What does ICD - 10 stand for?
The ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) is a system used by physicians and other healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
How many ICD 10 codes are there?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...
What is ICD 10 used for?
Used for medical claim reporting in all healthcare settings, ICD-10-CM is a standardized classification system of diagnosis codes that represent conditions and diseases, related health problems, abnormal findings, signs and symptoms, injuries, external causes of injuries and diseases, and social circumstances.
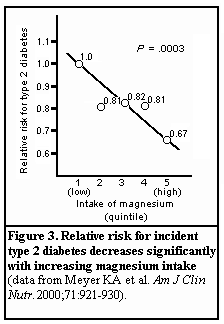
What is the medical code for magnesium?
Group 1CodeDescription83735MAGNESIUM
What is DX R68 89?
ICD-10 code R68. 89 for Other general symptoms and signs is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Can Z76 89 be used as a primary diagnosis?
The patient's primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient's primary diagnostic code is Z76. 89, look in the list below to see which MDC's "Assignment of Diagnosis Codes" is first.
What is DX R53 83?
Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
Is R68 89 a billable code?
R68. 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R68. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Z00 01?
ICD-10 code Z00. 01 for Encounter for general adult medical examination with abnormal findings is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is a diagnostic code Z76 9?
ICD-10 code: Z76. 9 Person encountering health services in unspecified circumstances.
What diagnosis codes Cannot be primary?
Diagnosis Codes Never to be Used as Primary Diagnosis With the adoption of ICD-10, CMS designated that certain Supplementary Classification of External Causes of Injury, Poisoning, Morbidity (E000-E999 in the ICD-9 code set) and Manifestation ICD-10 Diagnosis codes cannot be used as the primary diagnosis on claims.
Can Z51 11 be a primary diagnosis?
11 or Z51. 12 is the only diagnosis on the line, then the procedure or service will be denied because this diagnosis should be assigned as a secondary diagnosis. When the Primary, First-Listed, Principal or Only diagnosis code is a Sequela diagnosis code, then the claim line will be denied.
What is R53 81?
R53. 81: “R” codes are the family of codes related to "Symptoms, signs and other abnormal findings" - a bit of a catch-all category for "conditions not otherwise specified". R53. 81 is defined as chronic debility not specific to another diagnosis.
Is R53 83 a billable code?
R53. 83 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R53. 83 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What ICD-10 code covers Vitamin D?
For 82306: If more than one LCD-listed condition contributes to Vitamin D deficiency in a given patient and/or is improved by Vitamin D administration, coders should use: ICD-10 E55. 9 UNSPECIFIED VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY. This code should not be used for any other indication.
ICD-10-CM Code E61.2 - Magnesium deficiency
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code E61.2 and a single ICD9 code, 269.3 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E83.42: Hypomagnesemia
Serum Magnesium - Quest Diagnostics
LCD - Serum Magnesium (L36700) - CMS
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E53.8: Deficiency of other specified B ...
Bei Ihnen wurde ein Mangel an Magnesium festgestellt
Magnesium ist wichtig, damit Muskeln und Nerven richtig arbeiten können. Bei einem Magnesium-Mangel kann man Muskelkrämpfe bekommen. Mann kann sich auch reizbar oder trauriger fühlen als sonst. Manchmal fühlt man sich schwindlig. Man kann auch ein unangenehmes Kribbeln in den Händen und Füßen spüren.
Information
This information is not intended for self-diagnosis and does not replace professional medical advice from a doctor.
Source
Provided by the non-profit organization “Was hab’ ich?” gemeinnützige GmbH on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG).
What is magnesium deficiency?
Magnesium deficiency or hypomagnesia (not to be confused with hypomagnesemia) refers to inadequate intake of dietary magnesium or impaired absorption of magnesium, which can result in numerous symptoms and diseases. It is generally corrected by an increase of magnesium in diet, oral supplements, and in severe cases, intravenous supplementation.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code E61.2 and a single ICD9 code, 269.3 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for patient with recurrent inguinal hernia left side
- 2. icd 10 code for mass on jaw
- 3. icd 10 code for left arm lymphedema
- 4. icd 10 code for fall through ceiling
- 5. icd 10 code for history of stroke with residual effects
- 6. icd 10 code for migrsaine
- 7. billable icd 10 code for alzheimers disease
- 8. icd 10 code for contact dermatitis poison ivy
- 9. icd 10 code for high testosterone in female
- 10. icd-9 code for dyslipidemia