What are the signs of low potassium level?
Oct 01, 2021 · Hypokalemia. E87.6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.6 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E87.6 - other international versions of ICD-10 E87.6 may differ.
What to do for low potassium levels?
Disturbances of potassium balance of newborn. Neonatal potassium balance disturbance. ... Acute low back pain; Acute low back pain for less than 3 months; ... ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H54.2X21. Low vision right eye category 2, low vision left eye category 1. 2018 ...
What is considered low potassium levels?
Chronic hypokalemia; Hypokalemia (low potassium level); Hypokalemia chronic; Hypokalemic alkalosis due to diarrhea; Verner morrison syndrome; Potassium [K] deficiency. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E87.6. ... ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S68.419. Complete traumatic amputation of unspecified hand at wrist level.
What is the treatment for low potassium level?
500 results found. Showing 26-50: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E87.6 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Hypokalemia. Chronic hypokalemia; Hypokalemia (low potassium level); Hypokalemia chronic; Hypokalemic alkalosis due to diarrhea; Verner morrison syndrome; Potassium [K] deficiency. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E87.6.
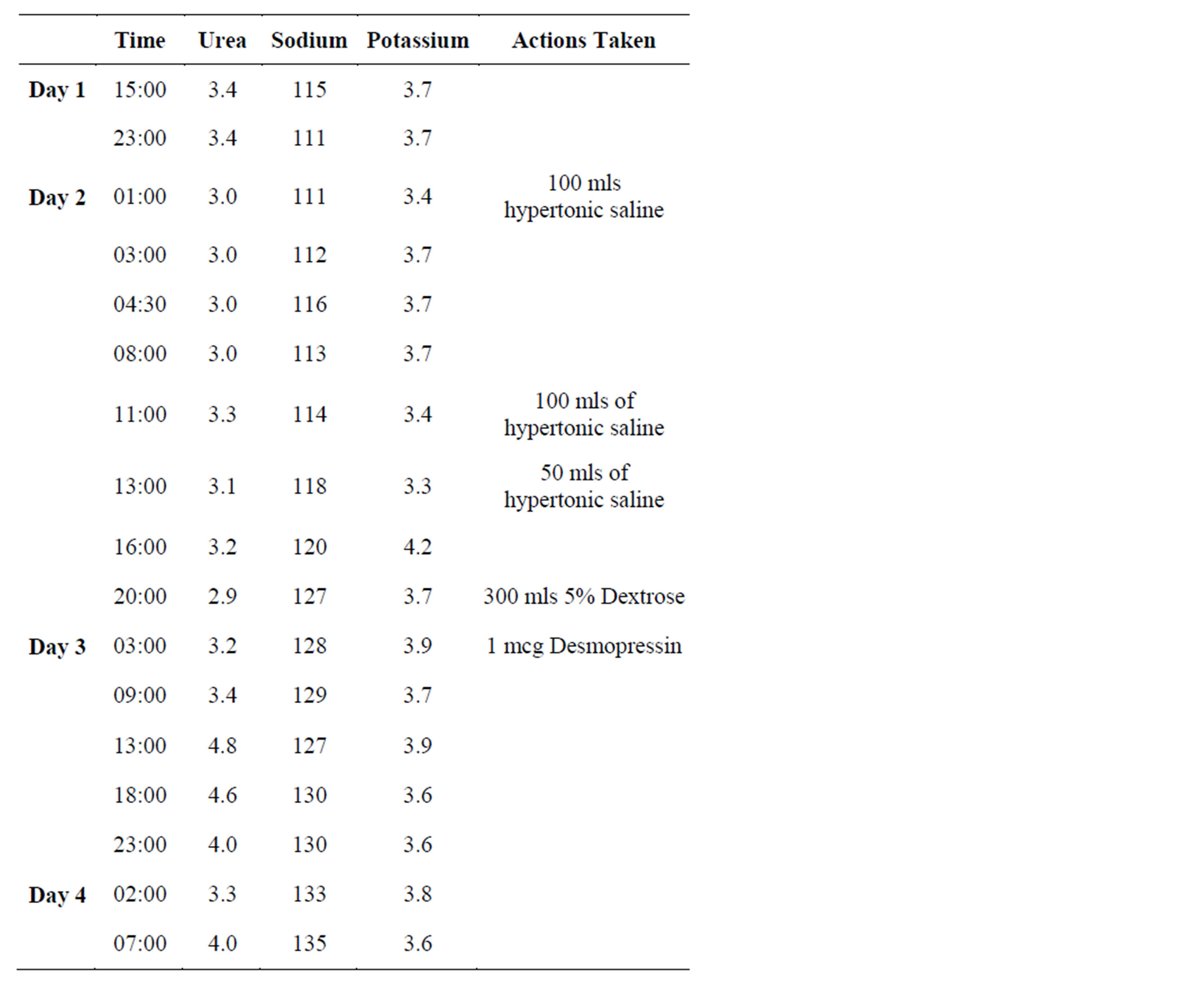
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal potassium level?
