What is the ICD 10 code for Kearns-Sayre syndrome?
Kearns-Sayre syndrome. H49.81 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H49.81 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H49.81 - other international versions of ICD-10 H49.81 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for Turner's syndrome?
Turner's syndrome, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code Female Dx POA Exempt. Q96.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Q96.9 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for Sayre syndrome?
Kearns-Sayre syndrome. H49.81 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H49.81 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for excluded note?
F84.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F84.0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of F84.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 F84.0 may differ. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes.
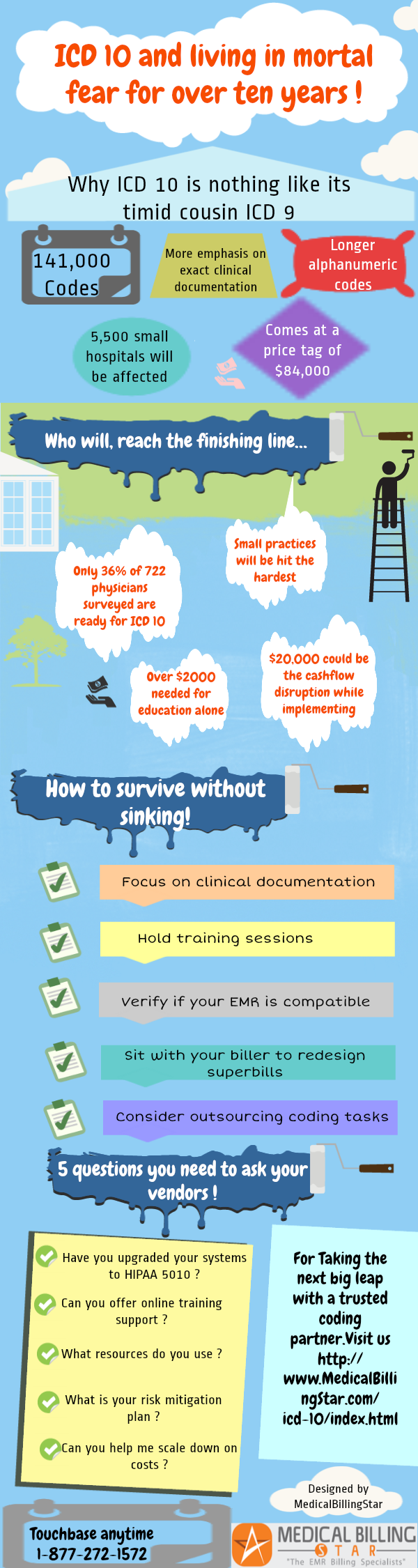
What is Kanner's syndrome?
Kanner's Syndrome This type of autism is also known as Classic Autistic Disorder, and its symptoms can include challenges communicating or understanding others, engaging in virtually no eye contact, and a hypersensitivity to stimuli (smell, light, noise, taste, or touch).
What is the diagnosis code for autism spectrum disorder?
The ICD-10-CM code for ASD—F84. 0 (autistic disorder)—should be the physician's or psychologist's diagnosis (typically required by payers) of the underlying medical condition, documented in the patient's medical record.
Is F84 0 a mental health diagnosis?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F84. 0: Autistic disorder.
What are the 5 disorders on the autism spectrum?
There are five major types of autism which include Asperger's syndrome, Rett syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, Kanner's syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder – not otherwise specified.
What are the 3 levels of autism?
Current Classifications of Autism Spectrum DisorderASD Level 1 – Level 1 ASD is currently the lowest classification. ... ASD Level 2 – In the mid-range of ASD is Level 2. ... ASD Level 3 – On the most severe end of the spectrum is Level 3 which requires very substantial support.
What level of autism is Aspergers?
Although the eponymous term 'Asperger's syndrome' had been in clinical and common usage since the early 1980s, the DSM-5 replaced the term Asperger's syndrome with the new diagnostic category of Autism Spectrum Disorder – Level 1.
What does F84 0 mean?
Diagnostic Criteria 299.00 (F84.0) Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back-and-forth conversation; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect; to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions.
What level is F84 0 autism spectrum disorder?
Level 3, “requiring very substantial support”, indicates the person's communication and behavioral difficulties make functioning very limited across all spheres of life. Further requirements in the DSM-5 include the symptoms to be present in early developmental periods.
