What are the ICD 10 codes for stroke?
Nov 16, 2018 · For FY 2019, ICD-10-CM has added a new code for reporting of lacunar cerebral infarction. This is good news for coders since we see this specific type of cerebral infarction documented often. The new code that is reported for lacunar infarction is: I63.81 —Other cerebral infarction due to occlusion or stenosis of small artery
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Pure motor lacunar syndrome Pure motor lacunar infarction ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G46.6 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Pure sensory lacunar syndrome Pure sensory lacunar infarction ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z82.3 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Family history of stroke
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Search Results. 497 results found. Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G46.5 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Pure motor lacunar syndrome. Pure motor lacunar infarction. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G46.5. Pure motor lacunar syndrome. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code.
What is the ICD - 10 code for brain stem stroke?
Oct 01, 2021 · I63.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I63.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I63.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 I63.9 may differ. Applicable To Stroke NOS Type 2 Excludes
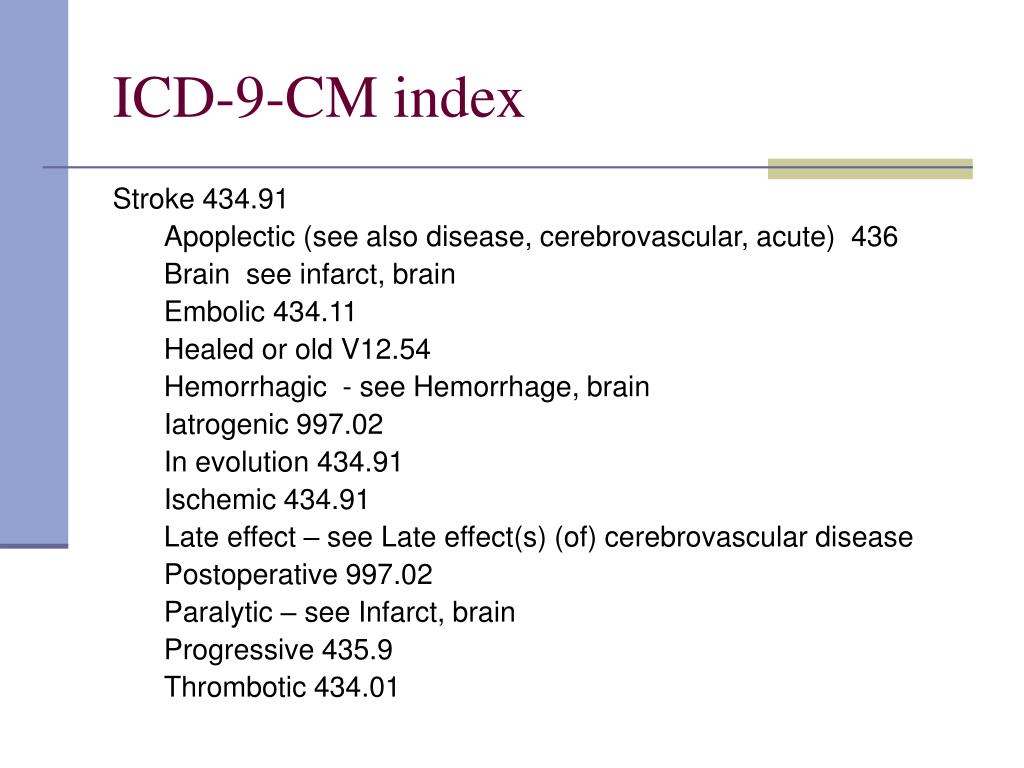
What is a lacunar stroke?
A stroke in a deep area of the brain (for example, a stroke in the thalamus, the basal ganglia or pons) is called a lacunar stroke. These deeper structures receive their blood flow through a unique set of arteries.Feb 13, 2019
What type of stroke is lacunar infarct?
Lacunar stroke is a type of ischemic stroke that occurs when blood flow to one of the small arteries deep within the brain becomes blocked. A stroke occurs when a blockage interrupts or prevents blood flow to the brain. Strokes that occur due to blockages in blood vessels within the brain are called ischemic strokes.
Is a lacunar stroke a mini stroke?
A quarter of all ischaemic strokes (a fifth of all strokes) are lacunar type. Lacunar infarcts are small infarcts (2–20 mm in diameter) in the deep cerebral white matter, basal ganglia, or pons, presumed to result from the occlusion of a single small perforating artery supplying the subcortical areas of the brain.
