What are signs of late onset autism?
When do children usually show symptoms of autism?
- Problems with eye contact
- No response to his or her name
- Problems following another person's gaze or pointed finger to an object (or "joint attention")
- Poor skills in pretend play and imitation
- Problems with nonverbal communication
What is the prognosis for early onset dementia?
Her diagnosis in 2014 was harrowing, and she became depressed. The single mum and her two grown-up daughters knew nothing about dementia. “The process is so negative, it focuses on what you have lost. They say there is nothing you can do and you’re ...
How to prevent early onset dementia?
Things You Need To Do:
- Exercise 3 – 5 times a week for at least 30 minutes (an hour is even greater). Remember, it’s never too late to start exercising. ...
- Walking improves cognitive function. ...
- If you are a senior, walking briskly, yoga, dancing, swimming, gardening, chair stands, bicep curls, and stationary cycling are great options.
- Playing any form of sports is good. ...
What are the symptoms of early onset Alzheimer's?
Early symptoms:
- Forgetting important things, particularly newly learned information or important dates
- Asking for the same information again and again
- Trouble solving basic problems, such as keeping track of bills or following a favorite recipe
- Losing track of the date or time of year
- Losing track of where you are and how you got there
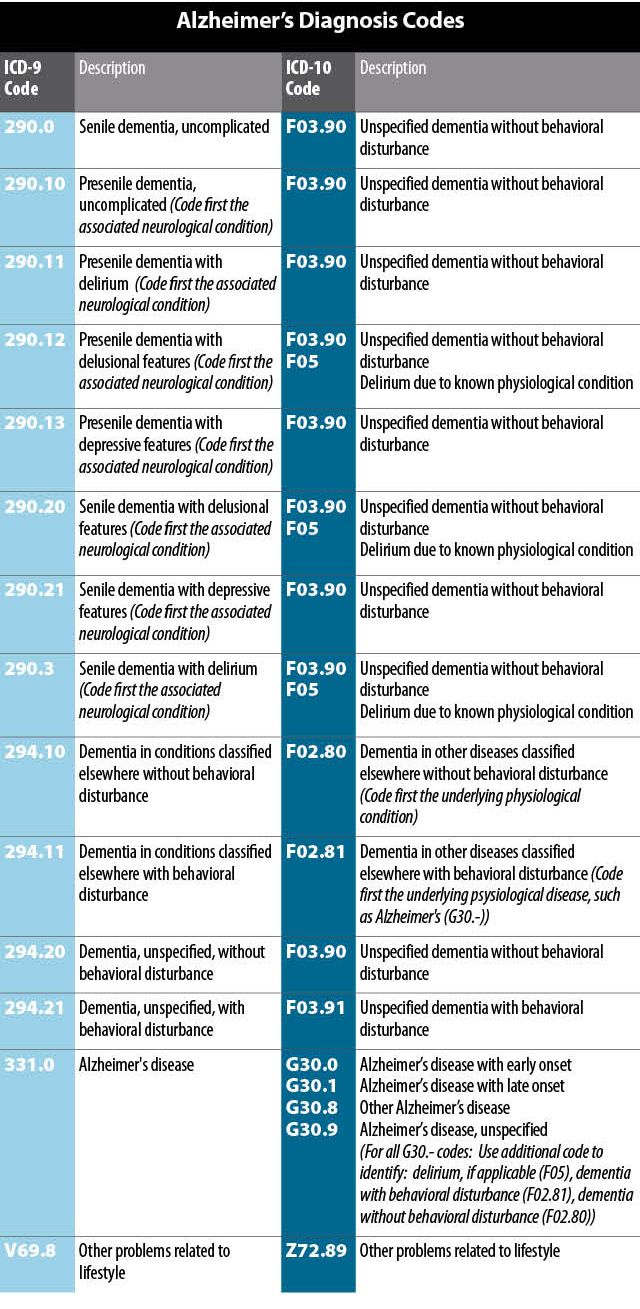
What is the ICD-10 code for Alzheimer's disease?
ICD-10 code G30. 9 for Alzheimer's disease, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is the ICD-10 code for late onset Alzheimer's disease without behavioral disturbance?
1.
What is late onset Alzheimer's?
Late-onset Alzheimer disease typically presents with progressive decline in episodic memory, with variable involvement of other cognitive domains. Progressive memory impairment can also be caused by other neurodegenerative processes affecting the medial temporal lobes.
What is F02 81 diagnosis?
ICD-10 code F02. 81 for Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with behavioral disturbance is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
What is diagnosis code G30?
ICD-10 code G30 for Alzheimer's disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is the code for a patient WHO has Alzheimer's disease with behavioral disturbances?
