What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for map dot fingerprint dystrophy?
· Question: What ICD-10 code do you recommend for Mat-Dot-Frequency (MDF) dystrophy? I'm told Anterior basement membrane dystrophy (ABMD) and MDF are very similar. Answer: The ICD-10-CM for Ophthalmology: The Complete Reference maps 371.52 Map- dot fingerprint corneal dystrophy to H18.59 Other hereditary corneal dystrophies.
What is map-dot-fingerprint corneal dystrophy?
Corneal Dystrophy: H18.5-. As previously, the fifth character of corneal dystrophy’s ICD-10 code (H18.5-) represents the type of dystrophy: What’s new is that the sixth character now indicates laterality: For example, a patient diagnosed with bilateral Fuchs dystrophy would be …
What is the ICD 10 code for endothelial corneal dystrophy?
· 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.52 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.52 Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 - Converted to Parent Code 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code H18.52 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What are corneal blebs in map dot fingerprint dystrophy?
· 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.59 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.59 Other hereditary corneal dystrophies 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 - Converted to Parent Code 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code H18.59 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is the ICD-10 code for anterior basement membrane dystrophy?
59 Anterior Corneal Dystrophies. Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) is a degenerative condition of the anterior layer of the cornea.
What is the cause of map dot fingerprint?
Corneal abnormalities associated with map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy are the result of a faulty basement membrane, which is thickened, multilaminar, and misdirected into the epithelium. Deeper epithelial cells that normally migrate to the surface can become trapped.
What is map dot corneal dystrophy?
Map Dot Fingerprint Dystrophy (MDF) is a hereditary disease of the “epithelium” or anterior “skin” cells of the cornea. Multiple names are used to describe this condition such as epithelial basement membrane dystrophy, Cogan's microcystic dystrophy, or anterior membrane dystrophy.
What is the ICD-10 code for corneal dystrophy?
Granular corneal dystrophy, unspecified eye H18. 539 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18. 539 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is epithelial corneal dystrophy?
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) is a disease that affects the anterior cornea, causing characteristic slit lamp findings which may result in decreased vision and/or recurrent corneal erosions.
What causes anterior basement membrane dystrophy?
There are generally two conditions which cause basement membrane dysfunction – one inherited, and one acquired by a deep corneal abrasion (scratch) which damages the basement membrane. This condition is common, treatable, and rarely leads to significant vision loss.
What does map-dot-fingerprint look like?
Map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy, which usually develops in both eyes, usually affects adults between the ages of 40 and 70, although it can develop earlier in life. Most often, the affected epithelium will have a map-like appearance: large, slightly gray outlines that look like a continent on a map.
What is the treatment for map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy?
Numerous treatment options are available, and like map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy itself, results are variable and differ from patient to patient. Hypertonic drops or ointment often are the first line of treatment. They may help both irregular astigmatism and recurrent corneal erosion problems.
How is corneal dystrophy diagnosed?
How Are Corneal Dystrophies Diagnosed? Most of the time your doctor will find a corneal dystrophy during a routine exam. A special tool called a slit lamp microscope let them see abnormal deposits on your cornea before you notice problems.
What is the ICD-10 code for endothelial corneal dystrophy?
Endothelial corneal dystrophy, unspecified eye H18. 519 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18. 519 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Which of the following diagnoses is reported with code H27 00?
Valid for SubmissionICD-10:H27.00Short Description:Aphakia, unspecified eyeLong Description:Aphakia, unspecified eye
How common is granular corneal dystrophy?
Granular corneal dystrophy is a rare, slow-progressing condition that affects the stromal (middle) layer of the cornea in both eyes.
What does the dot on the map mean?
Dot maps are a form of map design that uses dots to show the density of a particular phenomenon in an area. While more dots within a given area represents a higher value, fewer dots indicate a lower value or density. But it's important to understand that dot maps do not show the exact location of the phenomena.
What is the problem in drawing a dot map?
Dot maps are difficult and cumbersome to create appropriately; unless a good deal is known about the processes underlying the phenomenon (like the fact that alligators prefer swamps to deserts), dot maps should be avoided or used with caution and awareness.
What is location fingerprint?
The location fingerprinting technique connects location-dependent characteristics such as received signal strength (RSS), from known access points to a location, and uses these characteristics to infer the location. Locations within the entire area of interest are usually expressed as a set of rectangular grid points.
Do Down syndrome have fingerprints?
Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome): people with Down syndrome have a fingerprint pattern with mainly ulnar loops, and a distinct angle between the triradia a, t, and d (the 'adt angle').
What is Meesman's corneal dystrophy?
Meesman's corneal dystrophy. Clinical Information. An autosomal dominant form of hereditary corneal dystrophy due to a defect in cornea-specific keratin formation. Mutations in the genes that encode keratin-3 and keratin-12 have been linked to this disorder.
Can H18.52 be used for reimbursement?
H18.52 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is Fuchs corneal dystrophy?
Clinical Information. An autosomal dominant, bilateral, slowly progressive degeneration of corneal endothelial cells with thickening of descemet's membrane and accumulation of excrescences. It results in corneal edema and loss of vision.
What is the disorder of the central cornea?
Disorder caused by loss of endothelium of the central cornea; it is characterized by hyaline endothelial outgrowths on descemet's membrane, epithelial blisters, reduced vision, and pain.
When will the ICD-10-CM H18.51 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18.51 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the dots on a map?
The dots are gray-white opacities which can be round, comma-shaped or irregularly shaped.
What is the anterior layer of the cornea?
The anterior layer of the cornea is composed of the corneal epithelium and its underlying basement membrane. The basal cells of the corneal epithelium produce and adhere to the basement membrane via hemidesmosomes and basement membrane complexes.
What is differential diagnosis?
Differential diagnoses would include any diseases that present with corneal opacities or epithelial damage.
What is the pathophysiology of EBMD?
It should be noted that the underlying pathophysiology of EBMD lies in the basement membrance. Simple debridement of the epithelium does little to solve this problem, more likely just resetting the clock for future epithelial breakdown. Polishing the basement membrane with a diamond burr or photoablative removal of the defective basement membrane will produce far more effective and longer lasting benefits.
What is a corneal bleb?
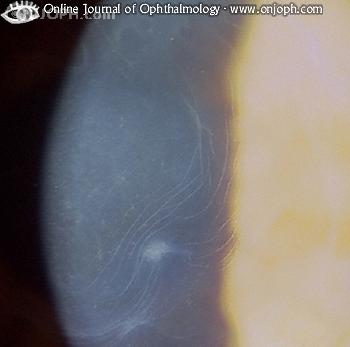
Corneal blebs are a less common manifestation of map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy. They are localized areas of fibrillogranular material or thickened basement membrane and vary in size from 0.05 millimeters to 0.2 millimeters in diameter. Blebs are best visualized with retroillumination.
How big are fingerprints?
The fingerprints are cluster of contoured concentric lines. They vary in length from 0.25 millimeters to 4 millimeters. Fingerprints are best visualized with retroillumination. Corneal blebs are a less common manifestation of map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy.
Does EBMD cause vision problems?
In most patients, the disease causes no significant structural deficit to the cornea, no symptoms and no functional vision problems. In patients with clinically significant EBMD, the abnormal deposits of basement membrane can result in the loss of hemidesmosomes between Bowman’s layer and the basal epithelial cells.
What is the diagnosis of MDF?
Diagnosis usually occurs with a slit lamp examination of the cornea during your eye examination. In its earliest of stages, MDF can be subtle and is often missed without a very careful examination.
What is MDF in medical terms?
What is Map Dot Fingerprint Dystrophy? Map Dot Fingerprint Dystrophy (MDF) is a hereditary disease of the “epithelium” or anterior “skin” cells of the cornea. Multiple names are used to describe this condition such as epithelial basement membrane dystrophy, Cogan’s microcystic dystrophy, or anterior membrane dystrophy.
Can MDF be removed?
Early on MDF can just be monitored and does not require treatment. If/When a patient’s vision becomes limited due to irregular astigmatism or painful corneal erosions occur , the irregular epithelium (MDF) can be removed and your eye will regenerate new, more healthy epithelium.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for axillary abscess
- 2. icd 10 pcs code for splinter was removed by tweezers
- 3. icd 10 code for mildly comminuted, mildly displaced right nasal bone fracture.
- 4. icd-10-pcs code for physical therapy for range of motion and mobility
- 5. icd 10 code for degenerative disc disease left knee
- 6. icd 10 code for tenosynovitis with high arch ankle
- 7. icd 10 code for abdominal tachycardia
- 8. icd code for ingrown toenail
- 9. icd 10 code for spleen lessions
- 10. billable icd 10 code for history of hyperkalemia