What is the ICD 10 code for alkalosis?
Oct 01, 2021 · E87.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.3 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E87.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 E87.3 may differ. Applicable To Alkalosis NOS Metabolic alkalosis
What is the ICD 10 code for metabolic acidemia?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O21.1. Hyperemesis gravidarum with metabolic disturbance. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Maternity Dx (12-55 years) Applicable To. Hyperemesis gravidarum, starting before the end of the 20th week of gestation, with metabolic disturbance such as carbohydrate depletion.
What is the ICD 10 code for urinalysis?
Metabolic disorders Other disorders of fluid, electrolyte and acid-base balance (E87) Alkalosis (E87.3) E87.2 E87.3 E87.4 ICD-10-CM Code for Alkalosis E87.3 ICD-10 code E87.3 for Alkalosis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - …
What is the ICD 10 code for acid base imbalance?
Metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis (disorder) ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'E87.3 - Alkalosis' The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code E87.3. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index. Acapnia (E87.3) Alkalemia (E87.3) Alkalosis (E87.3) Alkalosis (E87.3) +
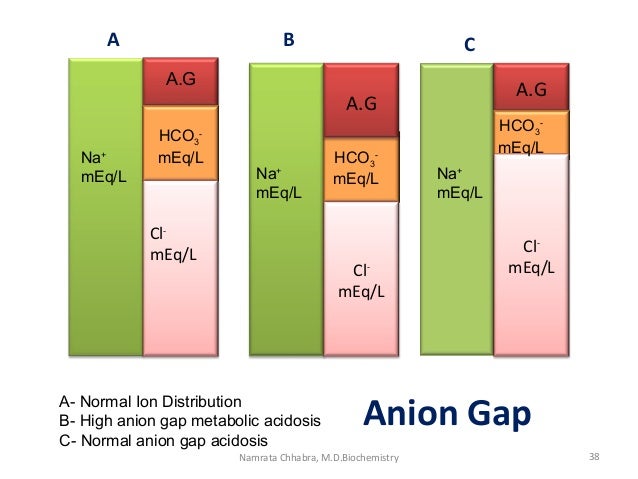
What is the icd10 code for metabolic acidosis?
E87.2ICD-10-CM Code for Acidosis E87. 2.
What is alkalosis metabolic?
Metabolic alkalosis occurs when digestive issues disrupt the blood's acid-base balance. It can also be due to conditions affecting the liver, kidneys or heart. Metabolic alkalosis is usually not life-threatening. It does not have lingering effects on your health once it is treated.May 10, 2021
What is the code E87 8?
8: Other disorders of electrolyte and fluid balance, not elsewhere classified.
What are the levels for metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is defined as elevation of the body's pH above 7.45.Dec 10, 2020
What labs show metabolic alkalosis?
In any event, the only definitive way to diagnose metabolic alkalosis is with a simultaneous blood gases analysis that shows elevation of both pH and PaCO2 and increased calculated bicarbonate. Because pH and PaCO2 are directly measured, bicarbonate can be calculated.Dec 10, 2020
How do you correct alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is treated by replacing water and mineral salts such as sodium and potassium (electrolytes) and correcting the cause. Respiratory alkalosis is treated by correcting the cause.
What is Hypochloremic?
So hypochloremia means that your concentration of blood chloride is below the normal range. If you have high levels of chloride in your blood, that's known as hyperchloremia. If you're healthy, your blood chloride levels don't change much during the day.Jun 1, 2021
What is the ICD-10-CM code for hypocalcemia?
ICD-10 | Hypocalcemia (E83. 51)
What is the ICD-10 code for electrolyte imbalance?
Other disorders of electrolyte and fluid balance, not elsewhere classified. E87. 8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What are three causes of metabolic alkalosis?
Causes of metabolic alkalosisLoss of stomach acids. This is the most common cause of metabolic alkalosis. ... Excess of antacids. ... Diuretics. ... Potassium deficiency (hypokalemia). ... Reduced volume of blood in the arteries (EABV). ... Heart, kidney, or liver failure. ... Genetic causes.
Which 4 of the following conditions would result in metabolic alkalosis?
Thus, metabolic alkalosis can only persist if the ability to excrete excess bicarbonate in the urine is impaired due to one of the following causes: hypovolemia; reduced effective arterial blood volume (due, for example, to heart failure or cirrhosis); chloride depletion; hypokalemia; reduced glomerular filtration rate ...Feb 6, 2022
What is metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis?
Normal human physiological pH is 7.35 to 7.45. A decrease in pH below this range is acidosis, an increase over this range is alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a disease state where the body's pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some metabolic process.Jul 22, 2021
The ICD code E873 is used to code Acid-base imbalance
Acid–base imbalance is an abnormality of the human body's normal balance of acids and bases that causes the plasma pH to deviate out of the normal range (7.35 to 7.45). In the fetus, the normal range differs based on which umbilical vessel is sampled (umbilical vein pH is normally 7.25 to 7.45; umbilical artery pH is normally 7.18 to 7.38).
Coding Notes for E87.3 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #640-641 - Misc disorders of nutrition, metabolism, fluids or electrolytes with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'E87.3 - Alkalosis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code E87.3. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 276.3 was previously used, E87.3 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What are some examples of metabolic disorders?
You can develop a metabolic disorder when some organs, such as your liver or pancreas, become diseased or do not function normally. Diabetes is an example.
What is the process of getting energy from food?
Metabolism is the process your body uses to get or make energy from the food you eat. Food is made up of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Chemicals in your digestive system break the food parts down into sugars and acids, your body's fuel.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for norovirus
- 2. icd 10 code for left-sided hemiplegia
- 3. icd 10 code for removal of nexplanon implant
- 4. icd 10 code for feet numbness
- 5. icd-10 code for invasive ductal carcinoma
- 6. icd 10 code for pressure sores l89.15
- 7. icd 10 code for postop ileus
- 8. icd 10 code for right ankle syndesmotic injury
- 9. icd code for infustion inpatient
- 10. icd 9 code for routine pap exam