is higher than normal and suggests someone might have blood clots.
What is left lower lobe Subsegmental atelectasis?
Atelectasis (at-uh-LEK-tuh-sis) is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid. Atelectasis is one of the most common breathing (respiratory) complications after surgery.
What is the ICD 10 code for atelectasis?
ICD-10 code J98. 11 for Atelectasis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What are the 3 types of atelectasis?
The term atelectasis can also be used to describe the collapse of a previously inflated lung, either partially or fully, because of specific respiratory disorders. There are three major types of atelectasis: adhesive, compressive, and obstructive.
What is the difference between pneumothorax and atelectasis?
A collapsed lung happens when air enters the pleural space, the area between the lung and the chest wall. If it is a total collapse, it is called pneumothorax. If only part of the lung is affected, it is called atelectasis.
What is atelectasis at the lung bases?
Atelectasis and other conditions may also be called collapsed lung. Atelectasis means that lung sacs cannot inflate properly, which means your blood may not be able to deliver oxygen to organs and tissues.
What type of atelectasis is the most common?
Obstructive atelectasis is the most common type and results from reabsorption of gas from the alveoli when communication between the alveoli and the trachea is obstructed. The obstruction can occur at the level of the larger or smaller bronchus.
What is the ICd 9 code for pulmonary consolidation?
It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation, in which they are filled with liquid. Specialty: Pulmonology. MeSH Code: D001261. ICD 9 Code: 518.0.
What is the ICD code for atelectasis?
J98.11 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of atelectasis. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for adenocarcinoma of the liver
- 2. icd 10 code for induction
- 3. icd 10 code for joint stiffness
- 4. icd 10 code for status orif ankle
- 5. icd 10 code for left hip primary osteoarthritis
- 6. icd 10 cm code for /metastatic squamous cell cancer
- 7. icd 10 code for weel woman exam with pap
- 8. icd 10 code for arf
- 9. icd 10 code for heel fissure
- 10. icd 10 code for shingles zoster