What is the ICD 10 code for paralysis of the diaphragm?
Diaphragmatitis; Paralysis of diaphragm; Relaxation of diaphragm ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G72.3 [convert to ICD-9-CM]
What is the ICD 10 code for paralysis of the larynx?
Paralysis of vocal cords and larynx, unspecified. J38.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM J38.00 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the new ICD 10 for diaphragmatic hernia?
Diaphragmatic hernia. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K44 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K44 - other international versions of ICD-10 K44 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for phrenic nerve paralysis?
Phrenic nerve paralysis as birth trauma Phrenic nerve paralysis due to birth trauma ICD-10-CM P14.2 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 791 Prematurity with major problems
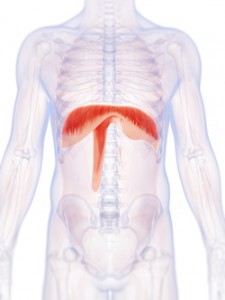
What is diaphragm paralysis?
Unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis is a condition in which either the right or left side of the diaphragm loses the ability to contract to allow proper inspiration. This can result from muscular issues in the diaphragm or loss of innervation from the phrenic nerve to the hemidiaphragm.
What is partial diaphragm paralysis?
This means that the diaphragm is partially functioning, and the part that is paralyzed will move higher into the chest cavity, taking up space meant for the lungs and interfering with breathing. Bilateral paralysis occurs when the entire diaphragm is paralyzed.
What is phrenic nerve paralysis?
Phrenic nerve paralysis is a common cause of elevation of one side of the diaphragm. It may be due to a variety of problems, including primary lung cancer, malignant mediastinal tumors, and surgery of the mediastinum. It may even be idiopathic.
What is the ICD 10 code for phrenic nerve palsy?
Phrenic nerve paralysis due to birth injury P14. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM P14. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is diaphragmatic Eventration?
Diaphragmatic eventration (DE) is the abnormal elevation of a portion or entire hemidiaphragm due to a lack of muscle or nerve function while maintaining its anatomical attachments. The abnormality can be congenital or acquired, thus presenting in both the pediatric and adult populations.
How is diaphragm paralysis diagnosis?
Computed tomography scanning of the chest, abdomen or both. Magnetic resonance imaging to determine if there is an underlying condition involving the spinal column or nerve roots. Ultrasound to see the activity of the diaphragm and to identify any unusual movement or lack of movement.
What is the difference between paresis and Plegia?
Paresis describes weakness or partial paralysis. In contrast, both paralysis and the suffix -plegia refer to no movement.
Is the phrenic nerve part of the vagus nerve?
The key difference between vagus and phrenic nerves is that vagus nerve is the tenth cranial nerve, which is an important parasympathetic cranial nerve, while phrenic nerve is a nerve of the thoracic region and is important for breathing.
Where does the left phrenic nerve pass through the diaphragm?
Left phrenic nerve Passes over the fibrous pericardium of the left ventricle and pierces the diaphragm close to the apex of the heart to reach the inferior (abdominal) surface of the diaphragm.
Is the phrenic nerve a cranial nerve?
The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve which originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration.
What is DX code G58 8?
Other specified mononeuropathiesICD-10 code G58. 8 for Other specified mononeuropathies is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
Where is the phrenic nerve?
The phrenic nerve must be identified in cervical and thoracic surgical dissection to preserve the neuromuscular pathways. Superior to the clavicle, the phrenic nerve can be located in the posterior triangle of the neck, superficial to the anterior scalene.
What is elevated left hemidiaphragm?
[1] Elevated hemidiaphragm occurs when one side of the diaphragm becomes weak from muscular disease or loss of innervation due to phrenic nerve injury. Patients may present with difficulty breathing, but more commonly elevated hemidiaphragm is found on imaging as an incidental finding, and patients are asymptomatic.
How can you tell the difference between diaphragmatic hernia and eventration?
Background: A hernia is due to a defect in the diaphragm. An eventration is due to a thinned diaphragm with no central muscle. Distinguishing right diaphragmatic hernia from eventration on chest radiographs can be challenging if no bowel loops are herniated above the diaphragm.
What is Bochdalek?
Bochdalek hernia is a developmental defect in the posterolateral diaphragm, allowing herniation of abdominal contents into the thorax causing mechanical compression of the developing lung parenchyma and sometimes causing lung hypoplasia.
What does eventration mean?
Medical Definition of eventration : protrusion of abdominal organs through the abdominal wall.
What can be done for a paralyzed diaphragm?
Prognosis for Diaphragmatic Paralysis Sometimes, patients recover without any medical intervention. The prognosis for bilateral paralysis also depends on the overall health of the patient but surgery may be the best option for patients who continue to have a poor quality of life.
Does paralyzed diaphragm repair itself?
Most patients with unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis are asymptomatic and do not require treatment. If the underlying causes are discovered, they can be treated. Even when the etiology is not known, many times paralysis resolves on its own, albeit slowly over a period of months to more than a year.
What does diaphragm paralysis feel like?
Diaphragm paralysis is the loss of control of one or both sides of the diaphragm. This causes a reduction in lung capacity. Patients with diaphragm paralysis may experience shortness of breath, headaches, blue lips and fingers, fatigue, insomnia, and overall breathing difficulty.
Can Covid cause diaphragm paralysis?
SARS-CoV-2 infection may be associated with diaphragm paralysis. Diabetes and raised body mass index are risk factors for diaphragm paralysis. Persistent dyspnoea in the absence of persistent lung parenchymal change following SARS-CoV-2 infection should prompt further investigation.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for peh
- 2. icd 10 code for dermatitis of glans
- 3. icd 10 code for left bicep tendenitis
- 4. what icd-10-cm code is reported for a routine exam when an abnormal finding is found?
- 5. icd 10 code for endometritis following delivery
- 6. icd 10 code for unspecified foreign body left index finger
- 7. icd 10 code for preterm pprom
- 8. icd 10 code for unstable housing
- 9. icd-10-cm code for deformity of the right pinna
- 10. icd 10 code for knee fracture with callus formation