What is the ICD-10 code for abdominal lipoma?
D17.5ICD-10-CM Code for Benign lipomatous neoplasm of intra-abdominal organs D17. 5.
What is the ICD-10 code for duodenal lipoma?
D13.2Benign neoplasm of duodenum The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D13. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
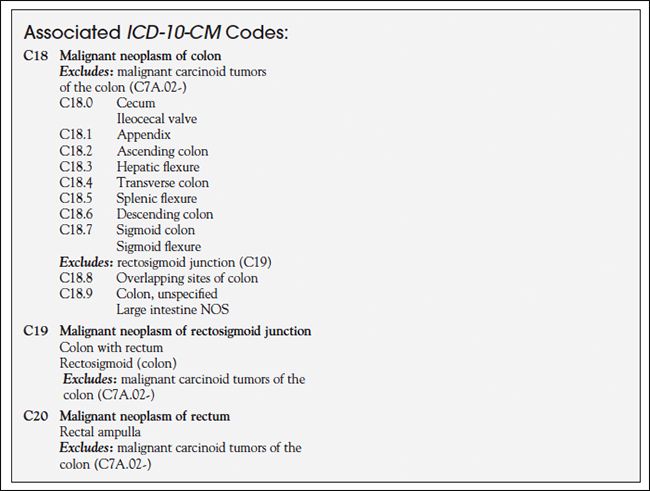
What is the ICD-10 code for sigmoid colon?
ICD-10 Code for Benign neoplasm of sigmoid colon- D12. 5- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for left flank Lipoma?
D17.1ICD-10 code: D17. 1 Benign lipomatous neoplasm of skin and subcutaneous tissue of trunk.
Is lipoma a neoplasm?
A lipoma is a non cancerous (benign) lump that forms due to an overgrowth of fat cells. You can get a lipoma anywhere on the body where you have fat cells. Lipomas are not cancer. Cancerous tumours of the fat cells are called liposarcomas.
What does Lipomatosis mean?
Medical Definition of lipomatosis : any of several abnormal conditions marked by local or generalized deposits of fat or replacement of other tissue by fat specifically : the presence of multiple lipomas.
What is an ascending colon polyp?
A colon polyp is a small clump of cells that forms on the lining of the colon. Most colon polyps are harmless. But over time, some colon polyps can develop into colon cancer, which may be fatal when found in its later stages. Anyone can develop colon polyps.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for ascending colon polyp?
K63. 5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K63.
What is malignant neoplasm of ascending colon?
The term "malignant neoplasm" means that a tumor is cancerous. A doctor may suspect this diagnosis based on observation — such as during a colonoscopy — but usually a biopsy of the lesion or mass is needed to tell for sure whether it is malignant or benign (not cancerous).
What is abdominal wall lipoma?
A lipoma is a slow-growing, fatty lump that's most often situated between your skin and the underlying muscle layer. A lipoma, which feels doughy and usually isn't tender, moves readily with slight finger pressure. Lipomas are usually detected in middle age. Some people have more than one lipoma.
What is the ICD 10 code for intramuscular lipoma?
2 for Benign lipomatous neoplasm of skin and subcutaneous tissue of limb is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Neoplasms .
What is benign lipomatous neoplasm of intra abdominal organs?
Lipoma is a benign soft tissue tumor, composed of mature fat, represents by far the most common mesenchymal neoplasm occurring throughout the whole body, but they rarely originate in the intestinal mesentery.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is lipomatous tumor?
A benign, usually painless, well-circumscribed lipomatous tumor composed of adipose tissue. Skin biopsy, diagnostic of pss: skin biopsy revealing increased compact collagen in the reticular dermis, thinning of the epidermis, loss of rete pegs, atrophy of dermal appendages, and hyalinization and fibrosis of arterioles.
What is a benign neoplasm?
A benign neoplasm composed of adipose tissue. A benign tumor composed of adipose (fatty) tissue. The most common representative of this category is the lipoma. A benign tumor composed of fat cells (adipocytes). It can be surrounded by a thin layer of connective tissue (encapsulated), or diffuse without the capsule.
What Is Lipoma?
The first thing that you should know is simple, lipoma is a skin disorder. This is an issue that comes from underneath the dermal layers. It’s a collection of fatty tissue that comes up, and forms a small lump. That lump has been medically noted as being a tumor.
