What is the ICD 10 code for posterior tibial tendinitis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S85.162A [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified injury of posterior tibial artery, left leg, initial encounter. Unsp injury of posterior tibial artery, left leg, init; Injury of left posterior tibial artery; Left posterior tibial artery injury. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S85.162A.
Is left posterior tibial tendon dysfunction a synovial disorder?
Oct 01, 2021 · Posterior tibial tendinitis, left leg 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code M76.822 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M76.822 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for tendinitis of feet?
Oct 01, 2021 · M76.821 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M76.821 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M76.821 - other international versions of ICD-10 M76.821 may differ.
What is wrong with my posterior tibial tendon?
M76.822 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of posterior tibial tendinitis, left leg. The code M76.822 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code M76.822 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like bilateral tendinitis of feet, …
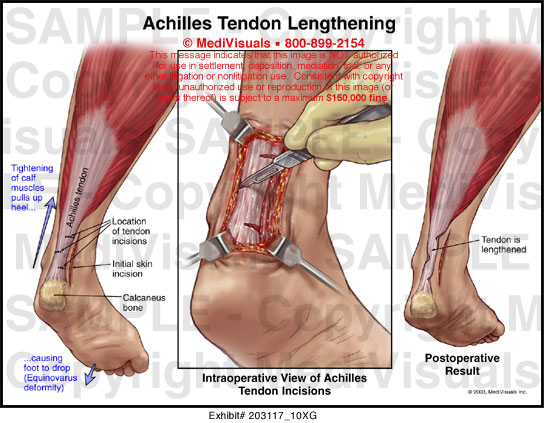
What is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction?
handout. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed or torn. As a result, the tendon may not be able to provide stability and support for the arch of the foot, resulting in flatfoot.
What is diagnosis code M76 822?
Posterior tibial tendinitis822: Posterior tibial tendinitis, left leg.
What is posterior tibial tendinitis left leg?
Posterior tibial tendonitis is a condition that results in pain on the inner side of the foot and ankle. It may cause instability while walking. Over time, the condition can lead to the arches becoming flattened, a condition called adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD). Diagnosis is made by physical examination.Oct 7, 2021
What is the CPT code for posterior tibial tendon repair?
Response: I would suggest CPT 28300-59 for the calcaneal osteotomy, and CPT 28200-59 for the repair of the posterior tibial tendon. The tendon transfer would be billed as CPT 27691-LT (transfer or transplant of single tendon [with muscle redirection or rerouting]; deep).
What is the ICD 10 code for pain in left ankle?
Pain in left ankle and joints of left foot M25. 572 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M25. 572 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for plantar fasciitis?
ICD-10 | Plantar fascial fibromatosis (M72. 2)
How do you diagnose posterior tibial tendonitis?
What tests can diagnose posterior tibial tendon dysfunction?X-rays: X-rays of the front, back and sides of both feet will provide detailed images of the bones. ... Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI can determine the health of your tendon and any surrounding muscles.More items...•Nov 4, 2021
Where is the posterior tibial tendon?
The posterior tibialis tendon is a strong cord of tissue. It is one of the most important tendons in your leg. It attaches the posterior tibialis muscle on the back of your calf to the bones on the inside of your foot. It helps support your foot and hold up its arch when you are walking.
What causes posterior tibial tendon?
There are several possible causes of an inflamed posterior tibial tendon, such as overuse, lack of healthy blood supply to the area, and poor biomechanics. Some are more prone to developing this condition, such as women, particularly those over the age of 40, and those with anatomical issues, such as flat feet.Mar 6, 2020
Is posterior tibial tendon a flexor or extensor?
Because the tibialis posterior (TP) originates from the posterior compartment of the lower leg, the tibialis posterior is also a secondary plantar flexor of the foot along with the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles.Aug 17, 2021
What is an FDL transfer?
A Flexor Digitorum Longus Tendon transfer is indicated for patients with dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, where the tendon has become stretched beyond its functional length or has ruptured.Sep 16, 2014
What is posterior tibial tendon debridement?
A 12- to 14-centimeter incision is made down the back of your lower leg, along the length of your posterior tibial tendon. The sheath covering your tendon is opened up. Any rough, inflamed, or damaged tissue is cut away (debrided), which smoothes the tendon surface and exposes the healthy tissue underneath.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for huntington's chorea
- 2. icd 10 code for lesion of lleft lower eyelid
- 3. icd 10 code for heart block unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for crush injury right thumb
- 5. icd 10 code for early food introduction
- 6. icd 10 code for hcg
- 7. icd 10 code for exophoria
- 8. icd 10 code for heart disease with hypertension
- 9. icd 10 code for chronic hypertension in obstetric
- 10. icd 10 code for anal ca