What is the diagnosis code for leukocytosis?
Leukocytosis; Leukocytosis (increase white blood cells in blood); Elevated leukocytes, unspecified; Leukocytosis, unspecified ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D72.829 Elevated white blood cell count, unspecified
What causes high leukocytes?
Oct 01, 2021 · D72.829 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D72.829 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D72.829 - other international versions of ICD-10 D72.829 may differ. Applicable To.
Why does my patient have leukocytosis?
288.60 - Leukocytosis, unspecified. 288.60 - Leukocytosis, unspecified is a topic covered in the ICD-10-CM. To view the entire topic, please log in or purchase a subscription. ICD-10-CM 2022 Coding Guide™ from Unbound Medicine. Search online 72,000+ ICD-10 codes by number, disease, injury, drug, or keyword.
What is leukocytosis and what causes it?
Apr 07, 2020 · ICD-10 Code: F03. 90 – Unspecified Dementia without Behavioral Disturbance. Keeping this in consideration, what is leukocytosis unspecified type? Leukocytosis is white cells (the leukocyte count) above the normal range in the blood.
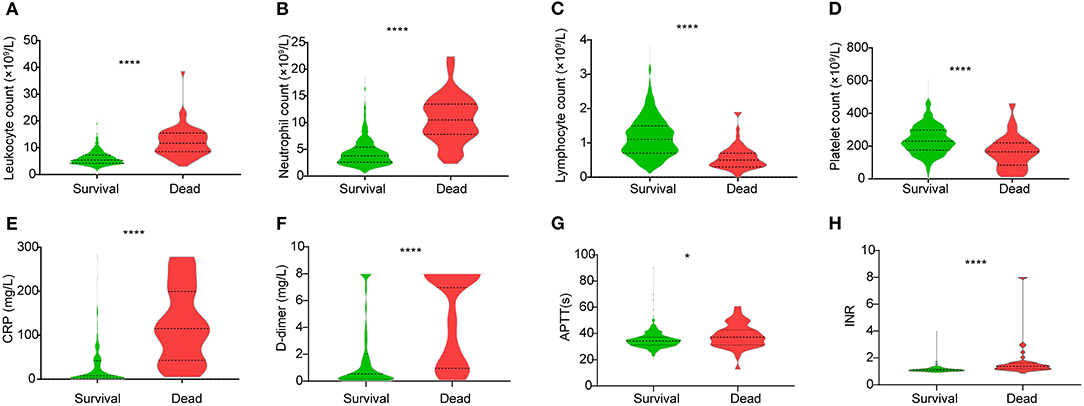
What is the ICD 9 code for leukocytosis?
ICD-9 code 288.60 for Leukocytosis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -DISEASES OF THE BLOOD AND BLOOD-FORMING ORGANS (280-289).
How is leukocytosis diagnosis?
Most of the time, doctors use a complete blood count (CBC) to check for leukocytosis. A CBC can be part of a routine physical, or your doctor might use it to help diagnose a specific illness. Another test, called a white blood cell differential or "diff," is sometimes done at the same time.Jun 1, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for low white blood cells?
ICD-10 | Decreased white blood cell count (D72. 81)
What leukocytosis mean?
Leukocytosis means you have a high white blood cell count. This means you have more white blood cells than normal. Leukocytosis is a normal immune response and isn't always a cause for concern. Most of the time, it means that your body is fighting off infection or inflammation.Jan 19, 2022
What is leukocytosis unspecified type?
Leukocytosis is condition characterized by increased levels of leukocytes in the blood. Although this typically occurs when you're sick, it can also be caused by several other factors, such as stress.
What is the difference between leukocytosis and leukopenia?
Leukocytosis is an elevation in the absolute WBC count (>10,000 cells/μL). Leukopenia is a reduction in the WBC count (<3500 cells/μL).
What is the medical term for low white blood cell count?
Low White Blood Cell Counts (Neutropenia)Feb 1, 2020
What is diagnosis code D72 819?
Decreased white blood cell count, unspecified2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D72. 819: Decreased white blood cell count, unspecified.
Why is my white blood cell count low?
A low white blood cell count usually is caused by: Viral infections that temporarily disrupt the work of bone marrow. Certain disorders present at birth (congenital) that involve diminished bone marrow function. Cancer or other diseases that damage bone marrow.Jun 15, 2005
What are 5 types of leukocytes?
Types of leukocytes are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells).
What are the causes of various forms of leukocytosis?
Causes. Leukocytosis is very common in acutely ill patients. It occurs in response to a wide variety of conditions, including viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection, cancer, hemorrhage, and exposure to certain medications or chemicals including steroids.
What is the neutrophil count?
A measure of the number of neutrophils in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell. They help the body fight infection. An absolute neutrophil count may be used to check for infection, inflammation, leukemia, and other conditions.
How old do you have to be to get pneumonia?
People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age , or already have health problems. If you have pneumonia, you may have difficulty breathing and have a cough and a fever. A physical exam and history can help determine if you have pneumonia.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, fevers, chills, chest pain, headache, sweating, and weakness. Inflammation of any part, segment or lobe, of the lung parenchyma. Inflammation of the lungs with consolidation and exudation. Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection.
What causes pneumonia in the lung?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection. Three common causes are bacteria, viruses and fungi. You can also get pneumonia by accidentally inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems.
What is lung parenchyma?
An acute, acute and chronic, or chronic inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma, due to infections (viruses, fungi, mycoplasma, or bacteria), treatment (e.g. Radiation), or exposure (inhalation) to chemicals.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for ge reflux
- 2. icd 9 code for acne vulgaris
- 3. icd 10 code for recurrent small bowl obstruction
- 4. icd 10 code for medial subluxation of left second toe mtp
- 5. icd 10 code for colon dilated
- 6. icd-10 code for sepsis due to uti
- 7. icd 10 code for exposure to blood bourne illness
- 8. icd 10 cm code for eyelash stuck in right eye
- 9. icd 9 code for inhaler teaching
- 10. icd 10 code for premenstrual dysphoric disorder