What is the ICD 10 code for left wrist injury?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S66.912A. Strain of unspecified muscle, fascia and tendon at wrist and hand level, left hand, initial encounter. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S60.212A [convert to ICD-9-CM] Contusion of left wrist, initial encounter. Left wrist contusion.
What is the ICD 10 code for wrist fracture?
Oct 01, 2021 · Other specified sprain of left wrist, initial encounter. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. S63.592A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S63.592A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for dislocation of the wrist?
Oct 01, 2021 · S63.591A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S63.591A became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S63.591A - other international versions of ICD-10 S63.591A may differ.
What is the ICD-10-CM for triangular fibrocartilage tear?
Oct 01, 2021 · S69.92XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Unsp injury of left wrist, hand and finger (s), init encntr. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S69.92XA became effective on October 1, 2021.
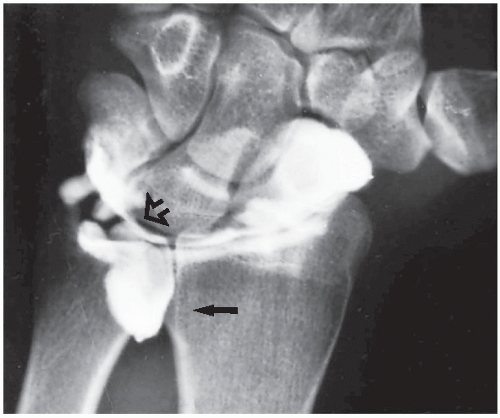
What is the ICD-10 for TFCC tear?
Generally occurs from fall on an outstretched arm with the wrist extended and the forearm pronated.
What is TFCC tear?
A TFCC tear is an injury to the triangular fibrocartilage complex, soft tissues in the wrist that cushion and support the carpal bones and help stabilize the forearm. Injuries range from mild to severe, but all can disable the wrist.
Where is TFCC located?
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a network of ligaments, tendons, and cartilage that sits between the ulna and radius bones on the small finger side of the wrist. The TFCC stabilizes and cushions the wrist, particularly when a person rotates their hand or grasps something with it.
How is a TFCC tear repair?
Surgery to treat a TFCC tear often involves minimally invasive arthroscopy. During this procedure, your doctor will repair the damaged part of your TFCC through a few small incisions around your wrist. In some cases, you may need traditional open surgery.
What is the TFCC in wrist?
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) connects the bones in your forearm with bones in your wrist. The structure — made up of ligaments, tendons and cartilage — helps support and stabilize your wrist. You can tear your TFCC if you fall on, twist or fracture your wrist.Oct 26, 2021
What is the TFCC made up of?
The TFCC consists of an articular disc, meniscus homologue, ulnocarpal ligament, dorsal & volar radioulnar ligament and extensor carpi ulnaris sheath.
What is the function of the TFCC?
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a load-bearing structure between the lunate, triquetrum, and ulnar head. The function of the TFCC is to act as a stabilizer for the ulnar aspect of the wrist.Aug 25, 2021
How common are TFCC tears?
It's not common in people under 30 years old, but it affects about half of those over 70 years old. If you have preexisting conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout, you're at high risk of a TFCC tear.Jun 21, 2021
How do you tape a wrist for a TFCC tear?
0:001:24Taping the TFCC (close up version) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAttach it to the base of that tab and that will help you pull across with a little bit more force.MoreAttach it to the base of that tab and that will help you pull across with a little bit more force. Only pull tightly. Through one side of the wrist we don't want to create too much compression.
Does a TFCC tear require surgery?
Recovery usually takes a few weeks for TFCC tears that don't require surgery. However, it may take anywhere from a few weeks to several months before you regain full use of your wrist if you do need surgery. Doing physical therapy and avoiding activities that strain your wrist can help speed up your recovery time.Feb 19, 2021
What section of TFCC can be repaired?
After curettage of the scar tissue in the fovea, the deep palmar and dorsal limbs of the TFCC are sutured back to the fovea using a suture anchor technique. Results Foveal TFCC tears could be repaired via a palmar surgical approach without violating the floor of the ECU tendon sheath and the superficial dorsal limb.
Can a TFCC tear heal without surgery?
The quick answer to this question is yes, a TFCC tear can heal without surgery. It's important to understand that the area toward the outside of the wrist will heal better without surgery, and it may take some time for your pain to improve.
What is the ICd 10 code for wrist degenerative tear?
M24.139 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other articular cartilage disorders, unspecified wrist. The code M24.139 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code M24.139 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like articular cartilage disorder of wrist or degenerative tear of triangular fibrocartilage complex of wrist.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like M24.139 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
What is the tube that runs through your wrist called?
Your wrist is made up of eight small bones known as carpals. They support a tube that runs through your wrist. That tube, called the carpal tunnel , has tendons and a nerve inside. It is covered by a ligament, which holds it in place. Wrist pain is common.
Why is cartilage important?
Injured, inflamed, or damaged cartilage can cause symptoms such as pain and limited movement. It can also lead to joint damage and deformity. Causes of cartilage problems include. Tears and injuries, such as sports injuries.
What is cartilage in the body?