The Medical Codes of ICD-9 and ICD-10 For Lipoma
Focusing on the billable elements, you’re going to find that the most common solutions include D17.9 and specific coding that comes from it, is listed as ICD-10-CM D17.9, and it has been effective as of October, 2017.
Lipoma Removal
It’s imperative to understand that lipoma could very well be removed for various needs. There are several options that you’ll want to take into consideration, but the removal process is linked to non-invasive surgical solutions. Lipoma removal comes within the confines of removing the fatty tissue, and that’s it.
What is the ICd 10 code for lipomatous neoplasm?
Benign lipomatous neoplasm of skin and subcutaneous tissue of trunk 1 D17.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Benign lipomatous neoplasm of skin, subcu of trunk 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM D17.1 became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D17.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 D17.1 may differ.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the code for inflammatory colon polyps?
Codes for inflammatory colon polyps, found in category K51, include a description of complications: K51.40 Inflammatory polyps of colon without complications. K51.411 Inflammatory polyps of colon with rectal bleeding. K51.412 Inflammatory polyps of colon with intestinal obstruction.
Is colon cancer benign?
Print Post. Colorectal cancer typically develops from colon polyps, which are abnormal growths of tissue (neoplasms). Most polyps are benign, but may become cancerous. When selecting an ICD-10 diagnosis code for polyp (s) of the colon, you will need to know the precise location of the polyp (s) and the type of polyp (e.g., benign, inflammatory, ...
What is a gastrointestinal lipoma?
Gastrointestinal lipomas are a rare benign non-epithelial neoplasms derived from mature adipocytes. The colon is the commonest organ involved in the entire digestive tract and has an incidence rate ~4.4% in autopsy series. Most of the colonic lipomas are asymptomatic and incidentally detected. Lipomas need to be distinguished from true neoplasia, because in most cases they do not need to be resected unless when they cause a clear symptom or they are large in size. Surgical rather than endoscopic resection is preferred for lipomas > 2 cm to avoid complications such as bleeding and perforation. We report a case of a 56-year-old female, a known case of locally advanced breast cancer and positive adenomatous polyposis coli mutation, who was found to have 4 cm ascending colon lipoma by imaging and confirmed by colonoscopy and histopathology.
How do you know if you have a colonic lipoma?
Most of the colonic lipomas cause no significant symptoms and the size of the lipoma is the main predictor of symptoms development . Lipomas > 2 cm in diameter are likely to be symptomatic. The most common symptoms are intermittent crampy abdominal pain, altered bowel habits and chronic blood loss.
Where are lipomas found?
Several studies have shown that the most common site of colonic lipomas is the ascending colon near the ileocecal valve (45%). Colonic lipomas tend to be solitary but in 10–20% can be multiple.
When were colonic lipomas first detected?
They are often incidentally detected during imaging, colonoscopy, surgery or autopsy. The first colonic lipoma was reported by Bauer in 1757 [ 1 ]. After the adenomatous polyp, colonic lipomas are the second most common benign tumors of the colon. The incidence of colonic lipomas ranges from 0.2 to 4.4% [ 2 ].
Is lipoma a hyperechoic lesion?
On EUS, lipoma appears as hyperechoic lesions with regular borders in the three layers. EUS is also useful in the determination of a possible extension into the muscularis propria before attempting endoscopic resection. For management of colonic lipomas, a follow-up is sufficient for a small and asymptomatic lesion.
Is colonic lipoma a pedunculated mass?
Endoscopically, colonic lipoma is recognized easily as a well-delineated, soft, round or ovoid, yellowish sessile or pedunculated mass. Although the mucosa overlying the lipoma is usually intact, however, in rare cases ulcerations and erythema can be seen on the mucosa, which may lead to impression of malignancy.
Can a colonic lipoma be resectioned?
However, symptomatic lipoma or asymptomatic but >2 cm in size should be considered for resection. Treatment options are various and include endoscopic and surgical resections.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for deliriun tremors due to withdrawal from cocaine dependence
- 2. icd 10 cm code for shakiness,
- 3. icd-10 code for hypertension benign with hert failue
- 4. icd 10 code for history of self mutilation
- 5. icd 9 code for lumbar laminectomy surgery
- 6. icd 10 code for bruising of toe
- 7. icd 10 code for atherosclerotic coronary vascular disease
- 8. icd 10 cm code for status asthmaticus
- 9. icd 10 code for enlarged lymph nodes cervical
- 10. icd 10 code for family history of factor v leiden deficiency