H90.12 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Conductive hearing loss, unilateral, left ear, with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side. It is found in the 2019 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2018 - Sep 30, 2019.
Which is best treatment for conductive hearing loss?
Oct 01, 2021 · H90.72 Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, left ear, with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side. H90.8 Mixed conductive and sensorineural …
What are the causes of conductive hearing loss?
Oct 01, 2021 · Conductive hearing loss, unilateral, left ear, with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side. H90.12 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a …
What is the treatment for conductive hearing loss?
Oct 01, 2021 · Conductive hearing loss, unilateral, left ear with restricted hearing on the contralateral side. 2017 - New Code 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. …
What is moderate conductive hearing loss?
Oct 01, 2021 · Conductive hearing loss, bilateral. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. H90.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate …
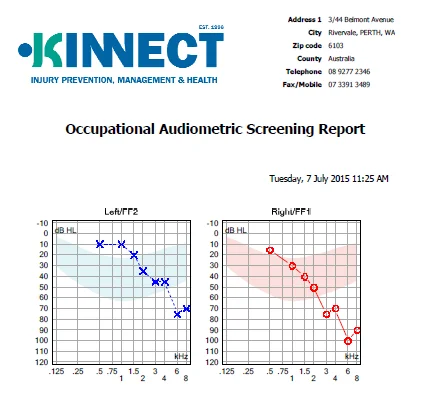
What is a conductive hearing loss?
What is the difference between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss?
What is diagnosis code H90 3?
What is diagnosis code H91 90?
Is otosclerosis conductive or sensorineural?
Is noise induced hearing loss conductive or sensorineural?
What is ICD-10 code for conductive hearing loss?
H90. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H90. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is CPT code V5261?
When do I code i11 9?
What is unspecified hearing loss?
What is the ICD-10 code for CAD?
What is presbycusis caused by?
What is nonsyndromic hearing loss?
Nonsyndromic hearing loss Nonsyndromic hearing loss is a partial or total loss of hearing that is not associated with other signs and symptoms. In contrast, syndromic hearing loss occurs with signs and symptoms affecting other parts of the body.Nonsyndromic hearing loss can be classified in several different ways.
What is occupational hearing loss?
Occupational hearing loss (Medical Encyclopedia) Otosclerosis (Medical Encyclopedia) Sensorineural deafness (Medical Encyclopedia) Nonsyndromic hearing loss Nonsyndromic hearing loss is a partial or total loss of hearing that is not associated with other signs and symptoms.
What is the medical term for hearing loss?
Hearing loss (Medical Encyclopedia) Occupational hearing loss (Medical Encyclopedia) Otosclerosis (Medical Encyclopedia) Sensorineural deafness (Medical Encyclopedia) Nonsyndromic hearing loss Nonsyndromic hearing loss is a partial or total loss of hearing that is not associated with other signs and symptoms.
What is DFNA1 hearing loss?
For example, DFNA1 was the first type of autosomal dominant nonsyndromic hearing loss to be identified.The characteristics of nonsyndromic hearing loss vary among the different types. Hearing loss can affect one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral).
Which part of the brain processes sound?
The inner ear processes sound and sends the information to the brain in the form of electrical nerve impulses. Less commonly, nonsyndromic hearing loss is described as conductive, meaning it results from changes in the middle ear.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code H90.12 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem conducting sound waves anywhere along the route through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). This type of hearing loss may occur in conjunction with sensorineural hearing loss (mixed hearing loss) or alone. Specialty: Otolaryngology.
What is the term for hearing loss in the middle ear?
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem conducting sound waves anywhere along the route through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). This type of hearing loss may occur in conjunction with sensorineural hearing loss (mixed hearing loss) or alone. Anatomy of the human ear.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for diabetes type 2
- 2. what is the icd 10 code for status post falls
- 3. icd 10 code for hep b titer
- 4. icd 9 code for health screening
- 5. what is the correct icd 10 code for old f05
- 6. icd 10 code for follow up er visit
- 7. icd 10 code for aclcoholism recovery
- 8. icd 10 code for left thalamus infarct
- 9. icd 10 code for joint
- 10. 2018 icd 10 code for chondrocalcinosis