What is the ICD 10 code for Lambert Eaton syndrome?
Lambert-Eaton syndrome, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code G70.80 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM G70.80 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for chondromalacia?
G70.80 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G70.80 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the pathophysiology of Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
Lambert-Eaton syndrome, unspecified. An autoimmune disease characterized by weakness and fatigability of proximal muscles, particularly of the pelvic girdle, lower extremities, trunk, and shoulder girdle. There is relative sparing of extraocular and bulbar muscles. Carcinoma, small cell of the lung is a frequently associated condition,...
What is the ICD 10 code for lumbar radiculopathy?
G70.80 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is Eaton syndrome?
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a very rare condition that affects the signals sent from the nerves to the muscles. It means the muscles are unable to tighten (contract) properly, resulting in muscle weakness and a range of other symptoms.
What is the characteristic feature of Eaton Lambert Syndrome?
The most frequent clinical manifestations of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome are proximal muscle weakness, autonomic dysfunction, and absent deep tendon reflexes. Symptoms are usually insidious in onset and progress more rapidly in SCLC-LEMS.
What is the primary etiology of Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
What causes Lambert-Eaton syndrome? This condition is often associated with a certain type of cancer called small cell lung cancer. This syndrome may result from your body's efforts to fight the underlying cancer. In some of the remaining cases, Lambert-Eaton syndrome develops following another autoimmune disease.
Is Eaton Lambert autoimmune?
General Discussion. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder of the neuromuscular junction. It is a miscommunication between the nerve cell and the muscles that lead to the gradual onset of muscle weakness. It starts in the proximal muscles of the legs or arms.
What is the difference between myasthenia gravis and Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
The difference between LEMS and myasthenia gravis (MG) This is very similar to myasthenia gravis, however the target of the attack is different in MG as the acetylcholine receptor on the nerve is affected, whereas in LEMS it's the voltage-gated calcium channel on the nerve.
How does Eaton Lambert syndrome interfere with the neuromuscular junction?
The attack occurs at the connection between nerve and muscle (the neuromuscular junction) and interferes with the ability of nerve cells to send signals to muscle cells. Specifically, the immune system attacks the calcium channels on nerve endings that are required to trigger the release of chemicals (acetylcholine).
Is Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome genetic?
The trigger for LEMS without cancer is unknown, but may have a genetic component linked to autoimmunity. In any case, these patients also make antibodies that target calcium channels, and the neuromuscular disease is the same as in those with cancer.
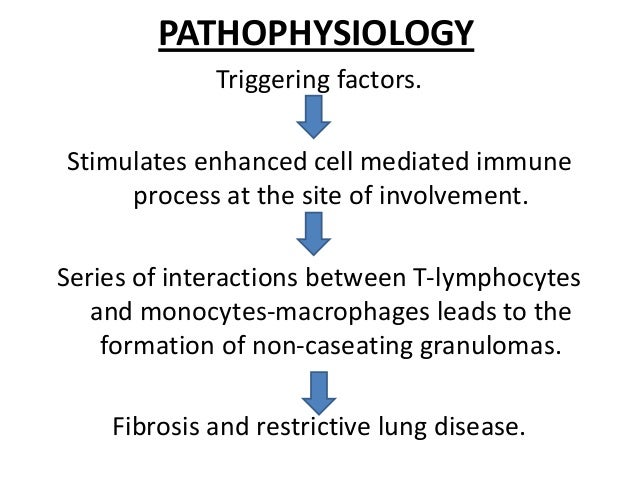
What is the main pathophysiology in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome?
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is an autoimmune disease that disrupts the normally reliable neurotransmission at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). This disruption is thought to result from an autoantibody-mediated removal of a subset of the P/Q-type Ca2+ channels involved with neurotransmitter release.
How is Lambert-Eaton syndrome treated?
Two potassium channel blockers are approved in the United States to treat LEMS. Firdapse (also known as 3,4-diaminopyridine, 3,4-DAP) was approved by the FDA in November 2018 for the treatment of adults with LEMS and is commercialized by Catalyst Pharmaceuticals.
How long can you live with Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
Median survival is 17-24 months, although the amount of patients with long-standing remission or cured is approximately 20% (compared to <2% of patients with a SCLC without LEMS).
Is LEMS a progressive disease?
The main problem created by LEMS is the progressive weakness that affects everyday activities and general quality of life. LEMS does not seem to affect the respiratory system as significantly as MG does.
Can you have Lambert-Eaton and myasthenia gravis?
The coexistence of myasthenia gravis (MG) and Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is very rare and remains controversial.
What is pathophysiology of myasthenia gravis?
Abstract. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) caused by antibodies that attack components of the postsynaptic membrane, impair neuromuscular transmission, and lead to weakness and fatigue of skeletal muscle.
Is Lambert Eaton myasthenic syndrome genetic?
The trigger for LEMS without cancer is unknown, but may have a genetic component linked to autoimmunity. In any case, these patients also make antibodies that target calcium channels, and the neuromuscular disease is the same as in those with cancer.
What is decremental response to repetitive nerve stimulation?
Repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS) is an effective way to fatigue the NMJ and cause acetylcholine depletion. These studies are abnormal in more than 60% of myasthenic patients. A decremental response on RNS is the electrical correlate of clinical muscle fatigue and weakness in myasthenic patients.
Why does LEMS improve with exercise?
Leg weakness often improves temporarily upon exertion. As you exercise, acetylcholine builds up in large enough amounts to allow strength to improve for a short time. There are several complications associated with LEMS.
The ICD code G70 is used to code Nervous system disease
Nervous system disease refers to a general class of medical conditions affecting the nervous system.
Coding Notes for G70.80 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'G70.80 - Lambert-Eaton syndrome, unspecified'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code G70.80. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 358.30 was previously used, G70.80 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
The ICD code G731 is used to code Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS, also Lambert–Eaton syndrome, or Eaton–Lambert syndrome) is a rare autoimmune disorder that is characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs.
Coding Notes for G73.1 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Type-1 Excludes mean the conditions excluded are mutually exclusive and should never be coded together. Excludes 1 means "do not code here."
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'G73.1 - Lambert-Eaton syndrome in neoplastic disease'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code G73.1. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 358.31 was previously used, G73.1 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for otitis effusion
- 2. icd 10 code for decubitus sacral ulcer
- 3. icd-10 code for pre op
- 4. icd 9 code for coarse echotexture
- 5. icd 10 code for lumbar stemosis
- 6. icd-10-cm code for dislocated left hip internal prosthesis initial encounter
- 7. icd 10 code for laceration of conjunctiva
- 8. what is the icd-10 code for pacemaker electrode broke upon insertion
- 9. icd 10 code for intramuscular injection
- 10. icd 10 code for poor eating habits