What is the ICD 10 code for total rotator cuff tear?
Complete rotator cuff tear or rupture of left shoulder, not specified as traumatic. M75.122 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10-CM for left shoulder injury?
Unspecified rotator cuff tear or rupture of left shoulder, not specified as traumatic. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M75.102 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M75.102 - other international versions of ICD-10 M75.102 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for left supraspinatus tear?
Left supraspinatus tendon tear. Traumatic left rotator cuff tear. ICD-10-CM S46.012A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 562 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh with mcc.
What is the ICD 10 code for left rotator cuff tendinitis?
Tendinitis of left rotator cuff ICD-10-CM M75.102 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 557 Tendonitis, myositis and bursitis with mcc 558 Tendonitis, myositis and bursitis without mcc
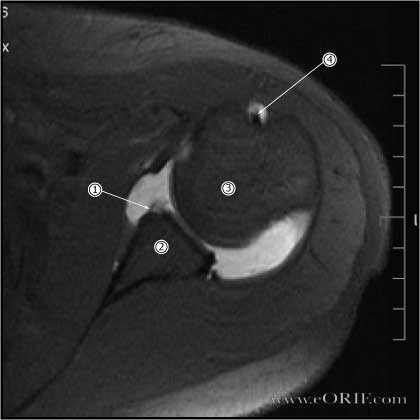
What is the ICD 10 code for subscapularis tear?
Rotator cuff muscle/tendon tear (infraspinatus, supraspinatus, subscapularis, and minor teres) – S46. 011A (right) or S46.
What is the ICD 10 code for supraspinatus tear?
Rotator cuff tear or rupture, not specified as traumatic The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M75. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M75.
What is the ICD 10 code for rotator cuff shoulder tear?
121 for Complete rotator cuff tear or rupture of right shoulder, not specified as traumatic is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Soft tissue disorders .
Is a supraspinatus tendon tear the same as a rotator cuff tear?
Definition/Description. A supraspinatus tear is a tear or rupture of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle. The supraspinatus is part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Most of the time it is accompanied with another rotator cuff muscle tear.
Is the subscapularis part of the rotator cuff?
The rotator cuff includes the following muscles[1][2][3]: Subscapularis. Infraspinatus. Teres minor.
Is the supraspinatus part of the rotator cuff?
Your rotator cuff is made up of muscles and tendons that keep the ball (head) of your upper-arm bone (humerus) in your shoulder socket. It also helps you raise and rotate your arm. Each one of these muscles is part of the rotator cuff and plays an important role: Supraspinatus.
What is rotator cuff tear in shoulder?
A rotator cuff tear is a rip in the group of four muscles and tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint and let you lift and rotate your arms (your rotator cuff). It's also called a complete tear or a full-thickness tear.
What is the supraspinatus tendon?
The supraspinatus tendon is located on the back of your shoulder and helps your arm to move throughout its full range of motion – and helps with power and strength.
What is unspecified rotator cuff tear?
101 - Unspecified rotator cuff tear or rupture of right shoulder, not specified as traumatic. M75. 101 - Unspecified rotator cuff tear or rupture of right shoulder, not specified as traumatic is a topic covered in the ICD-10-CM.
What is subscapularis tendon?
The subscapularis muscle is one of the four muscles that arise from the shoulder blade and attach to the humeral head. The tendons of these four muscles make up the rotator cuff. The subscapularis muscle comes off the front of the shoulder blade and helps you reach behind your back.
Is a full thickness rotator cuff tear the same as a complete tear?
Partial tears: Also called incomplete tears, the damage experienced by the tendon does not sever it completely. Complete tears: More commonly referred to as a full-thickness tear, this injury entirely separates the tendon from the bone.
What is a Type 1 rotator cuff tear?
Partial thickness tears. 0 Normal. 1 Minimal superficial bursal or synovial irritation or slight capsular fraying over a small area. 2 Fraying and failure of some rotator cuff fibres in addition to synovial bursal or capsular injury.
Where is the supraspinatus rotator cuff tear?
supraspinatus rotator cuff tear extending anterior right up to the exposed biceps tendon.
Why can't you use a rotator cuff capsule?
Just talked to some people in my office. They agreed/confirmed. The rotator cuff capsule one wouldn't be used because the rotator cuff is muscle/tendon. Muscles and tendons are STRAINS for acute. Ligaments and joints are SPRAINS. Yay! I hope this helped! So for your OP Report, I would use the S45.01_ _
What tissue covers the rotator cuff footprint?
taken posterior with the same repair. The rotator cuff tissue completely covered the rotator cuff footprint
What wire is used to trephinate rotator cuff?
rotator cuff footprint was trephinated with 1 mm K-wire with good extrusion of marrow component.
Where is the rotator cuff footprint?
dissection and dissection with an elevator. Next, the rotator cuff footprint right up to the biceps tendon
Is the anterior aspect of the shoulder debrided?
anterior aspect of the shoulder was debrided as was the rotator cuff tear to better visualize the rotator cuff. footprint. Also with the biceps pulled into the shoulder, there was some degenerative tearing of the. biceps, though 80-90% of thickness of the biceps still intact. This was gently debrided only of unstable.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for amputation left foot
- 2. icd 10 dx code for mandibular aeutinusty defect
- 3. icd 10 code for spinal fusion surgery
- 4. icd-10 cm code for fetal malnutrition
- 5. icd 10 cm code for nodular pulmonary tuberculosis
- 6. icd code for rhonchi
- 7. icd 10 code for nephrotic range proteinuria
- 8. icd 10 code for calculus of gallbladder without cholecystitis
- 9. icd-10 code for xenograft heart valve
- 10. icd 9 code for disoriented