What is the ICD 10 code for elevated transaminase and LDH?
Oct 01, 2021 · Elevation of levels of lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH] 2021 - New Code 2022 Billable/Specific Code. R74.02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R74.02 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for lactic acid dehydrogenase?
Oct 22, 2020 · Louisiana Medicaid – Medications Requiring ICD–10 Diagnosis Codes Generic – Brand Examples Diagnosis Description ICD–10 Codes ADHD/Narcolepsy – Stimulants and Related Agents (Applies to FFS and All MCOs as of 4/1/18 AND …
What is the ICD 10 code for lipoprotein deficiency?
Aug 25, 2021 · T78.2XXA. SOME FREQUENTLY USED LOUISIANA WIC QUALIFYING MEDICAL CONDITIONS AND ICD-9 & ICD-10 CODES FOR EXEMPT (Special) FORMULAS. The list below includes only a limited number of ICD 9/10 Codes. Please use the web page, ICD9Data.Com or ICD-9-CM International Coding Standard for other ICD-9/10 Codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated liver enzymes?
Oct 01, 2021 · R74.02 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Elevation of levels of lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH] . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
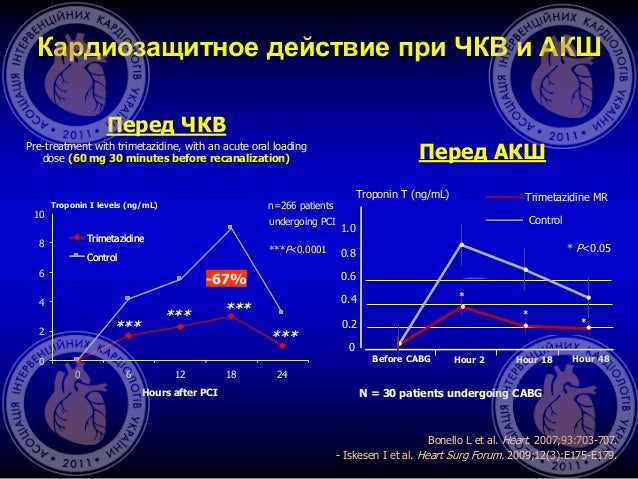
What ICD 10 codes cover LDH?
Valid for SubmissionICD-10:R74.02Short Description:Elevation of levels of lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH]Long Description:Elevation of levels of lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH]
What diagnosis covers LDH?
An LDH test is most often used to: Find out if you have tissue damage. Monitor disorders that cause tissue damage. These include anemia, liver disease, lung disease, and some types of infections.Dec 17, 2020
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated lactic acid level?
R74.0R74. 0 - Nonspecific elevation of levels of transaminase and lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH] | ICD-10-CM.
Is lactic acid and LDH the same thing?
Lactate dehydrogenase (also called lactic acid dehydrogenase, or LDH) is an enzyme found in almost all body tissues. It plays an important role in cellular respiration, the process by which glucose (sugar) from food is converted into usable energy for our cells.
What is the ICD 10 code for Hypoalbuminemia?
R77. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R77. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is medical term LDH?
One of a group of enzymes found in the blood and other body tissues, and involved in energy production in cells. An increased amount in the blood may be a sign of tissue damage and some types of cancer or other diseases. Also called lactate dehydrogenase and lactic acid dehydrogenase.
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated alkaline phosphatase?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97 R97.
What does elevated lactate indicate?
A high lactate level in the blood means that the disease or condition a person has is causing lactate to accumulate. In general, a greater increase in lactate means a greater severity of the condition. When associated with lack of oxygen, an increase in lactate can indicate that organs are not functioning properly.Nov 9, 2021
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated troponin?
Elevated Troponin should be coded to R74. 8 Abnormal levels of other serum enzymes. [Effective 11 Jul 2012, ICD-10-AM/ACHI/ACS 7th Ed.]
What is lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes?
