What is referred pain in left shoulder?
Nontraumatic tear of flexor tendon of bilateral shoulders; Nontraumatic tear of flexor tendon of left shoulder; Spontaneous rupture of flexor tendon of left shoulder; Spontaneous rupture of flexor tendons of left shoulder. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M66.312. Spontaneous rupture of flexor tendons, left shoulder.
Is the left shoulder the contralateral shoulder?
The ICD-10-CM code S43.432A might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anterior to posterior tear of superior glenoid labrum of left shoulder or glenoid labrum tear. S43.432A is an initial encounter code, includes a 7th character and should be used while the patient is receiving active treatment for a condition like superior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder. According …
Could I have a labral tear in my shoulder?
· What ICD10 code do you use for Posterior Inferior Labral Tear? This was the diagnosis on an MRI result. J jkunsag Guest Messages 7 Best answers 0 Nov 22, 2016 #2 I …
What is the amount for shoulder labral tear?
· ICD-10 Codes S43.431 SLAP lesion of right shoulder S43.432 SLAP lesion of left shoulder S43.439 SLAP lesion of unspecified shoulder Add seventh character for episode of …
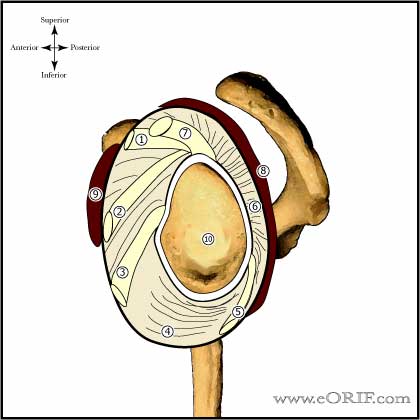
What is the ICD 10 code for left posterior labral tear?
S43.432ASuperior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder, initial encounter. S43. 432A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S43.
What is the ICD 10 code for posterior labral tear?
Icd 10 code for labral tear shoulder. M75. 00 is a specific ICD-10-CM diagnosis code M75. 00.
What is a posterior labral tear?
Posterior Labral Tear (Lesion) This is a condition of the shoulder which usually affects younger people. It is most commonly caused by a fall onto the arm or a direct blow e.g. a rugby tackle. It is also seen in people who do a lot of throwing. The glenoid has a rim of tissue (the labrum) around its edge.
What is the ICD 10 code for right shoulder posterior labral tear?
ICD-10-CM Code for Superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder, initial encounter S43. 431A.
What is the ICD-10 code for nontraumatic tear of the labrum of the shoulder?
829.
What is diagnosis code m7542?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M75. 42: Impingement syndrome of left shoulder.
Where is the posterior labrum located?
The head of your upper arm bone fits into a rounded socket in your shoulder blade. This socket is called the glenoid. Surrounding the outside edge of the glenoid is a rim of strong, fibrous tissue called the labrum. The labrum helps to deepen the socket and stabilize the shoulder joint.
What is a labral tear in the shoulder?
The labrum is a piece of fibrocartilage (rubbery tissue) attached to the rim of the shoulder socket that helps keep the ball of the joint in place. When this cartilage is torn, it is called a labral tear. Labral tears may result from injury, or sometimes as part of the aging process.
Is a rotator cuff tear the same as a labrum tear?
A classic overuse injury, swimmer's shoulder occurs when repetitive overhead motions (like swimming, throwing, etc.) cause inflammation in the rotator cuff, compressed tendons and reduced blood flow. Labral tears, on the other hand, can result from both the wear and tear of repetitive motion or from traumatic injury.
What is ICD-10 code for rotator cuff tear?
A traumatic rotator cuff diagnosis is defined as an injury of the rotator cuff ligaments, muscles, and tendons and maps to rotator cuff sprain/strain and/or tear/rupture. ICD-10 codes S46. 011A (right shoulder) and S46. 012A (left shoulder) are for strain/tear/rupture OR S43.
What is the ICD-10 code for left shoulder synovitis?
ICD-10 | Other synovitis and tenosynovitis, left shoulder (M65. 812)
What is the ICD-10 code for right shoulder synovitis?
ICD-10 | Other synovitis and tenosynovitis, right shoulder (M65. 811)
What is the ICd 10 code for glenoid labrum?
S43.432A is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of superior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder, initial encounter. The code S43.432A is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code S43.432A might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anterior to posterior tear of superior glenoid labrum of left shoulder or glenoid labrum tear.#N#S43.432A is an initial encounter code, includes a 7th character and should be used while the patient is receiving active treatment for a condition like superior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder. According to ICD-10-CM Guidelines an "initial encounter" doesn't necessarily means "initial visit". The 7th character should be used when the patient is undergoing active treatment regardless if new or different providers saw the patient over the course of a treatment. The appropriate 7th character codes should also be used even if the patient delayed seeking treatment for a condition.
