What are the symptoms of a femoral fracture?
Symptoms of a femoral stress fracture. Symptoms include a dull ache deep in the general area of the thigh. There is likely to be pain when a bending force is applied to the femur. This is known as the hang test. The patient allows their thigh to hang over the edge of a bench or chair.
What are complications of basilar skull fracture?
The symptoms of a skull fracture may include:
- a headache or pain at the point of impact
- a bump or bruise
- bleeding from a wound
- bleeding from the ears, nose, or eyes
- clear fluid leaking from the ears or nose
- bruising behind the ears or under the eyes
- feeling drowsy, confused, or irritable
- loss of speech or slurred speech
- difficulty swallowing
- loss of balance
What is a stress fracture of the femoral neck?
A femoral neck stress fracture is a worrisome cause of hip and groin pain in athletes. Typically they are seen in runners or other athletes who perform repetitive impact to the lower extremities.
What are femoral neck fractures?
Femoral neck fractures are a specific type of intracapsular hip fracture. The femoral neck connects the femoral shaft with the femoral head. The hip joint is the articulation of the femoral head with the acetabulum. The junctional location makes the femoral neck prone to fracture. The blood supply of the femoral head is an essential consideration in displaced fractures as it runs along the femoral neck.
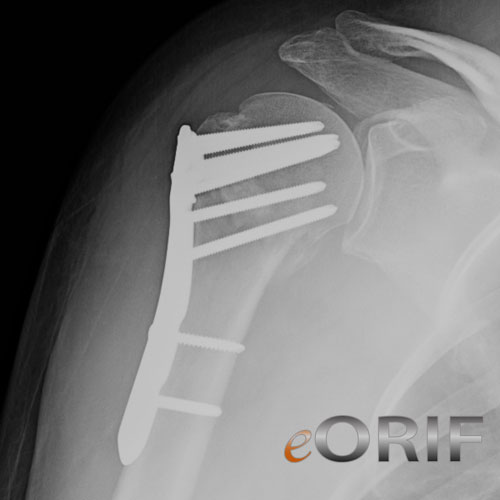
What is a Basicervical femoral neck fracture?
Basicervical fracture, defined as an extracapsular fracture, through the base of the femoral neck at its junction with the intertrochanteric region, corresponding to the AO type B2. 1 femoral neck at its junction with the intertrochanteric region.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for left femoral neck fracture?
ICD-10 Code for Fracture of unspecified part of neck of left femur, initial encounter for closed fracture- S72. 002A- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for right Subcapital femoral neck fracture?
ICD-10 code: S72. 03 Fracture of neck of femur: Subcapital.
What is a displaced femoral neck fracture?
Femoral neck fractures may be either displaced, where the bone is moved out of its original position, or non-displaced, where there is no instability of the bone. These fractures may disrupt the blood supply to the fractured portion of the bone.
What is the ICD-10 code for femur fracture?
Fracture of femur ICD-10-CM S72. 309A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0):
How do you code a fracture in ICD-10?
In ICD-10-CM a fracture not indicated as displaced or nondisplaced should be coded to displaced, and a fracture not designated as open or closed should be coded to closed. While the classification defaults to displaced for fractures, it is very important that complete documentation is encouraged.
What is the CPT code for ORIF femoral neck fracture?
CPT code 27236 (open treatment of femoral fracture, proximal end, neck, internal fixation or prosthetic replacement) would be used to report a hemiarthroplasty for a hip fracture.
What is ICD-10 code for left hip fracture?
ICD-10-CM S72. 002A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 521 Hip replacement with principal diagnosis of hip fracture with mcc. 522 Hip replacement with principal diagnosis of hip fracture without mcc.
Where is the Subcapital femoral neck?
subcapital is the femoral head and neck junction. transcervical is the mid portion of femoral neck. basicervical is the base of femoral neck.
Is a femoral neck fracture the same as a hip fracture?
A femoral neck fracture is a type of hip fracture of the thigh bone (femur)—just below the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint. This type of fracture disconnects the ball from the rest of the femur. It often causes groin pain that worsens when you putting weight on the injured leg.
What type of fracture is femoral neck fracture?
Femoral neck fractures are a specific type of intracapsular hip fracture. The femoral neck connects the femoral shaft with the femoral head. The hip joint is the articulation of the femoral head with the acetabulum. The junctional location makes the femoral neck prone to fracture.
How do you classify a femoral neck fracture?
Fractures of femoral neck in adults were first classified as intracapsular or extracapsular and later distinguished as subcapital, mid-cervical, basal, intertrochanteric, or pertrochanteric types. The subcapital was further divided into abduction, or impacted and adduction, or varus.
How are fractures of specified sites coded?
Fractures of specified sites are coded individually by site nd the level of detail furnished by medical record content. A fracture not indicated as open or closed should be coded to closed. A fracture not indicated whether displaced or not displaced should be coded to displaced.
What is a broken bone called?
Also called: Broken bone. A fracture is a break, usually in a bone. If the broken bone punctures the skin, it is called an open or compound fracture. Fractures commonly happen because of car accidents, falls, or sports injuries. Other causes are low bone density and osteoporosis, which cause weakening of the bones.
Where does the proximal end of the fracture line begin?
In this fracture group, the proximal end of the fracture line begins at some distance from the head. It comprises basicervical fractures, simple and multifragmentary transcervical fractures with a varus displacement, resulting from adduction injuries, and transcervical fractures caused by a vertical shear.
Where does the blood supply of the femoral head come from?
Most of the blood supply of the femoral head comes from the medial femoral circumflex artery (2), which gives rise to three or four branches, ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for type 2 dm uncontrolled
- 2. icd 10 cm code for hard to swollen
- 3. icd-10 code for 22q11 deletion syndrome
- 4. icd 9 code for chromosome abnormality q22
- 5. icd 10 code for chem 20
- 6. icd-10-pcs code for suture removal abdominal wall
- 7. icd-10-cm code for acute and chronic cervicitis
- 8. icd code for bilateral foot pain
- 9. icd 10 code for unsp viral hep c wo coma
- 10. bmi icd 10 code for child with bmi 25