What is the ICD-10 code for recent stroke?
When a patient has a history of cerebrovascular disease without any sequelae or late effects, ICD-10 code Z86. 73 should be assigned.
Why is it called lacunar stroke?
A lacunar stroke, also called a lacunar infarct, occurs when an artery that supplies blood to the deeper portions of the brain becomes blocked. Other types of strokes occur on the surface, or cortex, of the brain. Lacunar strokes represent anywhere from 15% to 25% of strokes.Nov 22, 2021
Is a lacunar infarct a stroke or TIA?
Although usually mild and transient, the symptoms caused by a TIA are similar to those caused by a stroke. Another type of stroke that occurs in the small blood vessels in the brain is called a lacunar infarct.
What are the characteristics of a lacunar stroke?
The infarct of this lacunar syndrome is usually in the thalamus. Symptoms consist of persistent or transient numbness and/or tingling on one side of the body (eg, face, arm, leg, trunk). Occasionally, patients complain of pain or burning, or of another unpleasant sensation. Unilateral sensory loss is observed.Jan 25, 2021
How is lacunar stroke diagnosed?
The gold standard to identify acute lacunar strokes is magnetic resonance (MR) with diffusion-weighted imaging. However, MR is not widely available for acute stroke assessment, and computed tomography (CT), due to its accessibility, cost, and few contraindications is routinely used for acute stroke assessment.Apr 9, 2020
What is a lacunar stroke NHS?
What is a Lacunar stroke? This is a type of ischaemic stroke that occurs when blood flow to one of the small arteries in the brain becomes blocked. This is known as Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (SVD).
What is the ICD-10 code for old lacunar infarct?
The new code that is reported for lacunar infarction is: I63. 81—Other cerebral infarction due to occlusion or stenosis of small artery.
What is the diagnosis code for a stroke?
9.
What is the code for a stroke?
For ischaemic stroke, the main codes are ICD-8 433/434 and ICD-9 434 (occlusion of the cerebral arteries), and ICD-10 I63 (cerebral infarction).Aug 20, 2015
What is the term for a loss of blood flow to the brain?
An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries. In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
How is a stroke classified?
Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810) A stroke is a medical emergency.
The ICD code G467 is used to code Lacunar stroke
Lacunar stroke or lacunar infarct (LACI) is a type of stroke that results from occlusion of one of the penetrating arteries that provides blood to the brain's deep structures.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'G46.7 - Other lacunar syndromes'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code G46.7. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code G46.7 and a single ICD9 code, 437.8 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Why do brain cells die?
It is usually caused by a blood clot that blocks or plugs a blood vessel in the brain. This keeps blood from flowing to the brain. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. Another cause is stenosis, or narrowing of the artery.
What does TIA mean in stroke?
Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) occur when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted briefly. Having a TIA can mean you are at risk for having a more serious stroke. Symptoms of stroke are. Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg (especially on one side of the body)
How to treat strokes?
It is important to treat strokes as quickly as possible. Blood thinners may be used to stop a stroke while it is happening by quickly dissolving the blood clot. Post-stroke rehabilitation can help people overcome disabilities caused by stroke damage. NIH: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
What is the best treatment for stroke?
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination. It is important to treat strokes as quickly as possible. Blood thinners may be used to stop a stroke while it is happening by quickly dissolving the blood clot.
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue?
stroke occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue, this leads to ischemia (deprivation of oxygen) and potentially infarction (dysfunctional scar tissue). Strokes can be either hemorrhagic, or embolic/thrombotic. Hemorrhagic strokes occur as a result of a ruptured cerebral blood vessel. Embolic/thrombic strokes occur as a result of an obstructed cerebral vessel.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
Explicitly document findings to support diagnoses of › Stroke sequela codes (ICD-10 category I69.-) should acute stroke, stroke and subsequent sequela of be used at the time of an ambulatory care visit stroke, and personal history of stroke without sequela, oce, which is considered subsequent to any acute

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for left ankle sprain with talus osteochondral defect
- 2. icd 10 code for sesamoid fracture
- 3. icd 10 code for tobacco dependence syndrome
- 4. icd 10 cm code for om with effusion
- 5. icd 10 code for astm
- 6. icd 10 cm code for missed a step and fell
- 7. icd 10 code for history of renal dysfunction
- 8. icd 10 code for prison as place of occurrence
- 9. icd code for needle stick injury
- 10. icd-10-cm code for sucked into jet engine