LDH is an enzyme found in many body tissues such as the heart, liver, kidney, skeletal muscle, brain, blood cells, and lungs. When body tissue is damaged, LDH is released into the blood. The LDH test helps determine the location of tissue damage.
Where is LDH found in the cell?
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is a hydrogen transfer enzyme that is found in the cytoplasm of most of the cells of the body.
Is LDH high in Covid?
Higher LDH levels have been found in COVID-19 patients than in patients with SARS-CoV-2 negative confirmed pneumonia (7). Yuan et al. found that COVID-19 mRNA clearance ratio was highly associated with LDH levels (8).
Why is it important to have a Rh negative mother?
Rh typing is also important during pregnancy because of the potential for mother and fetus Rh incompatiblity. If the mother is Rh negative but the father is Rh positive, the fetus may be positive for the Rh antigen.
What is a blood typing test?
Blood typing is a screening test to determine blood groups and Rh antigen for blood transfusion and pregnancy. The four blood groups A, B, O, and AB are determined by the presence of antigens A and B or their absence (O) on a patient's red blood cells. In addition to ABO grouping, most immunohematology testing includes evaluation of Rh typing tests for Rh (D) antigen. Blood cells that express Rh (D) antigen are Rh positive. Red blood cells found lacking Rh (D) are considered Rh negative. Rh typing is also important during pregnancy because of the potential for mother and fetus Rh incompatiblity. If the mother is Rh negative but the father is Rh positive, the fetus may be positive for the Rh antigen. As a result, the mother’s body could develop antibodies against the Rh antigen. These antibodies may cross the placenta and cause destruction of the baby’s red blood cells, resulting in a condition known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
What happens if you cross the placenta?
These antibodies may cross the placenta and cause destruction of the baby’s red blood cells, resulting in a condition known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Blood typing is performed by agglutination testing.
Why is it important to have blood transfusions?
Transfusion of blood components of the correct blood type is necessary in order to prevent an adverse immunologic reaction. These reactions can range from very mild and sub-clinical to very severe or fatal, depending upon the components involved and condition of the recipient.
Can group O blood be given to group A?
For example, group O Rh negative blood may be given to either group A or B or AB recipients, either Rh positive or Rh negative. Some situations, for example recent transfusion, may require more time than usual to resolve and may require communication between the laboratory and patient's caregiver.
Can platelets be concentrated?
For platelets, they can be concentrated if the ABO types are incompatible such that the amount of plasma given to the recipient is reduced to a minimum and the resulting hemolysis, if any, is reduced accordingly. Test Information. Methodology: Blood Bank - Hemagglutination. Specimen Type: Whole Blood.
What is a high density lipoprotein?
A metabolic disorder characterized by deficiency of high density (alpha) lipoprotein in the blood. A rare, autosomal recessive inherited disorder of cholesterol transport, resulting in severe reduction of the amount of high density lipoprotein in the plasma and accumulation of cholesterol esters in the tissues.
What is the definition of hypobetalipoproteinemia?
Hypobetalipoproteinemia, familial. Lipoprotein deficiency disorder. Clinical Information. A disorder of lipoprotein metabolism caused by mutations in the lcat gene. It is characterized by deficiency of the enzyme lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase.
What is autosomal recessive disorder?
An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by defective absorption of dietary fat, cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins. It results in multiple vitamin deficiencies. Signs and symptoms include failure to thrive, diarrhea, steatorrhea, acanthocytosis and ataxia. An autosomal recessive disorder of lipid metabolism.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for t69.1xxa
- 2. icd 10 code for 72887
- 3. icd 10 code for status post knee surgery
- 4. icd 10 code for color vision deficiency
- 5. icd 10 code for attention to wound care
- 6. icd 10 code for allergic reaction to adhesive tape
- 7. icd 10 code for moderate episode of recurrent major depressive disorder
- 8. icd 10 code for surgery
- 9. icd 10 code for chalazion
- 10. icd 10 code for 382.9