What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is the ICD 10 code for removal of stitches?
Suture Removal from Upper Extremity
- (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-PCS)
- (effective 10/1/2016): No change
- (effective 10/1/2017): No change
- (effective 10/1/2018): No change
- (effective 10/1/2019): No change
- (effective 10/1/2020): No change
What is the ICD 10 code for pelvic cyst?
Solitary bone cyst, right pelvis
- Approximate Synonyms
- Convert M85.451 to ICD-9 Code
- Information for Patients. The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code M85.451 its ICD-9 equivalent.
What is the ICD 10 code for small bowel resection?
- DRG 329 - MAJOR SMALL AND LARGE BOWEL PROCEDURES WITH MCC
- DRG 330 - MAJOR SMALL AND LARGE BOWEL PROCEDURES WITH CC
- DRG 331 - MAJOR SMALL AND LARGE BOWEL PROCEDURES WITHOUT CC/MCC
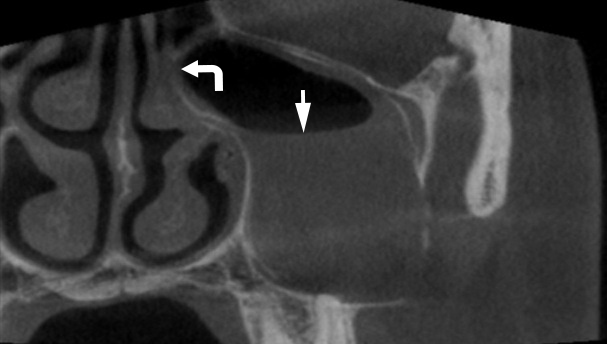
What is the ICD 10 code for retention cyst?
Cyst and mucocele of nose and nasal sinus J34. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J34. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a retention cyst maxillary?
A maxillary sinus retention cyst is a lesion that develops on the inside of the wall of the maxillary sinus. They are often dome-shaped, soft masses that usually develop on the bottom of the maxillary sinus. Fortunately, a retention cyst of the maxillary sinus is a benign lesion, or non-cancerous.
What is the meaning of mucous retention cyst?
A mucocele or mucous retention cyst is a benign pathologic lesion. The lesion is a result of the extravasation of saliva from an injured minor salivary gland. The collection of extravasated fluid develops a fibrous wall around itself forming a pseudocyst.
What is J34 89 diagnosis?
J34. 89 - Other specified disorders of nose and nasal sinuses | ICD-10-CM.
What is the difference between a Mucocele and mucous retention cyst?
It is important to observe the differentiation between mucoceles and retention cysts: mucoceles develop from sinus ostium obstruction, and the cavity becomes completely filled with mucus involved by the sinusal mucosa; on the other hand, retention cysts do not fill completely the cavity and are formed by the ductal ...
What is a retention cyst in the sphenoid sinus?
Sphenoid sinus mucocele (SSM) caused by obstruction of sinus ostium while sphenoid sinus retention cyst (SSRC) is due to obstruction of mucinous gland ostium which could enlarge to obstruct the sinus ostium and lead to acute sinusitis or mucocele1–3.
What is a retention cyst or polyp?
Retention cysts are seen on imaging as rounded dome-shaped lesions often situated on the maxillary sinus floor. They are slow-growing lesions, but mucosal and cortical integrity is preserved.
Where is the maxillary antrum?
The maxillary sinus, or antrum of Highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal sinuses. The alveolar process of the maxilla supports the dentition and forms the inferior boundary of the sinus.
Where is the maxillary sinus located?
noseA type of paranasal sinus (a hollow space in the bones around the nose). There are two large maxillary sinuses, one in each of the maxillary bones, which are in the cheek area next to the nose. The maxillary sinuses are lined with cells that make mucus to keep the nose from drying out.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is right concha bullosa?
A concha bullosa is a pneumatized (air-filled) cavity within a nasal concha, also known as a turbinate. Bullosa refers to the air-filled cavity within the turbinate. It is a normal anatomic variant seen in up to half the population.
Index to Diseases and Injuries
The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code (s). The following references for the code J34.1 are found in the index:
Approximate Synonyms
The following clinical terms are approximate synonyms or lay terms that might be used to identify the correct diagnosis code:
Convert J34.1 to ICD-9 Code
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code J34.1 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
Information for Patients
Your nose is important to your health. It filters the air you breathe, removing dust, germs, and irritants. It warms and moistens the air to keep your lungs and tubes that lead to them from drying out. Your nose also contains the nerve cells that help your sense of smell. When there is a problem with your nose, your whole body can suffer.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a C25.9?
mesothelioma ( C45.-) A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm involving the maxillary sinuses.
What is a retention cyst?
A maxillary sinus retention cyst is a lesion that develops on the inside of the wall of the maxillary sinus. They are often dome-shaped, soft masses that usually develop on the bottom of the maxillary sinus. Fortunately, a retention cyst of the maxillary sinus is a benign lesion, or non-cancerous. Still, if you have a maxillary sinus retention ...
How to remove cysts from sinuses?
Then, the cyst may be removed through a minor endoscopic sinus surgery that includes either enucleation, which is removing the entire lesion without rupturing it, or using curettage, which removes the cyst with a special loop-shaped instrument.
What are the symptoms of sinus pressure in the back of the teeth?
Symptoms may include: Facial pain, especially over the cheek and upper teeth. Tenderness or pain in the back teeth. Headache.
Can sinus cysts regress?
In fact, some maxillary sinus retention cysts will regress on their own. Your doctor may recommend monitoring it with periodic imaging. However, if your cyst is large or you are experiencing symptoms, treatment may be recommended. If you need the cyst removed, your doctor will likely order a CT scan prior to a procedure.
Is sinus retention cyst dangerous?
Typically, a maxillary sinus retention cyst is not dangerous, although there have been cases where a cyst has ruptured after head trauma.
Can a retention cyst cause numbness?
In most cases, these cysts have no symptoms and are only discovered in an imaging exam. Sometimes, however, a retention cyst in the maxillary sinus can cause an obstruction or it can grow very large, causing a number of symptoms. These may include: Tingling or numbness. Pain or sensitivity.
Can sinuses have mucous retention?
Most Common Symptoms of a Maxillary Sinus Retention Cyst. Some studies have found a relatively high incidence of mucous retention cysts in the paranasal sinuses. In fact, retention cysts are a common incidental finding during imaging tests such as computed tomography scans (CT scans), seen in up to 13 percent of scans of CT and magnetic resonance ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right ring finger middle phalanx fracture
- 2. icd 10 code for history transient ischemic attack
- 3. icd 10 code for presence of chest clips
- 4. icd 10 code for bunion on left foot
- 5. icd 10 cm code for gerd hx
- 6. icd 9 code for gastroesophageal varices
- 7. what is the icd-10 code for rectal cancer
- 8. icd 10 code for hx of gastric polyps
- 9. icd 10 code for wandering
- 10. icd 10 code for progressive cough