| ICD-10: | I44.4 |
|---|---|
| Short Description: | Left anterior fascicular block |
| Long Description: | Left anterior fascicular block |
What is the ICD 10 code for left anterior fascicular block?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I44.4 Left anterior fascicular block 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Questionable As Admission Dx I44.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I44.4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does hemiblock stand for?
Left peripheral anterior synechiae ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S86.202 Unspecified injury of muscle (s) and tendon (s) of anterior muscle group at lower leg level, left leg Unsp inj musc/tend anterior grp at lower leg level, left leg ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S86.292A [convert to ICD-9-CM]
What is the ECG criteria for left anterior fascicular block?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H26.042 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Anterior subcapsular polar infantile and juvenile cataract, left eye Ant subcapsular polar infantile and juv cataract, left eye ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S32.412K [convert to ICD-9-CM] Displaced fracture of anterior wall of left acetabulum, subsequent encounter for fracture with nonunion
What is the difference between LAFB and left posterior fascicular block?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I44.7 Left bundle-branch block, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Questionable As Admission Dx I44.7 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I44.7 became effective on October 1, 2021.
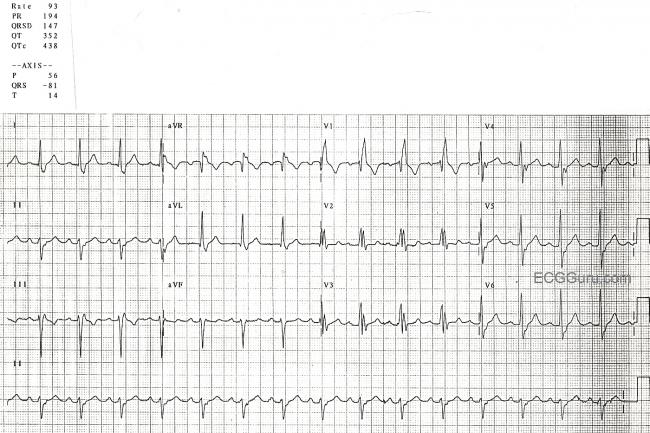
What is a Hemiblock left anterior?
What is the effect of left anterior hemiblock?
Is left anterior hemiblock serious?
What causes left posterior Hemiblock?
LPFB is caused by damage to the left posterior fascicle of the left bundle branch. It is less common than injury in the anterior fascicle because of its thicker structure and more protected location near the left ventricular inflow tract.
What is the meaning of Hemiblock?
How is left anterior fascicular block diagnosis?
Is left anterior hemiblock treatable?
Is left anterior hemiblock normal?
What causes myocardial fibrosis?
What does the left anterior fascicle supply?
Is left posterior Hemiblock serious?
Is left posterior Hemiblock normal?
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code I44.4 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is it called when your heart beats too fast?
An arrhythmia is a problem with the rate or rhythm of your heartbeat. It means that your heart beats too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular pattern. When the heart beats faster than normal, it is called tachycardia. When the heart beats too slowly, it is called bradycardia.
What causes a fast heartbeat?
The most common type of arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation, which causes an irregular and fast heart beat. Many factors can affect your heart's rhythm, such as having had a heart attack, smoking, congenital heart defects, and stress. Some substances or medicines may also cause arrhythmias.
What is left anterior fascicular block?
Left anterior fascicular block is due to anatomical or functional block in the anterior fascicle. Depolarization of the left ventricle will depend entirely on the posterior fascicle.
Is LAFB a conduction defect?
Isolated LAFB is considered a benign conduction defect. Roughly 7% of cases progress to bifascicular block (which means that the LAFB is accompanied by a right bundle branch block), while 3% progress to third-degree AV block (complete heart block).
What are fascicular blocks?
Fascicular blocks were previously referred to as hemiblocks, but the latter term has been deprecated. The left bundle branch is subdivided into the following two fascicles: (1) the anterior (anterosuperior) fascicle, which delivers the electrical impulse to the anterior wall of the left ventricle; (2) the posterior (posteroinferior) fascicle, which delivers the electrical impulse to the posterior and inferior walls of the left ventricle. Anatomical or functional block in the anterior fascicle leads to left anterior fascicular block. Similarly, left posterior fascicular block is due to block in the posterior fascicle. Approximately 5–10% of all individuals have a third fascicle – the median or centroseptal fascicle – which gives off Purkinje fibers to the interventricular septum.
Is LPFB more common than LAFB?
Left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) Left posterior fascicular block is much less common than LAFB. This is due to the fact that the posterior fascicle is larger and it has greater arterial supply. Depolarization of the left ventricle will depend entirely on impulses from the anterior fascicle if the posterior one is defect.

Popular Posts:
- 1. 207 icd 10 code for avulsion fracture of the medial femoral condyle
- 2. icd 10 code for orchitis right
- 3. icd 10 code for contusion of right ring finger without damage to nail, initial encounter
- 4. icd 10 code for hammertoe deformity left foot
- 5. icd 10 code for lower urinary tract symptoms
- 6. icd 10 code for left shoulder pain
- 7. icd 10 code for r chest pain cough
- 8. icd 10 code for head lice
- 9. icd 10 code for right shoulder torn rotator cuff
- 10. icd 10 code for absence seizure