What is the ICD 10 code for swollen mass and lump?
R22.33 ICD-10-CM Code for Localized swelling, mass and lump, left upper limb R22.32 ICD-10 code R22.32 for Localized swelling, mass and lump, left upper limb is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified.
What is the ICD 10 code for left upper limb swelling?
ICD-10 code R22.32 for Localized swelling, mass and lump, left upper limb is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified. Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now
How do you remove a scrotal mass?
scrotal mass, which was smaller. Lidocaine was used over the mass and a knife was used to make a horizontal incision over the mass. Pickups with under the scrotal skin, a little bit of bleeding was encountered. I did and submit that in whole.
How was the mass removed from the scrotum of the dog?
Lidocaine was used over the mass and a knife was used to make a horizontal incision over the mass. Pickups with under the scrotal skin, a little bit of bleeding was encountered.
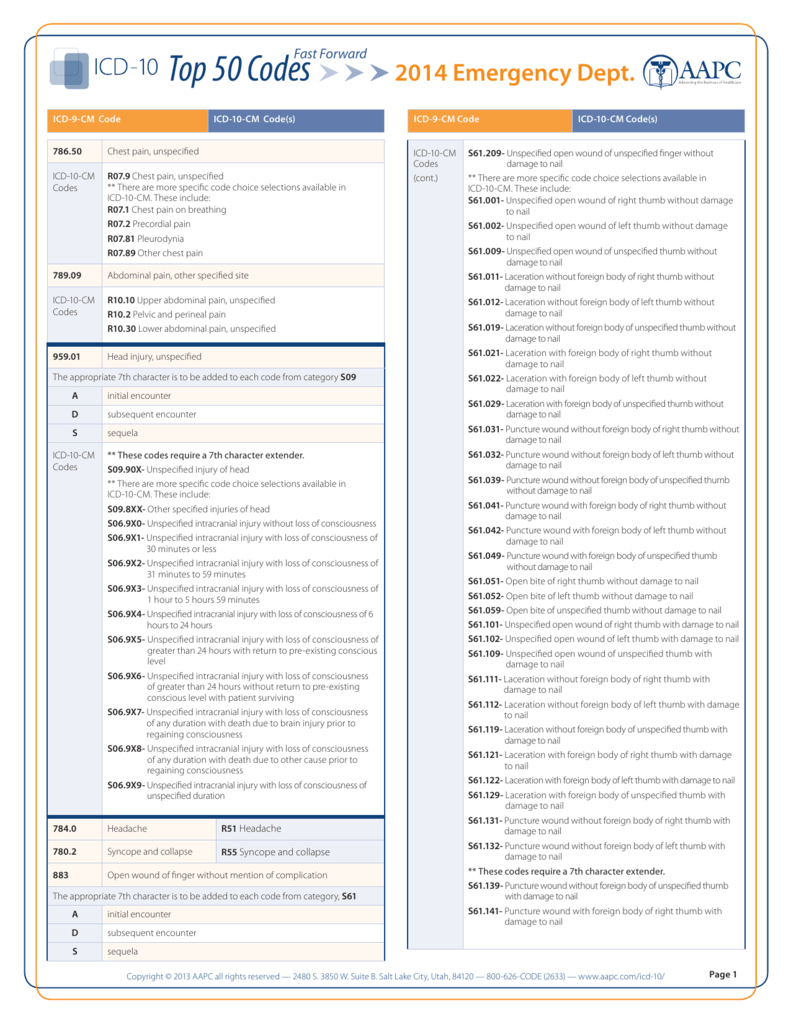
What is the ICD-10 code for scrotal mass?
Benign neoplasm of unspecified testis The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D29. 20 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D29. 20 - other international versions of ICD-10 D29.
What is the ICD-10 code for Scrotal lesion?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D29. 4: Benign neoplasm of scrotum.
What is the ICD-10 code for Scrotal swelling?
Inflammatory disorders of scrotum The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N49. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is scrotal mass?
A scrotal mass is a lump or bulge that can be felt in the scrotum. A hydrocele is a collection of fluid inside the area of the scrotum, surrounding the testicle. Hydroceles are common in newborn infants and normally resolve after a few months after birth.
What diagnosis is N50 89?
N50. 89 - Other specified disorders of the male genital organs | ICD-10-CM.
What is hydrocele testis?
Hydrocele is the type of scrotal swelling that occurs when fluid collects in the thin sheath that surrounds the testicle. A hydrocele can develop before birth. Normally, the testicles descend from the developing baby's abdominal cavity into the scrotum.
What is the ICD 10 code for left epididymitis?
ICD-10 code: N45. 9 Orchitis, epididymitis and epididymo-orchitis without abscess.
What is the ICD 10 code for epididymal cyst?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cyst of epididymis N50. 3.
What is the most common scrotal mass?
TESTES. Testicular tumors are the most common malignant tumors encountered in men 25 to 35 years of age. Histologic classification of these tumors is complex, and includes seminomas, choriocarcinoma, and a variety of teratomas, or germ cell tumors.
Where is the scrotal sac located?
The scrotum is a unique anatomical feature of humans and certain other species of land-dwelling mammals. It is continuous with the skin of the lower abdomen and is located directly behind the penis and in front of the anus. The scrotal wall is a thin layer of skin lined with smooth muscle tissue (dartos fascia).
What causes scrotal mass?
Traumatic injury, such as a direct blow to the testicles, is the most likely cause. Varicocele. This is the enlargement of the veins within the scrotum that carry oxygen-depleted blood from each testicle and the epididymis.
How do you treat a scrotal mass?
What Is the Treatment for a Scrotal Mass?Antibiotics and other medications to treat infections.Surgery to drain or remove a scrotal mass.Testicle removal through surgery, in the case of testicular cancer.
How do you get rid of scrotal cysts?
Surgery. If the cyst is causing problems, a doctor will likely suggest surgical removal. This will usually involve the doctor removing the cyst through a small incision on the scrotum. A doctor will often perform this outpatient procedure using local or general anesthesia.
What causes scrotal infection?
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the most common causes of epididymitis in young, sexually active men. Other infections. Bacteria from a urinary tract or prostate infection might spread from the infected site to the epididymis. Also, viral infections, such as the mumps virus, can result in epididymitis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for gilberts disease
- 2. 2016 icd 10 code for 573.3
- 3. icd-10-cm code for no eating due to cocaine dependency
- 4. icd 10 code for previous abnormal pap smear
- 5. icd 10 code for liver
- 6. icd 10 code for allergy to flexeril
- 7. icd 10 dx code for analcious
- 8. icd 10 code for hip click in newborn
- 9. icd 10 code for hepatic adenoma
- 10. what is the icd-10 code for 786.50