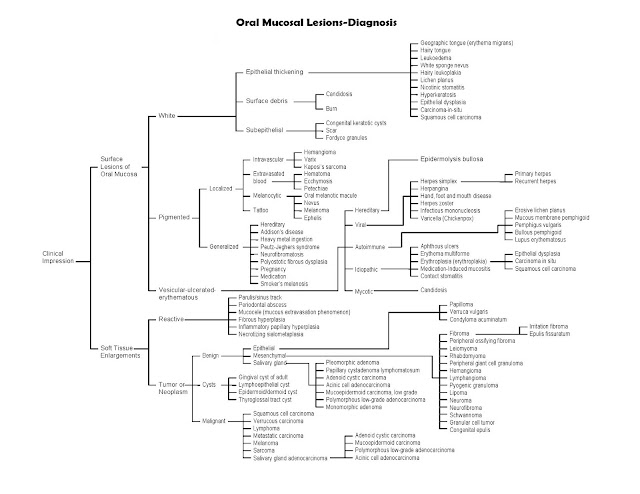
What is a lesion of the mucosa?
What is lesion in oral cavity?
What is oral mucosa?
What is the most common type of oral lesion?
WHO classification oral premalignant lesions?
What causes oral mucosal lesions?
Multiple etiologic factors contribute to these group of lesions, including microbial infections, local trauma or irritation, systemic diseases, and consumption of tobacco, betel quid, and alcohol [20].
What are the three types of oral mucosa?
What is the histology of oral mucosa?
What is oral mucosa made up of?
Are most oral lesions benign?
What is leukoplakia of oral mucosa?
What is the ICD 10 code for tongue lesion?
K13. 70 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K13. 70 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for oral mucosa?
K13.70 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of unspecified lesions of oral mucosa. The code K13.70 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code K13.70 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like disease of mouth, disorder of oral mucous membrane, drug-induced oral condition, finding by inspection , fixed drug reaction , fixed drug reaction affecting oral mucous membranes, etc.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like K13.70 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
What causes white spots on the cheeks?
Thrush - a yeast infection that causes white patches in your mouth. Leukoplakia - white patches of excess cell growth on the cheeks, gums or tongue, common in smokers. Dry mouth - a lack of enough saliva, caused by some medicines and certain diseases. Treatment for mouth disorders varies, depending on the problem.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code K13.70 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K13.70 - Unspecified lesions of oral mucosa'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K13.70. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code K13.70 and a single ICD9 code, 528.9 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for oral mucosa?
K13.7 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Other and unspecified lesions of oral mucosa. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
What does "excludes2" mean?
An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together.
What is a 3 character code?
A 3-character code is to be used only if it is not further subdivided. A code is invalid if it has not been coded to the full number of characters required for that code, including the 7 th character, if applicable.
What does NEC not elsewhere mean?
NEC Not elsewhere classifiable#N#This abbreviation in the Tabular List represents “other specified”. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the “other specified” code.
What is a list of terms?
List of terms is included under some codes. These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used. The terms may be synonyms of the code title, or, in the case of “other specified” codes, the terms are a list of the various conditions assigned to that code. The inclusion terms are not necessarily exhaustive.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What does "type 1 excludes" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D10.39. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. benign odontogenic neoplasms (.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right shoulder contusion
- 2. icd 10 code for muscle dystonia
- 3. icd 10 code for tbi w symptoms
- 4. icd 10 code for hot flashes and night sweats
- 5. 2015 icd 9 code for atheromatous changes
- 6. icd 10 code for swelling right index finger
- 7. icd 10 code for ferritin
- 8. icd 10 code for irritable bowel syndrome with constipation
- 9. icd 10 code for left heel stage 1
- 10. icd-10 code for elevated transaminases