What is map dot fingerprint dystrophy?
Dec 02, 2015 · Question: What ICD-10 code do you recommend for Mat-Dot-Frequency (MDF) dystrophy? I'm told Anterior basement membrane dystrophy (ABMD) and MDF are very similar. Answer: The ICD-10-CM for Ophthalmology: The Complete Reference maps 371.52 Map- dot fingerprint corneal dystrophy to H18.59 Other hereditary corneal dystrophies.
What is the ICD-10 code for Mat-dot-frequency (MDF) dystrophy?
Oct 01, 2021 · H18.59 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18.59 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H18.59 - other international versions of ICD-10 H18.59 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for corneal dystrophies?
Map Thalamus, Open Approach. ICD-10-PCS Procedure Code 00KA3ZZ [convert to ICD-9-CM] Map Hypothalamus, Percutaneous Approach. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G71.00 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Muscular dystrophy, unspecified. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G71.00. Muscular dystrophy, unspecified. 2019 - New Code 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code.
What are corneal blebs in map dot fingerprint dystrophy?
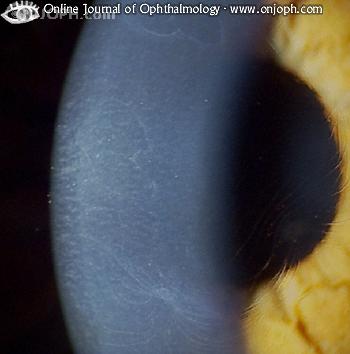
ICD-10 Diagnosis Code: H18.59 ... Corneal blebs are a less common manifestation of map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy. They are localized areas of fibrillogranular material or thickened basement membrane and vary in size from 0.05 millimeters to 0.2 millimeters in diameter.
What is map dot corneal dystrophy?
What is Map Dot Fingerprint Dystrophy? Map Dot Fingerprint Dystrophy (MDF) is a hereditary disease of the “epithelium” or anterior “skin” cells of the cornea. Multiple names are used to describe this condition such as epithelial basement membrane dystrophy, Cogan's microcystic dystrophy, or anterior membrane dystrophy.
What is the ICD 10 code for anterior basement membrane dystrophy?
H18.5959 Anterior Corneal Dystrophies. Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) is a degenerative condition of the anterior layer of the cornea.Aug 6, 2016
What is the ICD 10 code for corneal dystrophy?
Granular corneal dystrophy, unspecified eye H18. 539 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18. 539 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is anterior basement membrane dystrophy?
Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) is an inherited disorder of the cornea that may present with a variety of symptoms, including recurrent corneal erosions and/or blurred vision. ABMD is a type of corneal dystrophy that affects the thin outside layer of the cornea.
Can map dot fingerprint dystrophy be cured?
Treatment. Typically, map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy will flare up occasionally for a few years and then go away on its own, with no lasting loss of vision. Most people never know that they have map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy, since they do not have any pain or vision loss.
What causes epithelial basement membrane dystrophy?
EBMD usually is not inherited , occurring randomly in people with no family history of EBMD. However, familial cases with autosomal dominant inheritance have been reported. In some people with EBMD, a mutation in the TGFBI gene has been identified as the cause. However in most cases, the cause remains unknown.
What is the ICD 10 code for endothelial corneal dystrophy?
Endothelial corneal dystrophy, unspecified eye H18. 519 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18. 519 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Fuchs endothelial dystrophy?
Fuchs endothelial dystrophy is a condition that causes vision problems. The first symptom of this condition is typically blurred vision in the morning that usually clears during the day. Over time, affected individuals lose the ability to see details (visual acuity).
What is the ICD 10 code for endothelial dysfunction?
H18.512022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18. 51: Endothelial corneal dystrophy.
What is lattice dystrophy?
Lattice corneal dystrophy is a rare inherited condition characterized by amyloid deposition in the corneal stroma. It is a bilateral, slowly progressive disease that results in recurrent corneal erosions and decreased vision due to opacification of the cornea.Jun 4, 2019
What does Abmd stand for?
Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) is a condition that affects the cornea in both eyes and is more common as people age.
How do you treat anterior basement membrane dystrophy?
