What are the symptoms of left ventricular dysfunction?
the type of left ventricular failure as systolic, diastolic, or combined, if known ( I50.2- I50.43) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H69.82 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Other specified disorders of Eustachian tube, left ear. Dysfunction of left eustachian tube; Left eustachian tube dysfunction. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H69.82.
How to treat left ventricular hypertrophy naturally?
Oct 01, 2021 · Left ventricular failure, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 - Revised Code 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I50.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How serious is left ventricular hypertrophy?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Left ventricular failure, unspecified. Acute left sided congestive heart failure (chf); Acute left-sided congestive heart failure; Chronic left sided congestive heart failure (chf); Chronic left-sided congestive heart failure; Congestive heart failure (chf) left ventricle; Congestive heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction; …
What causes systolic dysfunction?
Oct 01, 2021 · This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 I50.2 may differ. Applicable To Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction [HFrEF] Systolic left ventricular heart failure Code Also end stage heart failure, if applicable ( …
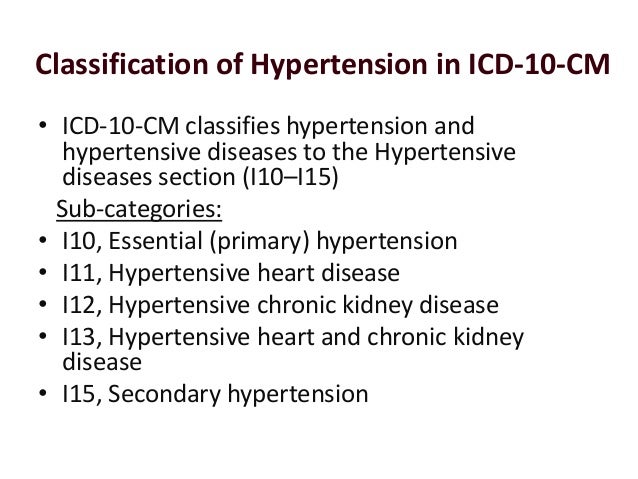
What is left ventricular systolic dysfunction?
Left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) is a common and serious complication of myocardial infarction (MI) that leads to greatly increased risks of sudden death and of heart failure. Effective and cost effective treatment is available for such patients that can reduce both morbidity and mortality.
What is the ICD-10 code for LV systolic dysfunction?
Left ventricular failure, unspecified I50. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is left ventricular dysfunction the same as systolic dysfunction?
Systolic dysfunction is clinically associated with left ventricular failure in the presence of marked cardiomegaly, while diastolic dysfunction is accompanied by pulmonary congestion together with a normal or only slightly enlarged ventricle.
How do you code systolic dysfunction?
When the provider has linked either diastolic or systolic dysfunction with acute or chronic heart failure, it should be coded as 'acute/chronic diastolic or systolic heart failure. ' If there is no provider documentation linking the two conditions, assign code I50. 9, Heart failure, unspecified.”Mar 27, 2018
What is left ventricular diastolic dysfunction?
Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (DD) is defined as the inability of the ventricle to fill to a normal end-diastolic volume, both during exercise as well as at rest, while left atrial pressure does not exceed 12 mm Hg.Nov 24, 2009
What is the ICD-10 code for decreased left ventricular function?
ICD-10 code I50. 1 for Left ventricular failure, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
Is left ventricular systolic function the same as ejection fraction?
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic heart dysfunction?
Systolic heart failure occurs when the left side of the heart becomes too weak to squeeze normal amounts of blood out of the heart when it pumps. Diastolic heart failure occurs when the left side of the heart is too stiff to relax and fill normally with blood.Jun 4, 2021
What is the difference between the systolic vs diastolic heart?
Systolic heart failure occurs during a heartbeat and relates to the pumping function, whereas diastolic heart failure occurs between heartbeats and is due to an issue with the relaxing function.Mar 15, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for valvular heart disease?
ICD-10-CM I35. 9 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 306 Cardiac congenital and valvular disorders with mcc. 307 Cardiac congenital and valvular disorders without mcc.
What is the ICD-10 code for left ventricular hypertrophy?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cardiomegaly I51. 7.
What is the ICD-10 code for mitral regurgitation?
ICD-10-CM Code for Nonrheumatic mitral (valve) insufficiency I34. 0.
What is the ICD-10 code for heart failure?
I50.22 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure. The code I50.22 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code I50.22 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like chronic systolic dysfunction of left ventricle, chronic systolic heart failure, decreased cardiac ejection fraction, decreased cardiac function, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction , left ventricular cardiac dysfunction, etc.#N#The code is commonly used in cardiology medical specialties to specify clinical concepts such as heart failure.
What does it mean when your heart is not pumping enough blood?
Information for Patients. Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Heart failure does not mean that your heart has stopped or is about to stop working. It means that your heart is not able to pump blood the way it should.
What does it mean when your heart is not working?
Heart failure does not mean that your heart has stopped or is about to stop working. It means that your heart is not able to pump blood the way it should. It can affect one or both sides of the heart. Common causes of heart failure are coronary artery disease, high blood pressure and diabetes.
How to diagnose heart failure?
Your doctor will diagnose heart failure by doing a physical exam and heart tests. Treatment includes treating the underlying cause of your heart failure, medicines, and heart transplantation if other treatments fail. NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Brain natriutetic peptide test (Medical Encyclopedia)
What causes a person to have a heart failure?
Blood and fluid to back up into the lungs. The buildup of fluid in the feet, ankles and legs - called edema. Tiredness and shortness of breath. Common causes of heart failure are coronary artery disease, high blood pressure and diabetes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for incesible loss of urinating
- 2. icd 10 cm code for obstructive jaundice
- 3. icd 10 code for aftercare following chest tube removal
- 4. what is icd-9 code for
- 5. icd 10 code for l08.82
- 6. icd 10 code for type 1 diabetes in pregnancy
- 7. icd-10 code for nutrition
- 8. icd 10 code for insomnioa
- 9. icd 10 code for playing baseball
- 10. icd 10 code for popliteal artery aneurysm