What are the ICD 10 codes for age-related macular degeneration (AMD)?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM) 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): No change 2019 (effective 10/1/2018): No change 2020 (effective 10/1/2019): No change 2021 (effective 10/1/2020): No change 2022 (effective 10/1/2021): No ...
What is the ICD 10 code for retinal pigment epithelium?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unspecified macular degeneration H00-H59 2022 ICD-10-CM Range H00-H59 Diseases of the eye and adnexa Note Use an external cause code following the code... H35 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H35 Other retinal disorders 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific...
What is the ICD 10 code for change in retinal vascular appearance?
Oct 01, 2021 · Dystrophies primarily involving the retinal pigment epithelium H35.54 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Dystrophies primarily w the retinal pigment epithelium The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H35.54 became ...
What is the ICD 10 code for retinal detachment?
Oct 01, 2021 · Changes in retinal vascular appearance, right eye. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. H35.011 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H35.011 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H35.011 - …
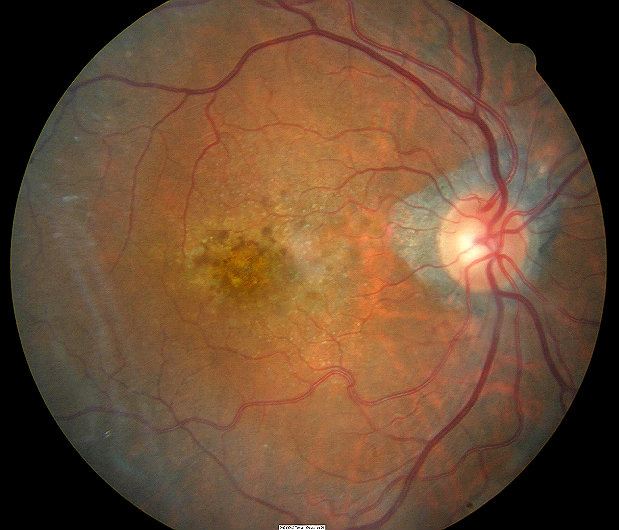
What is macular mottling?
Macular mottling is evident at an early age with attenuation and narrowing of the retinal arterioles. The pigmentary changes are salt-and-pepper in appearance but there are also areas of RPE atrophy with relative sparing of the fovea. Pigment clumping in the shape of bone spicules has been observed in the periphery.
What is the correct ICD-10 code for pigmentary retinal dystrophy?
H35.52ICD-10 | Pigmentary retinal dystrophy (H35. 52)
What are RPE changes?
The RPE specifically is known to undergo several structural changes, including loss of melanin granules, increase in the number of residual bodies, accumulation of the age pigment lipofuscin, accumulation of basal deposits on or within Bruch's membrane (BM), formation of drusen (between the basal lamina of the RPE and ...
What is RPE mottling?
Pigmentary retinopathy + Retinal pigment epithelial mottling + Mottling (spots or blotches with different shades) of the retinal pigment epithelium, i.e., localized or generalized fundal pigment granularity associated with processes at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium.
What is macular pigment changes?
In macular degeneration, clumps of yellowish material gradually accumulate within and beneath the retinal pigment epithelium. These deposits are visible to a doctor who looks inside the eye. The clumps appear as small yellow spots known as drusen (singular: druse).
What is the ICD-10 code for macular degeneration?
H35.30Unspecified macular degeneration H35. 30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is macular pigment?
Macular pigment (MP) is a generic term used to describe the yellow pigment composed principally of the three isomeric carotenoids meso-zeaxanthin (MZ), lutein (L), and zeaxanthin (Z), which accumulate in the macula [2, 3] (Fig. 1).Aug 15, 2016
What is RPE hyperpigmentation?
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a pigmented layer of the retina which can be thicker than normal at birth (congenital) or may thicken later in life. Areas of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) hypertrophy usually do not cause symptoms. They are typically found during routine eye examinations.
What causes pigment changes in the retina?
It develops when abnormal blood vessels grow underneath the retina and leak blood or other fluids, causing scarring and damage to the macula. AMD has three stages, partially defined by the size and number of drusen beneath the retina. People in early-stage AMD have medium-sized drusen and usually no vision loss.Jul 31, 2018
What causes macular mottling?
Your eye doctor will put drops in your eyes to dilate them and use a special instrument to examine the back of your eye. He or she will look for a mottled appearance that's caused by drusen – yellow deposits that form under the retina. People with macular degeneration often have many drusen.
What is macular scar?
Macular scarring is formation of the fibrous tissue in place of the normal retinal tissue on the macular area of the retina which provides the sharpest vision in the eyes. It is usually a result of an inflammatory or infectious process..
What are retinal pigments?
The pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that nourishes retinal visual cells, and is firmly attached to the underlying choroid and overlying retinal visual cells.
What is right macular degeneration?
Right macular degeneration. Clinical Information. A condition in which parts of the eye cells degenerate, resulting in blurred vision and ultimately blindness. A condition in which there is a slow breakdown of cells in the center of the retina (the light-sensitive layers of nerve tissue at the back of the eye).
What is the term for the damage to the eye cells?
injury (trauma) of eye and orbit ( S05.-) A condition in which parts of the eye cells degenerate, resulting in blurred vision and ultimately blindness. A condition in which there is a slow breakdown of cells in the center of the retina (the light-sensitive layers of nerve tissue at the back of the eye).
What causes loss of vision in the central portion of the retina?
Age-related loss of vision in the central portion of the retina (macula), secondary to retinal degeneration. Degenerative changes in the retina usually of older adults which results in a loss of vision in the center of the visual field (the macula lutea) because of damage to the retina. It occurs in dry and wet forms.
What is a macular hole?
It is most common in young children. Macular pucker - scar tissue on the macula. Macular hole - a small break in the macula that usually happens to people over 60. Floaters - cobwebs or specks in your field of vision.
What is the tissue in the back of the eye that senses light and sends images to the brain?
Information for Patients. Retinal Disorders. The retina is a layer of tissue in the back of your eye that senses light and sends images to your brain. In the center of this nerve tissue is the macula.
What is progressive degeneration of the retina?
Hereditary, progressive degeneration of the retina due to death of ROD PHOTORECEPTORS initially and subsequent death of CONE PHOTORECEPTORS. It is characterized by deposition of pigment in the retina. Retinal Drusen -. Colloid or hyaline bodies lying beneath the retinal pigment epithelium.
What is the term for the loss of vision in the center of the visual field?
Macular Degeneration -. Degenerative changes in the RETINA usually of older adults which results in a loss of vision in the center of the visual field (the MACULA LUTEA) because of damage to the retina. It occurs in dry and wet forms.
Can retinal detachment occur after cataract surgery?
Retinal detachment occurs more commonly in men than in women, in eyes with degenerative myopia, in aging and in aphakia. It may occur after an uncomplicated cataract extraction, but it is seen more often if vitreous humor has been lost during surgery. Macular Degeneration -.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for hidradenitis
- 2. icd 10 code for nonrheumatic mitral valve prolapse
- 3. icd-10-cm code for scabies
- 4. icd 10 code for infected groin wound
- 5. icd 10 code for soft tissue defect
- 6. icd 10 code for clab
- 7. icd 10 code meaning for i5030
- 8. icd-10 code for oa
- 9. icd 9 code for uti due to catheter
- 10. icd-10-pcs code for microvolt t-wave alternans