What does F84 0 autism spectrum disorder mean?
299.00 (F84.0) Diagnostic Criteria according to the Diagnostic Statistical Manual V. A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by the following, currently or by history (examples are illustrative, not exhaustive, see text):
What's the difference between autism and autism spectrum disorder?
They are one and the same. The Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is the clinical definition for autism. Some people chose to be referred to as “an autistic person”, while others prefer to be referred to “a person with autism”.
What are the 7 types of autism?
What are the types of autism?autism spectrum disorder (ASD)Asperger's syndrome.childhood disintegrative disorder.pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified.
What is the difference between autism and Aspergers?
Characteristics. What distinguishes Asperger's Disorder from classic autism are its less severe symptoms and the absence of language delays. Children with Asperger's Disorder may be only mildly affected, and they frequently have good language and cognitive skills.
What is the ICD 10 code for schizophrenia?
5. schizophrenia: acute (undifferentiated) (F23. 2)
What is the ICD 10 code for intellectual disability?
Intellectual Disabilities ICD-10-CM Code range F70-F79.
What is the ICD 10 code for cerebral palsy?
The ICD-10 Code for cerebral palsy is G80. 9.
What is the ICd code for Kearns-Sayre syndrome?
The ICD code H498 is used to code Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Kearns–Sayre syndrome (abbreviated KSS), also known as oculocraniosomatic disorder or oculocraniosomatic neuromuscular disorder with ragged red fibers, is a mitochondrial myopathy with a typical onset before 20 years of age. KSS is a more severe syndromic variant of chronic progressive ...
What is KSS in medical terms?
KSS is a more severe syndromic variant of chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (abbreviated CPEO), a syndrome that is characterized by isolated involvement of the muscles controlling movement of the eyelid (levator palpebrae, orbicularis oculi) and eye (extra-ocular muscles).
What is the ICD code for acute care?
H49.81. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code H49.81 is a non-billable code.
What is the use of additional code?
Use Additional Code. Use Additional Code note means a second code must be used in conjunction with this code. Codes with this note are Etiology codes and must be followed by a Manifestation code or codes. Code for other manifestation, such as: Heart block See code I45.9.
What is the ICd 10 code?
What Are ICD-10 Codes? The International Classification of Diseases tenth revision is a system that contains codes for various diseases, signs, symptoms, and abnormal findings. External causes for these conditions are taken into account.
What is Heller's syndrome?
Heller’s Syndrome is a vicious and regressive form of autism. It affects about every one or two children out of one hundred thousand. This condition causes developmental delays in language, social function, and motor skills.
Why is it important to know the ICD-10 code?
It’s important to know what each ICD-10 code means. You’ll likely be able to give your clients a better deal on insurance as a result, and you’ll understand how to treat your clients in the most effective manner.
Why are ICD-10 codes important?
ICD-10 Codes are primarily used for insurance purposes. They also provide valuable data when it comes to improving healthcare for patients because they allow clinicians to form a better understanding of various complex diseases.
What is the ICd code for autism?
The ICD code F840 is used to code Autism. Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired social interaction, verbal and non-verbal communication, and restricted and repetitive behavior. Parents usually notice signs in the first two years of their child's life. These signs often develop gradually, ...
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code F84.0 and a single ICD9 code, 299.01 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the name of the syndrome where the absence of a part of the sex chromosome is
A gonadal dysgenesis syndrome occurring in phenotypic females, characterized by the absence of a part or all of one of the sex chromosomes. Signs and symptoms include short stature, webbing of neck, low-set ears, hypogonadism, and sterility.
Is there a cure for turner syndrome?
They are at risk for health difficulties such as high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes, cataracts, osteoporosis and thyroid problems.other physical features typical of turner syndrome are. there is no cure for turner syndrome, but there are some treatments for the symptoms.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for injury at workplace
- 2. icd 9 code for eses
- 3. icd-10 code for constipation after anesthesia
- 4. icd 10 code for obesity hypoventilation syndrome with bronchitis
- 5. icd 10 code for neoplasm of breast cancer
- 6. icd 10 code for general medical screening exam
- 7. icd 10 code for nasal septum abrasion
- 8. icd 10 code for abnormal ferritin level
- 9. icd 10 code for gastrocutaneous fistula with delay
- 10. icd 10 code for chronic use of opioids