What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C80.1 Malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code C80.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C80.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10 code range for Malignant neoplasms C00-C96 is medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). ICD-10 Code range (C00-C96), Malignant neoplasms contains ICD-10 codes for Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx, Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs, Malignant neoplasms of respiratory and intrathoracic organs, Malignant …
How to code neoplasm?
Oct 01, 2021 · C34.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Malignant neoplasm of unsp part of unsp bronchus or lung The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What is the CPT code for benign neoplasm?
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes C50*: Malignant neoplasm of breast ICD-10-CM Codes › C00-D49 Neoplasms › C50-C50 Malignant neoplasms of breast › Malignant neoplasm of breast C50 Malignant neoplasm of breast C50- Use Additional code to identify estrogen receptor status ( Z17.0, Z17.1) Type 1 Excludes skin of breast ( C44.501, C44.511, C44.521, C44.591)
What is the ICD 10 code for malignant primary neoplasm unspecified?
Code C80. 1, Malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified, equates to Cancer, unspecified.Dec 3, 2018
Are neoplasms always malignant?
Tumors, or neoplasms, are groupings of abnormal cells that cluster together to form a mass or lump. They're formed when cells divide and grow excessively, and they can be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
What is malignant neoplasm unspecified?
A malignant neoplasm (NEE-oh-plaz-um) is another term for a cancerous tumor. The term “neoplasm” refers to an abnormal growth of tissue. The term “malignant” means the tumor is cancerous and is likely to spread (metastasize) beyond its point of origin.Feb 1, 2022
What is primary malignant neoplasm?
Definition. A malignant tumor at the original site of growth. [ from NCI]
What is malignant neoplasm of Endocervix?
The “endocervix” or cervical canal is made up of another kind of cell called columnar cells. The area where these cells meet is called the “transformation zone” (T-zone) and is the most likely location for abnormal or precancerous cells to develop. Most cervical cancers (80 to 90 percent) are squamous cell cancers.
What is an example of malignant neoplasm?
For example, lymphoma is a malignant neoplasm of lymphoid tissue, mesothelioma is a malignant neoplasm of the mesothelium, melanoma is a malignant neoplasm arising from melanocytes, and seminoma is a malignant neoplasm of the testicular epithelium.
How is malignant neoplasm diagnosed?
The term "malignant neoplasm" means that a tumor is cancerous. A doctor may suspect this diagnosis based on observation — such as during a colonoscopy — but usually a biopsy of the lesion or mass is needed to tell for sure whether it is malignant or benign (not cancerous).Sep 21, 2017
When coding malignant neoplasms the primary site is?
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site where they are found e.g. ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms of ovary are coded to ovary (C56), as per Tabular List note 6 at C00-D48.
What is neoplasm coding?
The Neoplasm Table gives the code numbers for neoplasm by anatomical site. For each site there are six possible code numbers according to whether the neoplasm in question is malignant, benign, in-situ, of uncertain behavior or of unspecified nature.Dec 3, 2018
What is benign and malignant neoplasm?
A benign tumor has distinct, smooth, regular borders. A malignant tumor has irregular borders and grows faster than a benign tumor. A malignant tumor can also spread to other parts of your body. A benign tumor can become quite large, but it will not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of your body.
What is the best definition for malignant?
Definition of malignant 1 : tending to produce death or deterioration malignant malaria especially : tending to infiltrate, metastasize, and terminate fatally a malignant tumor. 2a : evil in nature, influence, or effect : injurious a powerful and malignant influence.
What are the types of neoplasms?
ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is a malignant neoplasm?
A malignant neoplasm in which there is infiltration of the skin overlying the breast by neoplastic large cells with abundant pale cytoplasm and large nuclei with prominent nucleoli (paget cells). It is almost always associated with an intraductal or invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.
What is intraductal carcinoma?
An intraductal carcinoma of the breast extending to involve the nipple and areola, characterized clinically by eczema-like inflammatory skin changes and histologically by infiltration of the dermis by malignant cells (paget's cells). (Dorland, 27th ed) Breast cancer affects one in eight women during their lives.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as C50. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together , such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. skin of breast (.
Can breast cancer be detected early?
Breast self-exam and mammography can help find breast cancer early when it is most treatable. Treatment may consist of radiation, lumpectomy, mastectomy, chemotherapy and hormone therapy.men can have breast cancer, too, but the number of cases is small. nih: national cancer institute.
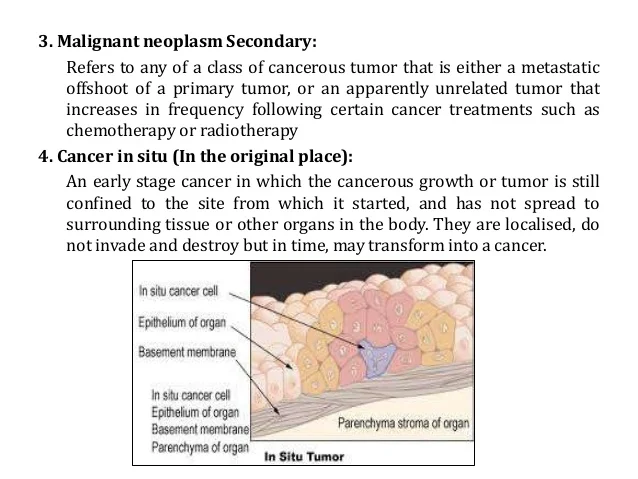
What is secondary malignant neoplasm?
Secondary malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified sites. Approximate Synonyms. Cancer metastatic to choroid. Cancer metastatic to cns (central nervous system) Cancer metastatic to nervous system. Cancer metastatic to spinal cord. Cancer metastatic to spinal meninges. Cancer of prostate with metastasis to eye.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for diplopia
- 2. icd-10 code for acute metabolic encephalopathy
- 3. icd-10 code for subcutaneous abcess to right thigh
- 4. icd 10 code for ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy
- 5. icd 9 code for diabetic foot ulcer with osteomyelitis
- 6. icd 10 code for migraine intractable without aura
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for disseminated mai in medical terms
- 8. icd 10 code for poly cystic
- 9. icd 10 cm code for congenital bicuspid aortic valve
- 10. icd 10 code for knee pain bilateral post op