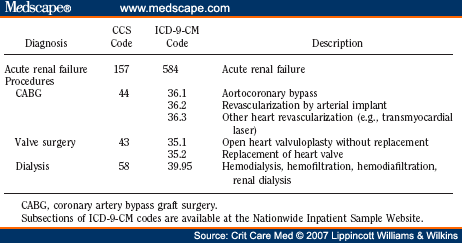
What causes renal infarction?
The causes of renal infarction include 1,2,4:
- thromboembolism most common from heart valve, ventricular or atrial thrombus, aorta
- aortic dissection
- renal artery dissection fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) renal trauma renal artery occlusion is considered a grade V renal injury
- iatrogenic (e.g. ...
- vasculitis 4
- malignant hypertension 4
What is treatment for renal infarction?
there is a potential renal targeted treatment for kidney injury caused by cisplatin, a widely used anti-cancer drug. One in four patients treated with cisplatin develop chronic kidney disease.
Are myocardial infarctions considered acute for 0 10 weeks?
myocardial infarction specified as acute or with a stated duration of 4 weeks (28 days) or less from onset A disorder characterized by gross necrosis of the myocardium; this is due to an interruption of blood supply to the area. Coagulation of blood in any of the coronary vessels.
What is an incidental retroaortic left renal vein?
Retroaortic left renal vein (RLRV) is one of the congenital anomalies of the left renal vein that posteriorly travels to the aorta and is compressed between the aorta and vertebral body. Clinical Mimickers of Renal Stones: Incidental Findings on Renal Stone Computed Tomography Protocol
What is left renal infarct?
Renal infarction results from interruption of the normal blood supply to part of, or to the whole kidney. The main imaging differential diagnosis includes pyelonephritis and renal tumors.
What is kidney infarction?
Discussion. Acute renal infarction involves occlusion of the arterial supply to the kidney and most commonly occurs as the result of thromboembolism.
What is the ICD-10 code for left renal lesion?
Neoplasm of unspecified behavior of left kidney D49. 512 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D49. 512 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is renal infarction an acute condition?
Acute renal infarction (ARI) refers to ischaemic damage of the renal parenchyma caused by the sudden interruption of blood flow. It is a rare cause of acute kidney failure, with an incidence rate in published series ranging from 0.007% to 1.4%.
What causes infarction of the kidneys?
The two major causes of renal infarction are thromboemboli and in situ thrombosis. Thromboemboli usually originate from a thrombus in the heart or aorta, and in situ thrombosis is usually due to an underlying hypercoagulable condition or injury to or dissection of a renal artery.
What does a renal infarct look like?
Renal Infarction In such situations, CEUS can demonstrate absence of enhancement of the affected renal tissue (Fig. 34.4). Acute infarcts typically are seen as wedge-shaped, nonenhancing areas within an otherwise normal-appearing kidney. Renal shape is preserved.
What is diagnosis code N28 89?
89 Other specified disorders of kidney and ureter.
What is the ICD 10 code for renal injury?
0: Injury of kidney.
What is the ICD 10 code for renal disease?
ICD-10 code N18. 9 for Chronic kidney disease, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
How is renal infarct diagnosed?
The diagnosis, once suspected, can be confirmed by contrast enhanced CT, isotope perfusion scanning or renal arteriography; conventional ultrasonography is insufficiently sensitive. On CT scanning in particular, a kidney infarct can be mistaken for malignant disease5 (as in case 2).
How do you treat a renal infarct?
The optimal treatment for renal infarction due to thromboemboli, in situ thrombosis, or renal artery dissection is uncertain because there are no comparative studies. Reported approaches include anticoagulation, endovascular therapy (thrombolysis/thrombectomy with or without angioplasty), and open surgery.
Does renal infarction cause hematuria?
Acute occlusion of the renal artery causes clear clinical symptoms (Halpern, 1967). Generally, a small renal infarction gives no symptoms. If symptoms exist, they are rather slight--flank pain, albuminuria, fever, and microscopic hematuria.
What is a Lacunar Infarction?
Lacunar infarctions result from occlusion in the deep penetrating single small perforating artery in the deep cerebral white matter, basal ganglia, thalamus and brain stem. These small arteries supplies blood to the subcortical areas (deep structures) of the brain. Most of these infarctions are silent.
Prevention of Lacunar Infarction
References wikipedia.org/wiki/Lacunar_stroke healthline.com/health/lacunar-stroke-symptoms drugs.com/health-guide/lacunar-stroke.html radiopaedia.org/articles/lacunar-infarct jnnp.bmj.com/content/76/5/617 neuropathology-web.org/chapter2/chapter2bCerebralinfarcts.html ICD-10-CM Alphabetic Index and Tabular AHA Coding Clinic for ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS, Fourth Quarter 2018, Page: 16.
Happy Coding!
The information contained in this coding advice is valid at the time of posting. Viewers are encouraged to research subsequent official guidance in the areas associated with the topic as they can change rapidly.
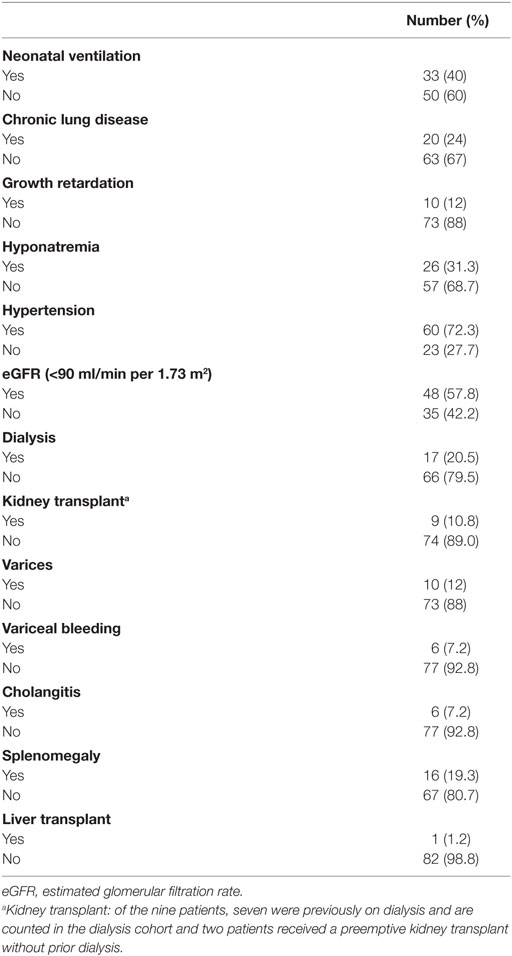
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for family history neck cancer
- 2. icd 10 code for dementia syndrome
- 3. icd 10 code for intentional ingestion of bleach
- 4. icd 10 code for restlessness
- 5. icd 10 code for joint pain left shoulder
- 6. icd 10 code for right upper lobe lung cancer
- 7. icd 10 code for cryptic tonisilitis
- 8. icd 10 code for lung disease, interstitial
- 9. icd -10 code for cytomegalovirus
- 10. what is the correct icd 10 code for a40.3