What is the ICD 10 code for chronic otitis media?
Otitis externa. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. H60 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H60 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is ICD 10 delayed?
In ICD-10-CM, Otitis externa is coded to H60 and H62. Example codes include: H60.2- Malignant otitis externa H60.3- Other infective otitis externa H60.5- Acute noninfective otitis externa H60.6- Unspecified chronic otitis externa
What is the ICD 10 code for impacted tooth?
· Other otitis externa, unspecified ear. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. H60.8X9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H60.8X9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does otitis interna mean?
· The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H60.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H60.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 H60.9 may differ. A disorder characterized by inflammation, swelling and redness to the outer ear and ear canal. An acute or chronic inflammatory process involving the skin of the ...
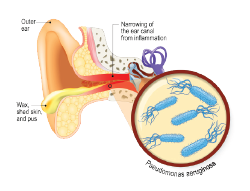
What are the two types of otitis externa?
Its different forms include acute diffuse otitis externa, circumscribed otitis externa, chronic otitis externa, and malignant (i.e., necrotizing) otitis externa.
What is the meaning of otitis externa?
Otitis externa, also called swimmer's ear, is an inflammation, irritation, or infection of the external ear canal.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the CPT code for otitis externa?
Based on the available documentation, the correct code is H60. 91 Unspecified otitis externa, right ear.
What is the difference between otitis media and otitis externa?
Otitis means inflammation of the ear. The inflammation is usually due to an infection. Otitis externa means that the inflammation is confined to the external part of the ear canal and does not go further than the eardrum. See separate leaflet called Ear Infection (Otitis Media), for an infection of the middle ear.
What is the most common form of otitis externa?
The most common cause of otitis externa is a bacterial infection, although fungal overgrowth is a principal cause in 10 percent of cases. 4 Otitis externa can also result from any of a broad range of noninfectious dermatologic processes.
What is the ICD-10 code for otitis media?
Otitis media, unspecified, unspecified ear H66. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H66. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for R11 0?
0: Nausea (without vomiting) R11. 0.
What is R53 83?
ICD-10 | Other fatigue (R53. 83)
What is the ICD-10 code for right ear pain?
01: Otalgia, right ear.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute pharyngitis?
9 Acute pharyngitis, unspecified.
What is serous otitis media?
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear space. It is also called serous or secretory otitis media (SOM). This fluid may accumulate in the middle ear as a result of a cold, sore throat or upper respiratory infection.
What is a necrotizing otitis externa?
Necrotizing (malignant) Otitis Externa – An infection that extends into the deeper tissues adjacent to the EAC. It primarily occurs in adult patients who are immunocompromised (e.g., as a result of diabetes mellitus or AIDS), and is rarely described in children. May result in cases of cellulitis and osteomyelitis.
How to tell if you have a blockage in your ear?
Moderate progression signs and symptoms include: Feeling of fullness inside the ear and partial blockage of ear canal by swelling, fluid, and debris. Advanced progression signs and symptoms include: Severe pain that may radiate to face, neck, or side of the head.
How to tell if you have a swollen ear?
Advanced progression signs and symptoms include: 1 Severe pain that may radiate to face, neck, or side of the head 2 Complete blockage of ear canal 3 Redness or swelling of outer ear 4 Swelling in the lymph nodes of the neck 5 Fever
Can swimmer's ear be worse?
Symptoms are usually mild, at first, but may worsen without treatment. Doctors often classify swimmer’s ear according to mild, moderate, and advanced stages of progression. Mild discomfort made worse by pulling on the outer ear. Moderate progression signs and symptoms include:
Who is John Verhovshek?
John Verhovshek. John Verhovshek, MA, CPC, is a contributing editor at AAPC. He has been covering medical coding and billing, healthcare policy, and the business of medicine since 1999. He is an alumnus of York College of Pennsylvania and Clemson University.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for flexor tenosynovitis right ring finger
- 2. icd-10 code for progesterone
- 3. icd 10 code for bilateralpulmonary infiltrates
- 4. icd 10 dx code for morbid obesity
- 5. icd 10 code for personal history of epilepsy
- 6. icd 10 code for fracture l thumb distal phalanax near the ip joint
- 7. what is the correct icd-9-cm code for addison's anemia
- 8. icd 10 code for stress fracture of the left hand, subsequent encounter with delayed healing
- 9. icd 10 code for allergic reaction to antibiotic
- 10. icd 10 cm code for arthritis due to lyme disease. icd-10-cm