First-line treatment for erosions includes topical antibiotic eye drops and in some cases, patching, placement of a soft contact lens, and/or debridement of loose corneal epithelium.
What are the dots on a map?
The dots are gray-white opacities which can be round, comma-shaped or irregularly shaped.
What is EBMD in medical terms?
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) is characterized by abnormal quantities of basement membrane and cytoplasmic debris that are misdirected into the corneal epithelium. Clinically, the abnormal deposits in EBMD appear as dot-like opacities, map-like patterns, or whorled fingerprint-like lines in the corneal epithelium. In many patients, the epithelial lesions change in appearance, location and number over time.
What is the size of a bleb?
They are localized areas of fibrillogranular material or thickened basement membrane and vary in size from 0.05 millimeters to 0.2 millimeters in diameter . Blebs are best visualized with retroillumination. In cases of active epithelial erosion, positive staining marks areas of epithlial breakdown.
What is the anterior layer of the cornea?
The anterior layer of the cornea is composed of the corneal epithelium and its underlying basement membrane. The basal cells of the corneal epithelium produce and adhere to the basement membrane via hemidesmosomes and basement membrane complexes.
Does map dot fingerprint go away?
Typically, map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy will flare up occasionally for a few years and then go away on its own, with no lasting loss of vision. Most people never know that they have map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy, since they do not have any pain or vision loss.
Can epithelial erosion cause blurred vision?
Epithelial erosions can be a chronic problem. They may alter the cornea's normal curvature, causing periodic blurred vision. They may also expose the nerve endings that line the tissue, resulting in moderate to severe pain lasting as long as several days. Generally, the pain will be worse on awakening in the morning.
What is lattice dystrophy?
Lattice dystrophy usually begins in childhood. It causes material to build up on the cornea in a lattice (grid) pattern. As the material builds up, it can cause vision problems. Map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy (also called epithelial basement membrane dystrophy) is most common in adults ages 40 to 70. It causes a layer of the cornea ...
How to tell if you have keratoconus?
Symptoms of keratoconus include: 1 Itchy eyes 2 Double vision 3 Blurry vision 4 Nearsightedness (when far-away objects look blurry) 5 Astigmatism (when things look blurry or distorted) 6 Sensitivity to light
What is the difference between a normal cornea and a keratoconus?
It causes the middle and lower parts of the cornea to get thinner over time. While a normal cornea has a rounded shape, a cornea with keratoconus can bulge outward and become a cone shape. This different cornea shape can cause vision problems.
What causes corneal erosion?
Lattice dystrophy and map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy can both cause corneal erosion, when the outer layer of the cornea isn’t attached to the eye correctly and starts to erode (wear away). Treatments include eye drops, ointments, and special eye patches or contact lenses that stop your eyelid from rubbing against your cornea.
What to do if your eye is watery?
Watery eyes. Treatments include eye drops, ointments, and special eye patches or contact lenses that stop your eyelid from rubbing against your cornea. If you have severe corneal erosions or corneal scarring, you may need a surgical treatment, like laser eye surgery or a corneal transplant. Last updated: June 26, 2019.
Can keratoconus cause eye pain?
Sensitivity to light. As keratoconus gets worse, it may cause eye pain and more serious vision problems. Most people with keratoconus can correct their vision problems by wearing glasses, soft contact lenses, or special hard contact lenses that change the shape of the cornea.
When will the ICD-10-CM code be updated?
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) has published an update to the ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes which became effective October 1, 2020. This is a new and revised code for the FY 2021 (October 1, 2020 - September 30, 2021).
What is the H18.551 code?
H18.551 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of macular corneal dystrophy, right eye. The code H18.551 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for scar tissue
- 2. icd 10 code for buttock skin abrasion
- 3. icd 10 cm code for dialysis treatment
- 4. icd 10 code for chronic dry mouth
- 5. icd 10 code for mammogram screening
- 6. icd 10 code for perineal pain
- 7. what is the correct icd 10 code for right cerebellar hematoma
- 8. icd 10 code for cellulitis of left upper arm
- 9. icd 9 code for gangrene
- 10. icd 10 code for lung mets