Crosswalk Information
| ICD-10 Code | ICD-9 Code | ICD-9 Description |
| H81.03 | 386.00 | Meniere's disease NOS |
| H81.03 | 386.01 | Actv Meniere,cochlvestib |
| H81.03 | 386.02 | Active Meniere, cochlear |
| H81.03 | 386.03 | Actv Meniere, vestibular |
What is the ICD 10 code for Meniere's disease?
Oct 01, 2021 · H81.03 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Meniere's disease, bilateral The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H81.03 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H81.03 - other international versions of ICD-10 H81.03 may differ.
What is Ménière's disease of the ear?
Meniere's disease, bilateral (H81.03) H81.02 H81.03 H81.09 ICD-10-CM Code for Meniere's disease, bilateral H81.03 ICD-10 code H81.03 for Meniere's disease, bilateral is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
Is there a cure for Ménière's disease?
H8103: Meniere's disease, bilateral. 1uphealth is the most comprehensive resource to lookup and find ICD codes (international classification of diseases) …
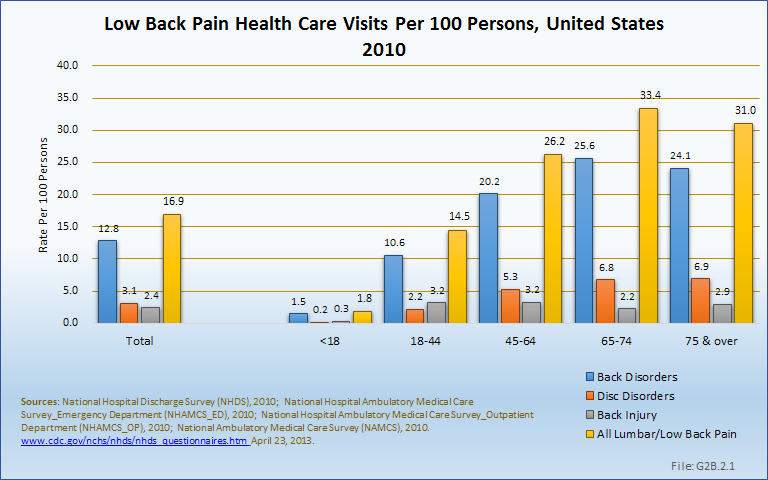
Is Meniere's disease bilateral or unilateral?
Objective: Meniere's disease (MD) progresses from unilateral to bilateral disease in up to 50% of patients, often chronically and severely impairing balance and hearing functions.Jun 8, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for History of Meniere's disease?
ICD-10 code H81. 0 for Meniere's disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral sensorineural hearing?
H90.3ICD-10 code: H90. 3 Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral - gesund.bund.de.
What is Meniere's disorder?
Meniere's disease is a disorder of the inner ear that can lead to dizzy spells (vertigo) and hearing loss. In most cases, Meniere's disease affects only one ear. Meniere's disease can occur at any age, but it usually starts between young and middle-aged adulthood.Dec 2, 2020
What is the ICD-code for Meniere's disease?
ICD-10 | Ménière's disease, unspecified ear (H81. 09)
What is the ICD-10 code for PVD?
ICD-10 | Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified (I73. 9)
What is the correct code for sensorineural hearing loss of both ears?
Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral H90. 3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is a bilateral hearing loss?
Bilateral hearing loss simply means that both ears are affected. Bilateral hearing loss usually occurs gradually over time. But in some (rare) cases, it can come on suddenly.
What is sensorineural hearing loss bilateral?
Sensorineural hearing loss can make. conversations a struggle to understand. Having sensorineural hearing loss means there is damage either to the tiny hair cells in your inner ear (known as stereocilia), or to the nerve pathways that lead from your inner ear to the brain. It normally affects both ears.Oct 29, 2019
What are the three stages of Meniere's disease?
Meniere's disease has phases: an aura, the early stage, attack stage, and in-between. There is also the late-stage of Meniere's disease.May 24, 2020
What's the difference between vertigo and Meniere's disease?
Meniere's disease can cause sudden and often disabling symptoms, including the following. Severe dizziness: Extreme feelings of unsteadiness may result in nausea or vomiting. Vertigo: Vertigo is the sensation of feeling as if you are moving or the world is spinning around you even if you're standing still.Jul 27, 2021
What test confirms Meniere's disease?
Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP) testing. This test shows promise for not only diagnosing, but also monitoring Meniere's disease. It shows characteristic changes in the affected ears of people with Meniere's disease.Dec 2, 2020
The ICD code H810 is used to code Ménière's disease
Ménière's disease /meɪnˈjɛərz/, also called endolymphatic hydrops, is a disorder of the inner ear that can affect hearing and balance. It is characterized by episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss. The hearing loss comes and goes for some time, alternating between ears, then becomes permanent.
Equivalent ICD-9 Codes GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H81.03 and a single ICD9 code, 386.04 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
How long does Ménière disease last?
Episodes are often associated with nausea and vomiting, and they can severely disrupt activities of daily living.The episodes associated with Ménière disease generally last several hours. Studies suggest that episodes can be triggered by stress, tiredness (fatigue), emotional upset, illness, and dietary factors.
What is the name of the disorder that affects balance and hearing?
Ménière disease Ménière disease is a disorder of the inner ear that affects balance and hearing. This condition is characterized by sudden episodes of extreme dizziness (vertigo), a roaring sound in the ears (tinnitus), a feeling of pressure or fullness in the ears, and fluctuations in hearing.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code H81.03 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
Can meniere's disease cause dizziness?
Some people with Meniere's disease have "drop attacks" during which the dizziness is so bad they lose their balance and fall. Scientists don't yet know the cause.
Can you cure hearing loss?
A hearing test can check to see how it has affected your hearing. There is no cure. Treatments include medicines to control dizziness, limiting salt in your diet, and taking water pills. A device that fits into the outer ear and delivers air pulses to the middle ear can help.
Can tinnitus cause dizziness?
It can cause severe dizziness, a roaring sound in your ears called tinnitus, hearing loss that comes and goes and the feeling of ear pressure or pain. It usually affects just one ear. It is a common cause of hearing loss. Attacks of dizziness may come on suddenly or after a short period of tinnitus or muffled hearing.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for anaphylaxis to food
- 2. icd 10 code for colles fracture
- 3. icd 10 code for underweight bmi
- 4. icd-10 code for ergocalciferol
- 5. icd 10 procedural code for anterior cervical discectomy'
- 6. icd 10 code for sprain of finger
- 7. icd 10 code for sacral pain
- 8. icd 10 code for status post aortic valve replacement
- 9. icd 10 code for endometriotic cyst
- 10. icd-10 code for 26 week pregnancy with gestational hypertension, multigravida patient