The Index provides the following documentation: Alzheimer's, early onset, with behavioral disturbance G30. 0 [F02. 81].
What is the meaning of late-onset?
(of a medical condition) occurring late in a person's life, esp in relation to other people with the condition.
What is the difference between early-onset and late-onset Alzheimer's?
Late-onset Alzheimer's disease is the much more common type, generally beginning after age 65. Early-onset (also called young-onset) Alzheimer's disease is a relatively rare form of the disease usually diagnosed in individuals under the age of 65 -- usually in their 40s and 50s.
What are the two types of Alzheimer's disease?
Types of Alzheimer's DiseaseEarly-onset Alzheimer's. This type happens to people who are younger than age 65. Often, they're in their 40s or 50s when they're diagnosed with the disease. ... Late-onset Alzheimer's. This is the most common form of the disease, which happens to people age 65 and older.
What does F43 23 mean?
ICD-Code F43. 23 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Adjustment Disorder with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood.
What is the DSM 5 code for Alzheimer's disease?
Major or Mild Neurocognitive Disorder Due to Alzheimers Disease DSM-5 331.0 (G30. 9)
Can F02 81 be a primary diagnosis?
The dysfunction may be primary, as in diseases, injuries, and insults that affect the brain directly and selectively; or secondary, as in systemic diseases and disorders that attack the brain only as one of the multiple organs or systems of the body that are involved.
What is Alzheimer's disease?
A disabling degenerative disease of the nervous system occurring in middle-aged or older persons and characterized by dementia and failure of memory for recent events, followed by total incapacitation and death. Types of the alzheimer syndrome are differentiated by the age of onset and genetic characteristics.
What is the most common form of dementia in older people?
A progressive, neurodegenerative disease characterized by loss of function and death of nerve cells in several areas of the brain leading to loss of cognitive function such as memory and language. Alzheimer's disease (ad) is the most common form of dementia among older people.
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer's?
A brain disorder that usually starts in late middle age or old age and gets worse over time. Symptoms include loss of memory, confusion, difficulty thinking, and changes in language, behavior, and personality.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code G30.1 and a single ICD9 code, 331.0 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICD code for alzheimer's disease?
G30.1 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of alzheimer's disease with late onset. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the ICD code for dementia?
Code is only used for patients 15 years old or older. G30.1 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of alzheimer's disease with late onset. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the term for the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, including death of neurons.
Neurodegeneration is the umbrella term for the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, including death of neurons. Many neurodegenerative diseases including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntington's occur as a result of neurodegenerative processes. Such diseases are incurable, resulting in progressive degeneration and/or death of neuron cells. As research progresses, many similarities appear that relate these diseases to one another on a sub-cellular level. Discovering these similarities offers hope for therapeutic advances that could ameliorate many diseases simultaneously. There are many parallels between different neurodegenerative disorders including atypical protein assemblies as well as induced cell death. Neurodegeneration can be found in many different levels of neuronal circuitry ranging from molecular to systemic.
What are the parallels between neurodegenerative disorders?
There are many parallels between different neurodegenerative disorders including atypical protein assemblies as well as induced cell death. Neurodegeneration can be found in many different levels of neuronal circuitry ranging from molecular to systemic. Specialty:
What is Alzheimer's disease?
A disabling degenerative disease of the nervous system occurring in middle-aged or older persons and characterized by dementia and failure of memory for recent events, followed by total incapacitation and death. Types of the alzheimer syndrome are differentiated by the age of onset and genetic characteristics.
What is dementia in the brain?
Clinical Information. A brain disorder that usually starts in late middle age or old age and gets worse over time. Symptoms include loss of memory, confusion, difficulty thinking, and changes in language, behavior, and personality. A degenerative disease of the brain characterized by the insidious onset of dementia.
What is the most common form of dementia in older people?
A progressive, neurodegenerative disease characterized by loss of function and death of nerve cells in several areas of the brain leading to loss of cognitive function such as memory and language. Alzheimer's disease (ad) is the most common form of dementia among older people.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is dementia in other diseases?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. Alzheimer's disease ( G30.-) "Includes" further defines, or give examples of, the content of the code or category.
What is neurocognitive disorder?
Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for dysmenorrhea
- 2. icd 10 code for circulating neuralgia
- 3. icd 10 code for pre op clearance chest x-ray
- 4. icd 10 code for personal history of benign brain tumor
- 5. icd 10 code for right foot ulceration
- 6. icd 10 code for pericardial infusion
- 7. icd 10 code for severe rheumatoid arthritis
- 8. icd-9 code for tight binding of chest
- 9. icd 10 code for clerance for resprator use
- 10. icd-10 code for speech therapy