What causes arthritis in the thumb joint?
What causes thumb arthritis?
- Osteoarthritis ("wear-and-tear")
- Injury to the thumb joints
- Rheumatoid arthritis
What is the treatment for thumb joint arthritis?
Treatments for Arthritis of the Thumb
- Symptoms. Pain when opening jars, turning keys, etc. ...
- Nonsurgical Thumb Arthritis Treatments. Anti-inflammatory medications: A simple anti-inflammatory medication is often a good first step in the treatment process.
- Surgical Options for Thumb Arthritis. ...
- Other Causes of Thumb Pain. ...
What thumb brace is best for thumb arthritis?
Some of the best thumb braces for arthritis
- Bracoo Thumb Stabilizer. This breathable, moisture-wicking neoprene thumb brace can fit both the right and left hand. ...
- BraceAbility Thumb Splint. ...
- BraceUP Thumb Brace. ...
- Vive Gel Thumb Support. ...
- FLA Orthopedics 3D Adjustable Thumb Brace. ...
- Copper Compression Long Thumb Brace. ...
- U.S. ...
What are the symptoms of arthritis in the thumb?
Other symptoms may include the following:
- Swelling and tenderness at the base of the thumb
- An ache after prolonged use of the thumb
- Loss of strength when gripping or pinching with your thumb
- Limited motion
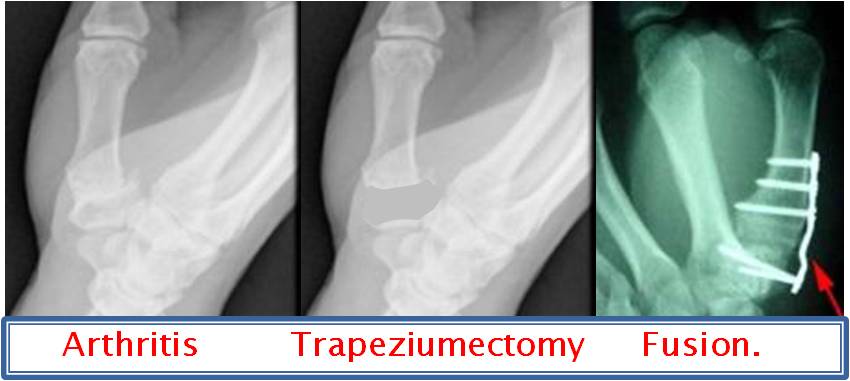
What is the basilar joint?
The basal joint is where the metacarpal bone of the thumb meets the trapezium bone in the wrist. This condition can be very disabling because use of the thumb is necessary for nearly every manual, from writing to opening a jar to buttoning a shirt.
What is the CMC joint of the thumb?
The thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint, a biconcave-convex saddle joint, consists of the articulation between the first metacarpal of the thumb and the trapezium carpal bone. Other significant articulations of the trapezial bone are the scaphoid and trapezoid carpal bones and the second metacarpal bone.
What is basal joint arthritis?
Basal joint arthritis is a very common type of arthritis that affects the part of the thumb that's right next to your wrist. It occurs when cartilage wears away from the ends of the bones that form the joint at the base of your thumb. It causes pain, especially when you try to pinch or grab things.
Where is the CMC joint located?
The CMC joints are located between the distal carpal row and the metacarpal bones (Fig. 13.54). Each metacarpal and its associated phalanges make up a ray of the hand.
Where is the basal joint of the thumb?
The thumb basal joint, also known as the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint, is a specialized saddle-shaped joint that is formed by a small wrist bone (trapezium) and the first of the three bones in the thumb (metacarpal).
What is the joint at the base of the thumb called?
Thumb arthritis is common with aging and occurs when cartilage wears away from the ends of the bones that form the joint at the base of your thumb — also known as the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint.
What is basilar thumb arthritis?
Basal thumb arthritis is a type of osteoarthritis affecting the base of the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint. This joint consists of the articulation of a wrist bone called the trapezium with the first metacarpal bone, which forms the base of the thumb.
How is basal thumb arthritis diagnosed?
For the physical examination, your doctor will hold the basal joint while rocking your thumb back and forth, Dr. Luo says. If that causes pain or a grinding sound, it means the bones are rubbing directly against each other and likely have thumb arthritis. An X-ray can confirm the diagnosis.
What type of joint is the thumb?
Interphalangeal Joint (IP) The thumb digit has only two phalanges (bones) so it only has one joint. The thumb interphalangeal (IP) joint is similar to the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint in the fingers.
Is the CMC joint part of the wrist?
The carpometacarpal joints (CMC) are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the fivemetacarpal bones.
Is the thumb joint a ball and socket?
Found in the thumb or first carpometacarpal joint, for example, these joints permit the same range of motion as condoloid joints. A spherical head on one bone fits into a round socket of a second bone to form a ball and socket joint, as in the shoulder and hip joints.
What is a CMC in anatomy?
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are articulations between the carpal bones (carpo-) and metacarpal bones (-metacarpal) of the hand.
Why is CMC joint so painful?
Why it is so painful is because the hand is highly innervated and occupies a large amount of sensory motor space in the brain. The CMC joint is a saddle joint and is the second most mobile joint in the human body. Often simple tasks involving the thumb create pain.
What can you do for CMC joint pain?
The following are nonsurgical treatment options:Activity modification.Massage.Over the counter NSAID's (ibuprofen or naproxen)Anti-inflammatory herbs such as turmeric or ginger.Topical pain relief creams/gels.Occupational/physical therapy.Corticosteroid injections.Prescription anti-inflammatory medications.
How is CMC arthritis treated?
As we get older, that CMC joint in particular often wears out, causing pain at the base of the thumb.” Treatment for thumb arthritis starts conservatively with the patient wearing a soft brace. If that doesn't work, injections at the base of the palm may work. And if there still isn't relief, surgery is an option.
What is CMC joint degenerative changes?
Carpometacarpal osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition of the hand that causes pain, stiffness and weakness. It is the second most common site of degenerative disease in the hand after arthritis of the distal interphalangeal joints. 1.
When will the ICD-10 Z96.691 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z96.691 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a Z77-Z99?
Z77-Z99 Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status
When will the ICD-10 Z96.693 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z96.693 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a Z77-Z99?
Z77-Z99 Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status
What is the ICd 10 code for a sprain of the thumb?
Unspecified sprain of left thumb, initial encounter 1 S63.602A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S63.602A became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S63.602A - other international versions of ICD-10 S63.602A may differ.
When will the ICD-10-CM S63.602A be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S63.602A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hx kidney stones
- 2. icd-10-cm code assigned for residual condition
- 3. icd 10 code for chronic acl tear
- 4. icd-10-cm code for threatened shock due to hypotension
- 5. icd 10 code for k58.0
- 6. icd 10 code for impacted fracture of the shoulder lymphedema
- 7. how to icd 10 code for positive nipt test
- 8. icd 9 code for prophylactic mastectomy
- 9. icd 10 code for interstitial
- 10. 2017 icd 10 code for instrument miscount