How to diagnose shoulder pain?
Health care providers diagnose shoulder problems by using your medical history, a physical exam, and imaging tests. Often, the first treatment for shoulder problems is RICE. This stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Other treatments include exercise and medicines to reduce pain and swelling.
Why are the shoulders unstable?
Your shoulders are the most movable joints in your body. They can also be unstable because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the shoulder socket that holds it. To remain in a stable or normal position, the shoulder must be anchored by muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
What is the effect of the labrum on the shoulder?
If the labrum or capsule is injured, such as in the Bankart lesion, this suction is lost, and this decreases the stability of the shoulder.
What is posterior shoulder instability?
Posterior shoulder instability may result in injury to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament as well as the posterior labrum, or a reverse Bankart lesion. Tears can extend to involve multiple regions of the labrum and have other associated injuries.
What is the most common injury to the labrum?
Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum. The most studied injury to the labrum is the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear. Anterior dislocations of the shoulder can be associated with a disruption of the anteroinferior labrum and anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament, also known as a Bankart lesion. Posterior shoulder instability may result in injury to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament as well as the posterior labrum, or a reverse Bankart lesion. Tears can extend to involve multiple regions of the labrum and have other associated injuries. The SLAP tear and Bankart lesion are the most common and for that reason are the focus of this discussion.
What is the labrum?
The labrum also serves as an attachment point for the long head of the biceps tendon, the glenohumeral ligaments, and the long head of the triceps tendon, forming a periarticular system of fibers that gives the shoulder joint much needed stability [ 4 ]. The vascular supply to the labrum is from the posterior humeral circumflex artery, ...
What is a type I tear?
Type I: degenerative tear of the undersurface of the superior labrum with the biceps anchor intact . Type II: tear of the superior labrum as well as of the biceps anchor. Type III: bucket-handle tear of the superior labrum with biceps anchor intact.
How to tell if you have anterior instability?
Symptoms of anterior instability are usually obvious as the patient states that there has been a dislocation and continues to complain of pain and instability in that shoulder. Sometimes there is not a history of overt dislocation, but instead the patient has multiple episodes of instability without a complete dislocation. The patient will complain of pain and feeling of impending dislocation with the arm in abduction and external rotation. Important historical variables include the patient’s age at first dislocation, need for formal reduction, number of recurrent instability episodes, voluntary instability, and anticipated future sports activities.
How many types of slap tears are there?
Snyder [ 8] classified SLAP tears into four types, which was further modified by Morgan and Maffet. Most physicians think that the four-class system ( Fig. 15.2) is sufficient and that the additional classifications could be placed within these basic types, so it is the preferred classification.
How to diagnose shoulder pain?
Health care providers diagnose shoulder problems by using your medical history, a physical exam, and imaging tests. Often, the first treatment for shoulder problems is RICE. This stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Other treatments include exercise and medicines to reduce pain and swelling.
Why are the shoulders unstable?
Your shoulders are the most movable joints in your body. They can also be unstable because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the shoulder socket that holds it. To remain in a stable or normal position, the shoulder must be anchored by muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
What is posterior labral tear?
Posterior Labral Tear. A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex , and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder.
What are the symptoms of a posterior shoulder?
vague, nonspecific posterior shoulder pain is the most common symptoms. worsens with provocative activities that apply a posteriorly directed force to the shoulder. ex: pushing heavy doors, bench press, push-ups. clicking or popping in the shoulder with range of motion . sense of instability.
Which branch of the axillary nerve is at risk during arthroscopic stabilization?
posterior branch of the axillary nerve is at risk during arthroscopic stabilization. travels within 1 mm of the inferior shoulder capsule and glenoid rim. at risk during suture passage at the posterior inferior glenoid. Overtightening of posterior capsule. can lead to anterior subluxation or coracoid impingement.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for antiplatelet or antithrombotic long-term use
- 2. what code may be used for fracture of an ankle in icd
- 3. icd 10 code for closed fracture of left thumb
- 4. icd-10-cm code for abdominal aorta atherosclerosis
- 5. icd 9 code for finger nail infected
- 6. icd 10 code for pain left leg
- 7. icd 10 code for spider bite on left forearm
- 8. icd 10 code for superficial injury upper right thigh
- 9. what is the icd 10 code for c difficile infection recurrent c
- 10. icd 10 code for right metatarsal fracture