What is the ICD 10 code for neoplasm of brain?
2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C71.9 Malignant neoplasm of brain, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code C71.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 9 code for late effects of radiation?
The Medicare NCD for HBO coverage of late effects of radiation cross-walked the old ICD-9 code 909.2 to L59.9. I don't think this is really correct and the L59.8 is the best because you do have a specified condition.
What is the ICD 10 code for neoplasm of unspecified behavior?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D49.6 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Neoplasm of unspecified behavior of brain. Disorder of visual cortex associated with neoplasm; Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor; Germ cell tumor of the brain; Neoplasm of brain; Neoplasm of brain, germ cell; Neoplasm, dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial (dnet);
What is the new ICD 10 for neoplasm?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D33.2 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D33.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 D33.2 may differ. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not.
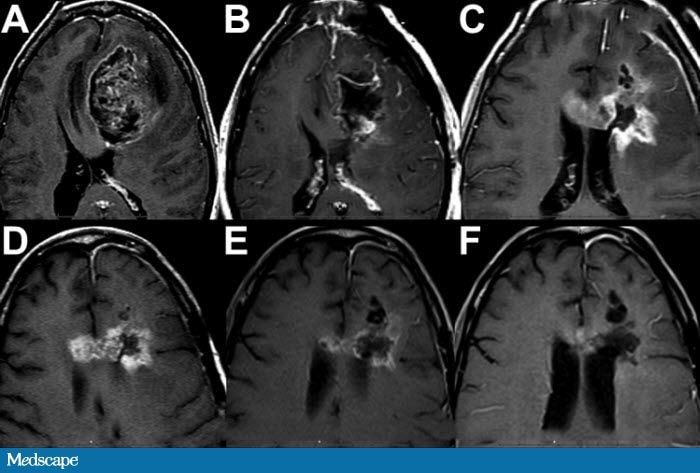
What is ICD-10 code for delayed milestones?
R62.0ICD-10 code R62. 0 for Delayed milestone in childhood is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Is there a time limit on when a late effect code can be used how many codes does it typically take to code a late effect what would be the proper sequencing of these codes?
Sequela (Late Effects) There is no time limit on when a sequela code can be used. The residual may be apparent early, such as in cerebral infarction, or it may occur months or years later, such as that due to a previous injury.
What is diagnosis code Z71 89?
Other specified counselingICD-10 code Z71. 89 for Other specified counseling is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
How do you code developmental delays?
315.9 - Unspecified delay in development. ICD-10-CM.
What is the difference between residual and late effects?
0:177:41Late Effect vs. Residual Effect Medical Coding - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSorry late effect versus residual effect a PC says a late effect is the residual effect that remainsMoreSorry late effect versus residual effect a PC says a late effect is the residual effect that remains after the acute phase of an illness or injury has terminated.
What's the difference between subsequent and sequelae?
D (subsequent encounter) describes any encounter after the active phase of treatment, when the patient is receiving routine care for the injury during the period of healing or recovery. S (sequela) indicates a complication or condition that arises as a direct result of an injury.
Can Z76 89 be a primary diagnosis?
The patient's primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient's primary diagnostic code is Z76. 89, look in the list below to see which MDC's "Assignment of Diagnosis Codes" is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
What is the age limit for ICD-10 code Z00 129?
0 - 17 years inclusiveZ00. 129 is applicable to pediatric patients aged 0 - 17 years inclusive.
What does CPT code 99401 mean?
Preventative medicine counselingCPT 99401: Preventative medicine counseling and/or risk factor reduction intervention(s) provided to an individual, up to 15 minutes may be used to counsel commercial members regarding the benefits of receiving the COVID-19 vaccine.
What is developmental delay?
• When a child's progression through predictable developmental phases slows, stops, or reverses. •Symptoms include slower-than-normal development of motor, cognitive, social, and emotional skills.
What is ICD-10 code F88?
ICD-10 code: F88 Other disorders of psychological development.
When do you use Z13 89?
Z13. 89 Encounter for screening for other disorder (when not listed elsewhere in the ICD-10 codes) – usually not necessary to report in addition to a well-child exam.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified ( C25.9 ). benign neoplasm of meninges ( D32.-) A primary, slow growing, noninvasive neoplasm of the brain.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Is astrocytoma a benign tumor?
In children, astrocytomas of the cerebellum represent relatively common benign brain neoplasms. In adults meningio mas, neurilemomas and pituitary tumors comprise the majority of benign tumors. Primary neoplasms of the brain which are noninvasive and tend to grow slowly.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the ICd 10 code for complications of surgical and medical care?
Complication of surgical and medical care, unspecified, sequela 1 T88.9XXS is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Complication of surgical and medical care, unsp, sequela 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM T88.9XXS became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T88.9XXS - other international versions of ICD-10 T88.9XXS may differ.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for staph aureus sinusitis
- 2. icd 10 code for remote right frontal lobe cva
- 3. icd 10 code for occasional alcohol drinker
- 4. icd 10 code for snuff use
- 5. icd 10 code for 696.1
- 6. icd 10 code for right scaphoid nonunion
- 7. icd 10 code for lip abrasion with infection
- 8. icd 10 code for unhealthy drinking behavior
- 9. icd-10-cm code for mediastinum massd
- 10. icd 10 cm code for necrotizing fasciitis