Information for Patients. Cartilage is the tough but flexible tissue that covers the ends of your bones at a joint. It also gives shape and support to other parts of your body, such as your ears, nose and windpipe. Healthy cartilage helps you move by allowing your bones to glide over each other.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code M24.139 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What causes wrist pain?
Some wrist fractures are a result of osteoporosis. Other common causes of pain are. Sprains and strains. Tendinitis. Arthritis. Gout and pseudogout.
Can repetitive motion cause wrist pain?
Repetitive motion can damage your wrist. Everyday activities like typing, racquet sports or sewing can cause pain, or even carpal tunnel syndrome. Wrist pain with bruising and swelling can be a sign of injury. The signs of a possible fracture include misshapen joints and inability to move your wrist.
What causes a TFCC tear?
Damage to the TFCC is often caused by: A fall on an outstretched hand; A drill-bit injury where the wrist rotates rather than the bit; A distraction force onto the volar forearm or wrist; or. A sequela of a distal radius fracture. Excessive load on the ulnocarpal joint can cause a TFCC tear.
What is the function of TFCC?
A primary function of the TFCC is to facilitate forearm rotation with a flexible connection between the distal radius and ulna, stabilizing the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) and supporting the ulnocarpal structures. The TFCC provides a continuous gliding surface across the distal radius/ulna for flexion, extension, supination, pronation, and radial/ulnar deviation. Damage to the TFCC is often caused by:
What are some examples of unbundling?
It’s important to understand payer guidelines and National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) bundling rules. Common examples of unbundling and miscoding errors include: 1 Reporting a ganglion cyst excision (25111 Excision of ganglion, wrist (dorsal or volar); primary) in addition to a synovectomy of the wrist (25118 Synovectomy, extensor tendon sheath, wrist, single compartment ): 25111 is bundled into the 25118. 2 Reporting a partial synovectomy (29844 Arthroscopy, wrist, surgical; synovectomy, partial) in addition to an arthroscopic TFCC repair (29846 Arthroscopy, wrist, surgical; excision and/or repair of triangular fibrocartilage and/or joint debridement) when the synovectomy is included in the repair. 3 Reporting 25215 Carpectomy; all bones of proximal row for a carpectomy of all proximal row bones when not all three bones (scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum) are excised. 4 Reporting a trapezium excision (25210 Carpectomy; 1 bone) in addition to a carpometacarpal joint arthroplasty (25447 Arthroplasty, interposition, intercarpal or carpometacarpal joints ). 5 Separately reporting bone grafts (20900 Bone graft, any donor area; minor or small (eg, dowel or button) or 20902 Bone graft, any donor area; major or large) with procedures that include these grafts. 6 Billing for initial application of a short-arm cast (29075 Application, cast; elbow to finger (short arm)) or short-arm splint (29125 Application of short arm splint (forearm to hand); static) with a surgical procedure on the wrist. 7 Coding fracture of carpal bone (S62.1- Fracture of other and unspecified carpal bone (s)) when the diagnosis is a distal radius fracture (S52.5- Fracture of lower end of radius ).
How many bones are in the wrist?
Match Wrist Parts to Diagnosis Codes. The wrist, or carpus, contains eight carpal bones. There are three bones in the proximal row (scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum) and five bones in the distal row (trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate, and pisiform). The trapezium is also known as the greater multangular, the trapezoid as ...
Who is Ken Camilleis?
Ken Camilleis, CPC, CPC-I, COSC, CMRS, CCS-P, is an educational consultant and PMCC instructor with Superbill Consulting Services, LLC. He is also a professional coder for Signature Healthcare, a health system covering much of southeastern Massachusetts. Camilleis’ primary coding specialty is orthopedics. Camilleis is a member of the Cape Coders local chapter in Hyannis, Mass.
What is a scapholunate advanced collapse?
A wrist defect often requiring surgical intervention is scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC.) SLAC is a condition of progressive instability that causes advanced radiocarpal and midcarpal osteoarthritis. SLAC describes a specific pattern of progressive subluxation with loss of articulation between the scaphoid and lunate bones. SLAC usually results from trauma to the wrist, but may be caused by a degenerative process such as calcinosis or as a sequela of a prior injury. SLAC is estimated to account for more than half of all non-traumatic wrist osteoarthritis cases.#N#Signs and symptoms of SLAC include:
What is the name of the inflammation of the first dorsal extensor compartment?
De Quervain’s disease (radial styloid tenosynovitis) is an inflammation of the first dorsal extensor compartment; this is entrapment tendinitis causing tendon thickening, which leads to restricted motion and a grinding sensation with tendon movement (crepitus).

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for lower gi bleed
- 2. icd 10 code for lymphadenopathy abdominal
- 3. icd 10 code for left knee peripheral tear of lateral meniscu
- 4. icd 10 code for left temporal bone fracture
- 5. icd 10 code for clogged fistula
- 6. icd 10 code for status post left knee meniscus repair
- 7. icd 10 code for laceration left brow and forehead
- 8. icd 10 code for intraparenchymal hemorrhage of brain
- 9. icd 10 code for erythematous scaling
- 10. icd 9 code for internal carotid artery stenosis