What is the ICD-10 code for potassium?
What does hypokalemia mean?
How do you code hypokalemia?
What is the ICD-10 code for anemia?
What is the correct ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia?
What are the seven signs of low potassium?
What causes low potassium in elderly?
What causes critically low potassium?
Drinking too much alcohol. Drugs, including diuretics (which cause urination), antibiotics, and corticosteroids. Not taking in enough potassium due to a poor diet (less common) Adrenal disorders (rarely, overactive adrenal disorders such as Cushing's syndrome, primary aldosteronism)Mar 12, 2018
What is the ICD-10 code for hypocalcemia?
What is the ICD-10 code for hypoxia?
What is the ICD-10 code for hypercalcemia?
What is the ICd 10 code for abnormal blood chemistry?
R79.9 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of abnormal finding of blood chemistry, unspecified. The code R79.9 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code R79.9 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like abnormal blood test, blood chemistry abnormal, chloride level - finding, decreased vitamin b12 level, full blood count abnormal , serum chloride level abnormal, etc.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like R79.9 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
When should unspecified codes be used?
Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code R79.9 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is the difference between blood cells and white blood cells?
Red blood cells (RBC) deliver oxygen from your lungs to your tissues and organs. White blood cells (WBC) fight infection and are part of your immune system. Platelets help blood to clot when you have a cut or wound. Bone marrow, the spongy material inside your bones, makes new blood cells.
What is the role of platelets in the immune system?
White blood cells (WBC) fight infection and are part of your immune system. Platelets help blood to clot when you have a cut or wound. Bone marrow, the spongy material inside your bones, makes new blood cells. Blood cells constantly die and your body makes new ones.
How long do platelets live?
Red blood cells live about 120 days, and platelets live about 6 days. Some white blood cells live less than a day, but others live much longer. There are four blood types: A, B, AB, or O. Also, blood is either Rh-positive or Rh-negative. So if you have type A blood, it's either A positive or A negative.
Is blood rh positive or negative?
Also, blood is either Rh-positive or Rh-negative. So if you have type A blood, it's either A positive or A negative. Which type you are is important if you need a blood transfusion. And your Rh factor could be important if you become pregnant - an incompatibility between your type and the baby's could create problems.
Does potassium decrease with low pH?
Low potassium is much more significant with a low pH than with a high pH. When pH increases by 0.1, potassium decreases approximately 0.6 mmol/L. With low pH, as in ketoacidosis, as therapeutic adjustment towards normal is made, plasma/serum K + levels will decrease.
Is hypokalemia a cause of hypertension?
Hypokalemia (low potassium) has been found in >90% of hypertensive patients with primary aldosteronism (Conn syndrome). This uncommon entity is a curable cause of hypertension. Low potassium occurs with endogenous or exogenous increase in other corticosteroids, including that in Cushing syndrome as well as with dietary or parenteral deprivation of potassium (eg, parenteral therapy without adequate potassium replacement). Hypokalemia occurs with vomiting, diarrhea, fistulas, laxatives, diuretics, burns, excessive perspiration, Bartter syndrome, some cases of alcoholism and folic acid deficiency, in alkalosis and in renal tubular acidosis as well as in other entities.
Does thiazide cause hypercalcemia?
Hypokalemia has been reported in slightly over one-half of a series of 32 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia, 1 but thrombocytosis can increase serum potassium levels, vide supra. Thiazide/chlorthalidone therapy may cause hyperuricemia and hypercalcemia as well as hypokalemia.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for hormone replacement therapy
- 2. icd 10 code for back painm
- 3. icd 10 code for infected surgical wound of lower lip
- 4. icd 10 code for draining postoperative wound
- 5. icd 10 code for heel l preesure
- 6. icd 10 cm code for thoracolumbar djd
- 7. icd 10 code for right elbow ucl tear
- 8. icd 9 code for squamous cell carcinoma hand
- 9. icd 10 code for prolapse of female genital organs
- 10. icd 10 code for insect bite to waist