What is ICD 10 code for excess estrogen in males?
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Male Dx POA Exempt. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Q56.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Male pseudohermaphroditism, not elsewhere classified. Male pseudohermaphroditism; 46, XY with streak gonads; Male pseudohermaphroditism NOS. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Q56.1.
What is the prognosis of hypogonadism?
hypogonadotropic E23.0. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E23.0. Hypopituitarism. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Fertile eunuch syndrome. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Idiopathic growth hormone …
Is there any treatment for hypogonadism?
Nov 30, 2020 · What is the diagnosis code for hypogonadism? E29. 1 – Testicular hypofunction. ICD-10-CM. What is hypogonadism diagnosis? Hypogonadism can be of hypothalamic-pituitary origin or of testicular origin, or a combination of both, which is increasingly common in the aging male population.
What is the treatment for hypogonadism?
3 result found: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E29.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Testicular hypofunction. Hypogonadism, male; Hypotestosteronism; Male hypogonadism; Testicular failure with hypogonadism; postprocedural testicular hypofunction (E89.5); Defective biosynthesis of testicular androgen NOS; 5-delta-Reductase deficiency (with male pseudohermaphroditism); …
What is male hypogonadism?
Male hypogonadism is a condition in which the body doesn't produce enough of the hormone that plays a key role in masculine growth and development during puberty (testosterone) or enough sperm or both. You can be born with male hypogonadism, or it can develop later in life, often from injury or infection.Sep 29, 2021
What is secondary male hypogonadism?
Secondary: This type of hypogonadism indicates a problem in the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland – parts of the brain that signal the testicles to produce testosterone.
What is the ICD 9 code for hypogonadism?
257.2ICD-9 code 257.2 for Other testicular hypofunction is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -DISEASES OF OTHER ENDOCRINE GLANDS (249-259).
Is hypogonadism the same as testicular hypofunction?
Testicular hypofunction from the age of puberty onward may lead to testosterone deficiency, infertility, or both. Such hypofunction may be primary in the testes (primary hypogonadism) or secondary to deficiency of pituitary gonadotropic hormones (secondary hypogonadism).Mar 22, 2015
What is the ICD 10 code for hypogonadism?
E29.1ICD-10-CM Code for Testicular hypofunction E29. 1.
What is hypogonadism diagnosis?
Hypogonadism can be of hypothalamic-pituitary origin or of testicular origin, or a combination of both, which is increasingly common in the aging male population. It can be easily diagnosed with measurement of the early morning serum total testosterone level, which should be repeated if the value is low.
What is the ICD 9 code for testicular hypofunction?
ICD-9-CM 257.2 converts directly to: 2022 ICD-10-CM E29. 1 Testicular hypofunction.
What is the difference of total testosterone and free testosterone in the diagnosis of hypogonadism?
Total Testosterone: What's the difference? Approximately 98% of the testosterone the body produces is bound to either sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG), or albumin. This is referred to as “bound testosterone.” The 2% that's left is known as “free testosterone.”May 15, 2018
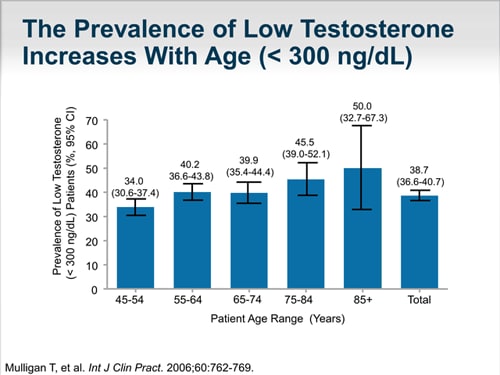
What percent of men have hypogonadism?
Nearly 39 percent of men ages 45 years and older have low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, which is generally defined as a level below 300 nanograms per deciliter.Jun 22, 2017
What is the difference between primary and secondary hypogonadism?
Primary hypogonadism can also occur due to abuse of testosterone and/or performance enhancers. Secondary hypogonadism occurs when the testicles function normally but the pituitary gland and/or the hypothalamus are functioning incorrectly.Mar 2, 2015
What is secondary hypogonadism?
Secondary hypogonadism, also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, is caused by a problem with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are located in the brain and help regulate various body functions, including the production of sex hormones.
How is secondary hypogonadism diagnosed?
The patient has secondary hypogonadism if his serum testosterone concentration and/or the sperm count are low and/or his serum LH and FSH concentrations are not elevated, as they would be if gonadotroph cell function were normal.
Can you treat secondary hypogonadism?
In most cases, hypogonadism can be treated effectively with HRT. This treatment consists of taking medications containing the hormone that your body is lacking, such as testosterone, estrogen and progesterone, or pituitary hormones to replace the ones that the body no longer produces.
What is hypogonadism diagnosis?
Hypogonadism can be of hypothalamic-pituitary origin or of testicular origin, or a combination of both, which is increasingly common in the aging male population. It can be easily diagnosed with measurement of the early morning serum total testosterone level, which should be repeated if the value is low.
What is the difference between primary and secondary hypogonadism?
Primary hypogonadism is associated with low levels of testosterone and high-normal to high levels of LH and FSH. Secondary hypogonadism is associated with low levels of testosterone and normal to low levels of LH and FSH.
How do you know if you have primary or secondary hypogonadism?
Levels of FSH and LH also help determine whether hypogonadism is primary or secondary. High gonadotropin levels, even with low-normal testosterone levels, indicate primary hypogonadism, whereas gonadotropin levels that are low or lower than expected for the level of testosterone indicate secondary hypogonadism.
What diagnosis covers testosterone?
Testosterone testing is used to evaluate androgen excess or deficiency related to gonadal function, adrenal function, or tumor activity. Testosterone levels may be helpful in men for the diagnosis of hypogonadism, hypopituitarism, Klinefelter syndrome, and impotence (low values).
What is the ICd 10 code for testicular hypofunction?
E29.1 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of testicular hypofunction. The code E29.1 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code E29.1 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like acquired male infertility, acquired testicular failure, atypical ichthyosis vulgaris with hypogonadism, bird-headed dwarfism with progressive ataxia, insulin-resistant diabetes, goiter, and primary gonadal insufficiency, boucher neuhäuser syndrome , central obesity, etc.#N#The code E29.1 is applicable to male patients only. It is clinically and virtually impossible to use this code on a non-male patient.
What is the ICd 10 list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code E29.1:
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for severe osteoporosis
- 2. icd 10 code for spondylolisthesis scapular
- 3. icd 10 code for cad with previos ptca
- 4. icd 10 cm code for dm with hyperlipedemia
- 5. icd 10 code for thoracic t11 compression fracture
- 6. icd 10 code for lower elevated lfts
- 7. icd 10 code for an
- 8. what is icd 10 code for 625.9
- 9. icd 10 cm code for enterococcis.
- 10. icd 10 cm code for metabolic syndrome